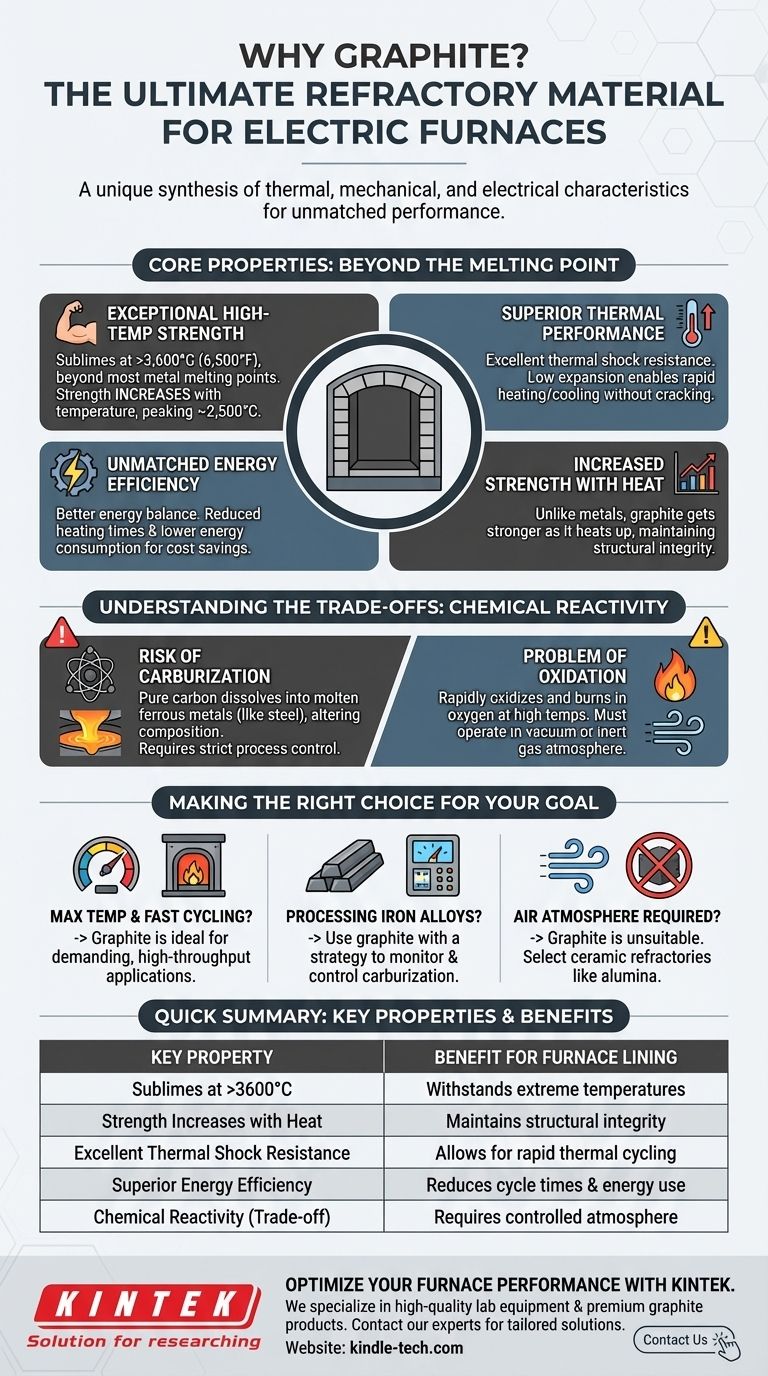
Graphite's unique combination of properties makes it the standard refractory material for many electric furnaces. It is not chosen for one reason, but for a synthesis of thermal, mechanical, and electrical characteristics, chief among them being its extremely high sublimation point and its ability to maintain strength at temperatures that would melt nearly any other material.
While many materials can withstand high heat, graphite is chosen for electric furnace linings because it uniquely balances extreme temperature tolerance with superior energy efficiency and predictable chemical behavior, offering an unmatched performance-to-cost ratio.

The Core Properties of a Graphite Lining
To understand graphite's role, we must look beyond its melting point and analyze the properties that directly impact furnace performance and operational cost.
Exceptional High-Temperature Strength
Graphite does not melt at atmospheric pressure; instead, it sublimes at over 3,600°C (6,500°F). This is well above the operating temperatures required for melting most industrial metals and alloys.
Unlike metals, which weaken as they get hotter, graphite's mechanical strength actually increases with temperature, peaking at around 2,500°C. This ensures the furnace lining remains structurally sound during the most intense phases of operation.
Superior Thermal Performance
Graphite has excellent thermal shock resistance. Its low coefficient of thermal expansion means it can endure rapid heating and cooling cycles without cracking or spalling, which is a common failure mode for brittle ceramic refractories.
This stability allows for reduced heating and cooling times. As noted in high-temperature applications like induction furnaces, this leads directly to shorter process cycles and lower overall energy consumption.
Unmatched Energy Efficiency
While graphite can absorb significant heat, its overall thermal profile often results in a better energy balance compared to other refractories.
This efficiency means that once the furnace is at temperature, less energy is required to maintain it. For an energy-intensive process like operating an electric furnace, these savings are a significant economic advantage.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Chemical Reactivity
Graphite is not a universally perfect solution. Its primary component, carbon, creates specific chemical challenges that must be managed.
The Risk of Carburization
Because graphite is a source of pure carbon, it can dissolve into certain molten metals, particularly iron and steel. This process is known as carburization.
Uncontrolled carburization can alter the chemical composition and mechanical properties of the final alloy, turning a critical furnace component into a potential contaminant. Process control is therefore essential when melting ferrous materials in a graphite-lined furnace.
The Problem of Oxidation
Graphite is highly stable in a vacuum or an inert gas atmosphere (like argon). However, it will readily oxidize and burn away in the presence of oxygen at high temperatures.
This limitation means graphite linings are unsuitable for furnaces that operate with an air atmosphere. The integrity of the lining depends entirely on maintaining a controlled, non-oxidizing environment.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting a refractory material requires matching its properties to the specific demands of your process.
- If your primary focus is maximum temperature and fast cycling: Graphite's unparalleled thermal stability and shock resistance make it the ideal choice for demanding, high-throughput applications.
- If you are processing iron-based alloys: You must use graphite with a clear strategy to monitor and control for carburization to ensure the quality of your final product.
- If your process requires an air atmosphere: Graphite is unsuitable due to oxidation, and you must select a ceramic refractory like alumina or specialized anti-carburizing bricks instead.
Understanding these critical trade-offs is the key to leveraging graphite's power while avoiding its inherent limitations.
Summary Table:
| Key Property | Benefit for Furnace Lining |
|---|---|
| Sublimes at >3600°C | Withstands extreme temperatures beyond most metals' melting points. |
| Strength Increases with Heat | Maintains structural integrity at peak operating temperatures. |
| Excellent Thermal Shock Resistance | Allows for rapid heating/cooling cycles without cracking. |
| Superior Energy Efficiency | Reduces process cycle times and lowers energy consumption. |
| Chemical Reactivity (Trade-off) | Requires controlled atmosphere to prevent oxidation and carburization. |
Ready to optimize your furnace performance with the right refractory solution?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including premium graphite products tailored for demanding thermal processes. Our experts can help you select the perfect materials to enhance your furnace's efficiency, durability, and output quality.
Contact our team today to discuss your specific application and discover how KINTEK's solutions can drive your success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace IGBT Experimental Graphitization Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
- Ultra-High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Vertical High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of graphite furnace? Achieve High-Temperature Precision and Purity
- What is the temperature of a graphite furnace? Achieve Extreme Heat Up to 3000°C
- What are the applications of graphite material? Leveraging Extreme Heat and Precision for Industrial Processes
- What temperature can graphite withstand? Unlocking Its Extreme Heat Potential
- What is the purpose of a graphite furnace? Achieve Extreme Temperatures for Advanced Materials



















