Yes, CVD diamonds are an excellent choice for many buyers. They are physically and chemically identical to natural diamonds, offering the same brilliance and durability, but with significant advantages in cost and ethics. However, whether they are the "best" choice for you depends entirely on your personal priorities.
CVD diamonds represent a modern triumph in material science, offering the beauty and strength of a mined diamond without the ethical and environmental baggage. The key is to understand that while they are real diamonds, their specific manufacturing process creates a unique set of trade-offs compared to other lab-grown and natural stones.

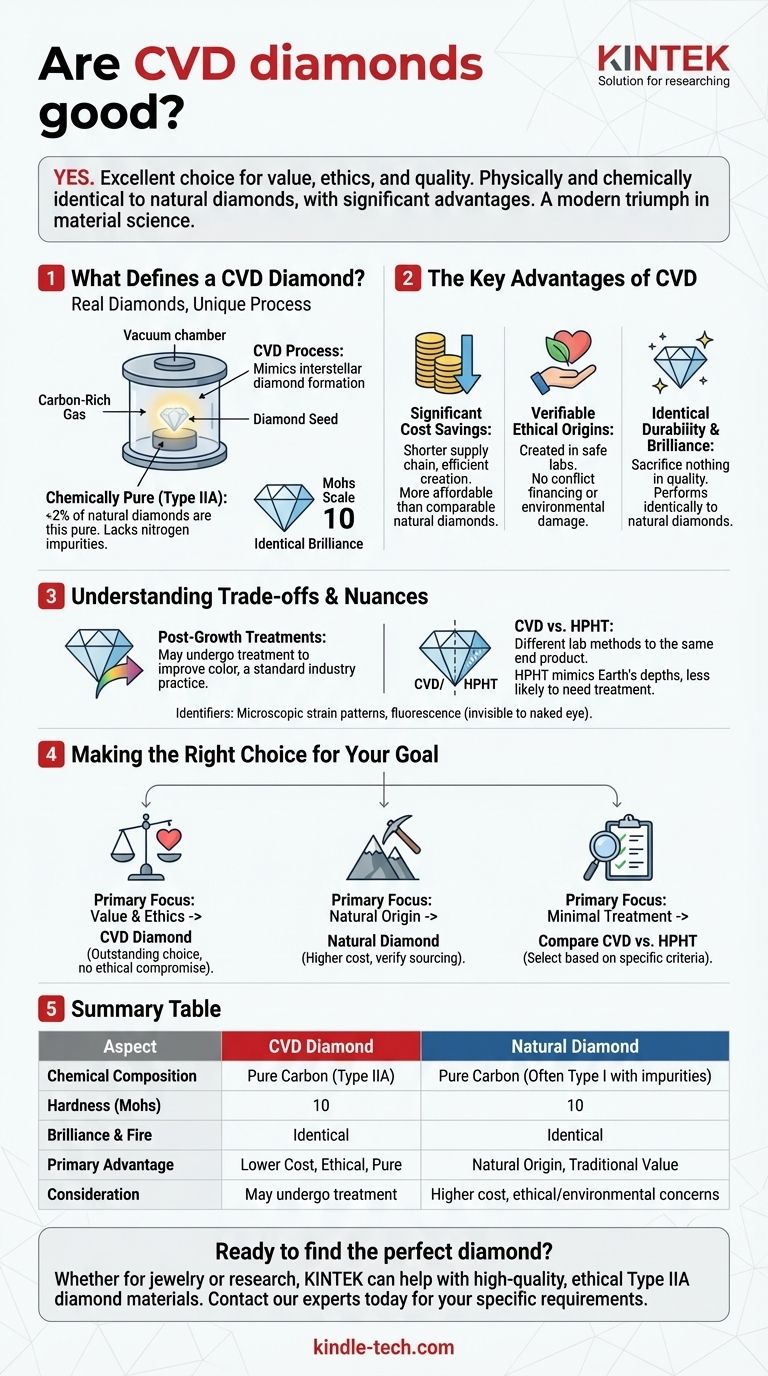
What Defines a CVD Diamond?
To understand if a CVD diamond is "good," you first need to understand what it is. It's not a substitute or imitation; it is a true diamond defined by its unique creation process.
They Are Real Diamonds
A diamond created via Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is not a "fake." It has the same internal crystal structure, chemical composition, and physical properties as a diamond mined from the earth.
It scores a 10 on the Mohs scale of hardness, making it exceptionally durable, and it exhibits the same fire and sparkle. Without specialized gemological equipment, a CVD diamond is indistinguishable from a natural one.
The Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) Process
The CVD process mimics the way diamonds form in interstellar gas clouds. It begins with a thin diamond "seed" placed inside a sealed vacuum chamber.
This chamber is heated to a moderate temperature and filled with a carbon-rich gas. The gas molecules break apart, and carbon atoms attach to the diamond seed, growing a larger, high-quality diamond crystal over several weeks.
A Chemically Pure Diamond (Type IIA)
CVD diamonds are classified as Type IIA, a category that includes only 2% of the world's natural diamonds.
This means they are chemically very pure, lacking the nitrogen impurities that cause the common yellowish tint in many natural diamonds. This purity is a direct result of the highly controlled laboratory environment.
The Key Advantages of CVD
Consumers are drawn to CVD diamonds for a clear set of compelling benefits that directly challenge the traditional diamond market.
Significant Cost Savings
Perhaps the most significant advantage is price. Because the supply chain is shorter and the creation process is efficient, CVD diamonds are considerably more affordable than natural diamonds of comparable size and quality.
Verifiable Ethical Origins
CVD diamonds are created in safe, controlled laboratory environments. This completely sidesteps the ethical concerns associated with diamond mining, including environmental damage and the financing of conflict ("blood diamonds").
Identical Durability and Brilliance
You sacrifice nothing in terms of quality or appearance. A well-cut CVD diamond performs identically to a well-cut natural diamond, offering the longevity and visual impact that people expect from this precious stone.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Nuances
While CVD diamonds have clear benefits, an objective evaluation requires understanding their unique characteristics and how they differ from other lab-grown diamonds.
The Role of Post-Growth Treatments
The CVD growth process can sometimes produce diamonds with a brownish hue. To counteract this, many CVD diamonds undergo a post-growth treatment process to improve or remove their color permanently.
This is a standard, accepted practice in the industry, but it's an important distinction. The final product is a beautiful, stable, colorless diamond, but it may have required an extra step to get there.
CVD vs. HPHT: A Key Distinction
The other primary method for creating lab-grown diamonds is High-Pressure, High-Temperature (HPHT). HPHT mimics the geological conditions deep within the Earth.
While both methods produce real diamonds, HPHT diamonds are less likely to require color treatment after growth. Neither method is inherently "better," but they represent different paths to the same end product, each with its own technical nuances.
Identifying Characteristics
While invisible to the naked eye, CVD diamonds can sometimes have unique microscopic features, such as specific strain patterns or a distinct fluorescence under UV light. These are not flaws but are simply fingerprints of their growth process, which gemologists use for identification.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Ultimately, a "good" diamond is one that aligns with your budget and your values.
- If your primary focus is value and ethics: A CVD diamond is an outstanding choice, delivering a larger or higher-quality stone for your budget without ethical compromise.
- If your primary focus is a "natural" origin story: You will prefer a mined diamond, but be prepared for a significantly higher cost and the need to verify its sourcing.
- If your primary focus is a lab-grown diamond with minimal treatment: You may wish to compare high-quality CVD options alongside HPHT diamonds to see which specific stone best meets your criteria.
Choosing a CVD diamond is a smart, modern, and responsible decision that allows you to own a beautiful piece of technology and art.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | CVD Diamond | Natural Diamond |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Composition | Pure Carbon (Type IIA) | Pure Carbon (Often Type I with impurities) |
| Hardness (Mohs Scale) | 10 | 10 |
| Brilliance & Fire | Identical | Identical |
| Primary Advantage | Lower Cost, Ethical, Pure | Natural Origin, Traditional Perceived Value |
| Consideration | May undergo post-growth color treatment | Higher cost, potential ethical/environmental concerns |
Ready to find the perfect diamond for your needs?
Whether you're a jeweler seeking high-quality, ethical stones or a researcher requiring pure Type IIA diamond material, KINTEK can help. As specialists in advanced materials and laboratory equipment, we understand the precise qualities of CVD diamonds.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our materials can meet your specific requirements for brilliance, purity, and value.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- CVD Diamond Domes for Industrial and Scientific Applications
- CVD Diamond Cutting Tool Blanks for Precision Machining
- Laboratory CVD Boron Doped Diamond Materials
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of lab-grown diamonds? Identical Quality, Ethical & Cost Benefits
- Can CVD diamonds change color? No, their color is permanent and stable.
- What is microwave plasma CVD? A Guide to High-Purity Diamond and Material Synthesis
- Can you chemically make diamonds? Yes, CVD & HPHT Create Real Diamonds
- What is MPCVD? Unlock Atom-by-Atom Precision for High-Purity Materials
- Are lab-grown diamonds as durable as natural? Yes, they are identical in hardness and resilience.
- Are all lab grown diamonds CVD? Understanding the Two Main Methods
- What specific advantages does the MPCVD method have for preparing diamond films? Achieve High-Purity Synthesis



















