In short, yes, a standard diamond tester can give a reading on other stones—but often, it's an incorrect one. While these devices are effective at identifying many common diamond simulants, certain gemstones, most notably moissanite, have properties so similar to diamond that they can easily produce a false positive reading.
A basic diamond tester is not a "diamond detector" but a "thermal conductivity meter." It works by measuring how quickly a stone pulls heat away from its tip. Because some gems, like moissanite, are also excellent thermal conductors, they can fool the device, making it an unreliable tool for definitive identification.
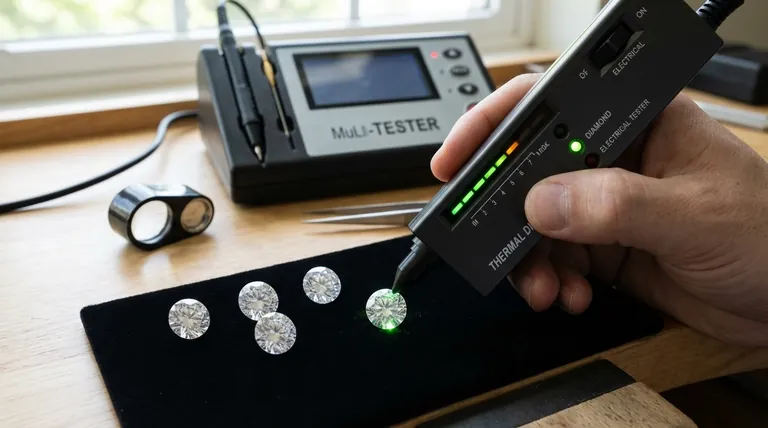

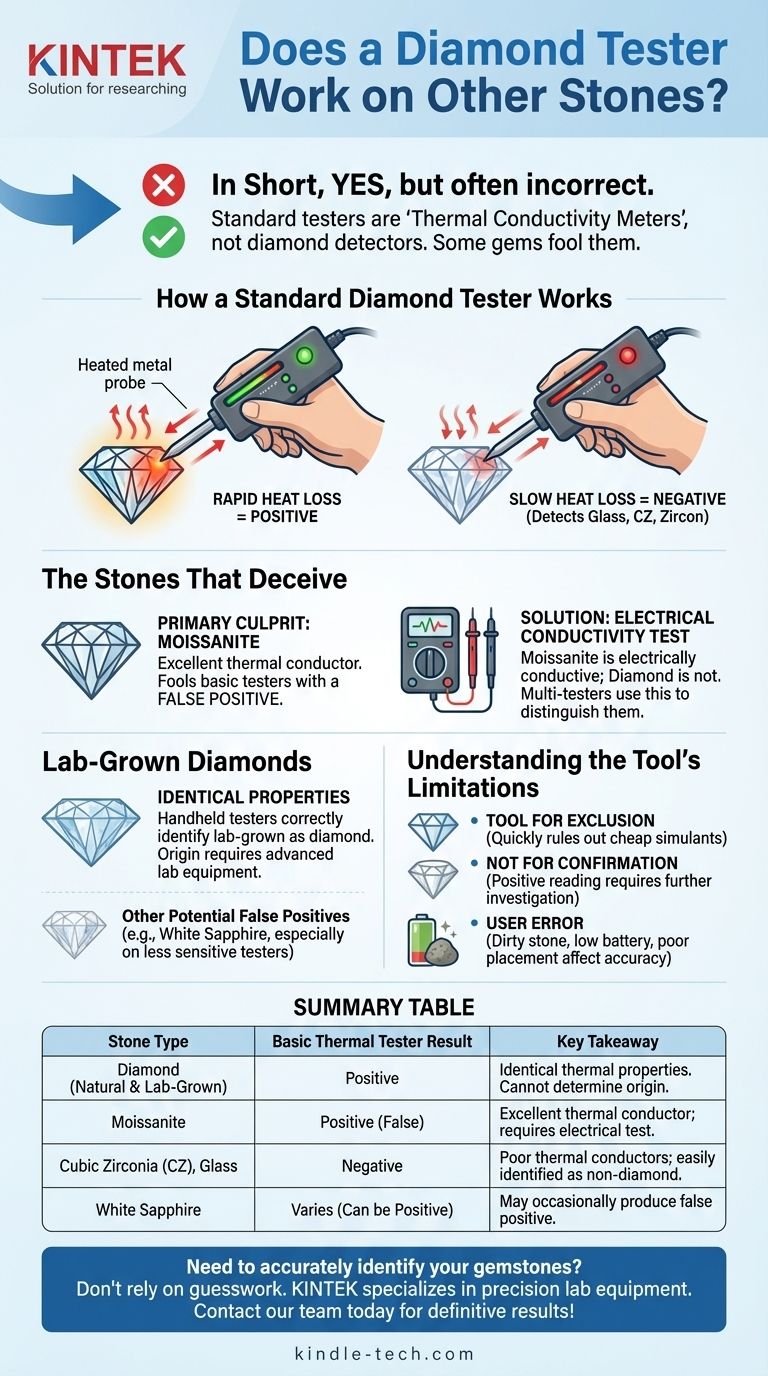
How a Standard Diamond Tester Works
The Principle of Thermal Conductivity
Diamond testers operate on a simple but effective principle: thermal conductivity. Diamonds are one of the most thermally conductive materials on earth.
When the heated metal tip of the tester touches the surface of a diamond, heat is rapidly transferred from the probe into the stone. The device measures this rate of heat loss and, if it's fast enough, signals that the stone is likely a diamond.
What It Reliably Detects
This method is highly effective for weeding out common, inexpensive diamond imitations.
Materials like glass, zircon, or cubic zirconia (CZ) are poor thermal conductors. When the tester touches them, heat leaves the probe very slowly, resulting in a negative reading.
The Stones That Deceive the Tester
The primary limitation of a thermal tester is that it's not the only stone that conducts heat well. Any material with high thermal conductivity can trick the device.
Moissanite: The Primary Culprit
Moissanite is the most common diamond alternative capable of fooling a basic tester. It is also an excellent thermal conductor, and a standard thermal probe cannot distinguish it from a diamond.
For this reason, a positive result from a thermal-only tester is inconclusive. It confirms the stone is not glass or CZ, but it does not confirm it is a diamond.
The Electrical Conductivity Test
To solve the moissanite problem, more advanced multi-testers were developed. These tools perform two tests: one for thermal conductivity and a second for electrical conductivity.
While their thermal properties are similar, diamond and moissanite differ electrically. Moissanite is electrically conductive, whereas diamond (with rare exceptions) is not. A multi-tester that detects electrical conductivity will correctly identify moissanite.
Lab-Grown Diamonds: Identical Properties
It is critical to understand that lab-grown diamonds are real diamonds. They share the exact same chemical, physical, and thermal properties as natural diamonds.
Therefore, any handheld device designed to identify a diamond—whether thermal or electrical—will correctly identify a lab-grown diamond as a diamond. Specialized laboratory equipment is required to determine a diamond's origin.
Other Potential False Positives
While far less common than moissanite, other stones like white sapphire can occasionally register as diamond on less sensitive testers, especially if the user is inexperienced.
Understanding the Tool's Limitations
A Tool for Exclusion, Not Confirmation
The best way to view a basic diamond tester is as a tool for exclusion. It is excellent for quickly confirming that a stone is not a cheap simulant like glass or CZ.
However, it should never be used as the sole method for positively confirming a stone is a diamond. A positive reading simply means more investigation is needed.
The Risk of User Error
The accuracy of these devices also depends on proper usage. A dirty stone, a low battery, or not placing the probe firmly and perpendicularly on the stone's surface can all lead to false or inconsistent readings.
Making an Informed Assessment
- If your goal is to quickly screen out fake glass or cubic zirconia: A basic thermal diamond tester is a reliable and cost-effective tool for this specific task.
- If you need to differentiate a diamond from moissanite: You must use a multi-tester that checks for both thermal and electrical conductivity, or a dedicated moissanite tester.
- If you need to confirm origin (natural vs. lab-grown) or require absolute certainty: The only definitive method is an evaluation by a qualified gemologist or a reputable grading laboratory.
Ultimately, understanding a tool's capabilities and limitations is the key to making an accurate assessment.
Summary Table:
| Stone Type | Basic Thermal Tester Result | Key Takeaway |
|---|---|---|
| Diamond (Natural & Lab-Grown) | Positive | Identical thermal properties. Tester cannot determine origin. |
| Moissanite | Positive (False) | Excellent thermal conductor; requires an electrical conductivity test. |
| Cubic Zirconia (CZ), Glass | Negative | Poor thermal conductors; easily identified as non-diamond. |
| White Sapphire | Varies (Can be Positive) | May occasionally produce a false positive on less sensitive testers. |
Need to accurately identify your gemstones? Don't rely on guesswork. KINTEK specializes in precision lab equipment and consumables for all your analytical needs. Our experts can help you select the right tools, from advanced multi-testers to full laboratory solutions, ensuring you get definitive results. Contact our team today to discuss your requirements and enhance your lab's capabilities!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Filter Testing Machine FPV for Dispersion Properties of Polymers and Pigments
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Head Tweezers with Pointed Elbow Zirconia Ceramic Tip
- CVD Diamond Cutting Tool Blanks for Precision Machining
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Slap Vibrating Sieve
People Also Ask
- Is there a battery tester for lithium batteries? Unlock Accurate Health Diagnostics Beyond Voltage
- What is the significance of compression set? Predict Material Failure and Ensure Long-Term Reliability
- What is the minimum coating thickness? How Steel Thickness Determines Your Galvanizing Needs
- Why are PTFE beakers required for hafnium metal ICP-OES validation? Ensure Pure Sample Dissolution
- What is the water content of pyrolysis oil? A Key Factor in Bio-Oil Quality and Use



















