Yes, in the vast majority of cases, true annealing requires furnace cooling. The defining characteristic of the annealing process is not just the heating of a material, but the extremely slow and controlled rate at which it is cooled. Using the furnace itself is the most common and effective method to achieve this precise control.
The core principle of annealing is to relieve internal stresses and maximize softness by allowing the material's atomic structure to realign into its most stable, lowest-energy state. This realignment can only happen with a very slow, controlled cooling rate, which is best achieved within the insulated environment of a furnace.

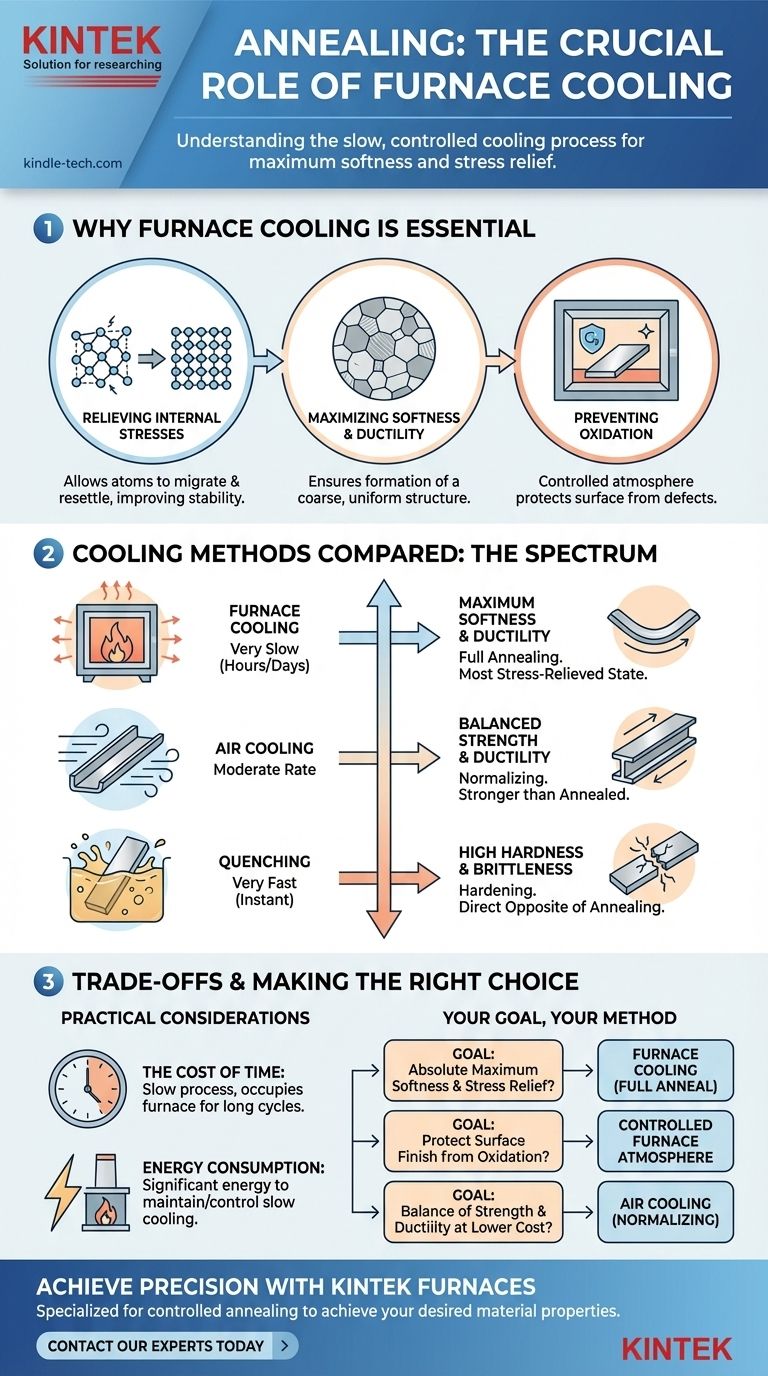
The Purpose of Controlled Cooling
The cooling phase is where the final properties of the annealed material are locked in. A slow, controlled cool is non-negotiable for achieving the primary goals of a full anneal.
Relieving Internal Stresses
As a material is worked, bent, or machined, stress is introduced into its crystal structure. Rapid cooling traps these stresses.
Furnace cooling allows the material's atoms ample time to migrate and resettle into a uniform, stress-free lattice, which significantly improves its stability and workability.
Maximizing Softness and Ductility
The ultimate goal of annealing is to make a material as soft and ductile as possible. This is a direct result of the microstructure formed during cooling.
A slow cool ensures the formation of a coarse-grained, uniform microstructure (like pearlite and ferrite in steel). Faster cooling methods, such as air cooling (normalizing) or liquid cooling (quenching), create harder, more brittle structures.
Preventing Oxidation and Surface Defects
Many materials, especially stainless steels and non-ferrous metals, are highly reactive to oxygen at elevated temperatures.
Keeping the material inside a furnace with a controlled, protective atmosphere during the vulnerable cooling phase is critical. This prevents oxidation, scale formation, and decarburization, ensuring a clean and consistent surface finish.
Furnace Cooling vs. Other Cooling Methods
Understanding annealing requires contrasting its cooling rate with other common heat treatments. The cooling method is the primary variable that differentiates these processes.
Annealing: Furnace Cooling
This is the slowest method. The furnace is turned off, and the material cools gradually along with the furnace's insulated chamber over many hours or even days. This results in the softest, most ductile, and most stress-relieved state.
Normalizing: Air Cooling
After heating, the material is removed from the furnace and allowed to cool in still air. This is faster than furnace cooling but slower than quenching. It produces a material that is stronger and harder than an annealed one, but less ductile.
Quenching: Liquid Cooling
The material is rapidly cooled by submerging it in a liquid like water, brine, or oil. This extremely fast cooling traps the crystal structure in a very hard, brittle state (like martensite in steel). This process is used for hardening, the direct opposite of annealing.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While furnace cooling is essential for a true anneal, it comes with practical considerations that are important to understand.
The Cost of Time
The primary drawback of furnace cooling is the time it takes. A furnace can be occupied for an entire production cycle just for the cooling phase. This makes annealing a relatively slow and expensive process compared to other heat treatments.
Energy Consumption
Maintaining control and allowing a furnace to cool slowly from a high temperature consumes a significant amount of energy, either through programmed cooling steps or simply through the opportunity cost of having the equipment tied up.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct cooling method is entirely dependent on the final properties you need from your material.
- If your primary focus is to achieve the absolute maximum softness, ductility, and stress relief: A slow furnace cool is the only option. This is the definition of a full anneal.
- If your primary focus is to protect the surface finish from oxidation: Cooling within the furnace's controlled atmosphere is essential, especially for high-value or reactive metals.
- If your primary focus is a balance of strength and ductility for a lower cost: You should consider normalizing (air cooling), which provides enhanced strength without the extreme hardness of quenching.
Ultimately, recognizing that annealing is fundamentally defined by its slow, controlled cooling process empowers you to select the precise heat treatment for your desired outcome.
Summary Table:
| Cooling Method | Cooling Rate | Resulting Properties | Common Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| Furnace Cooling | Very Slow | Maximum Softness & Ductility | Full Annealing |
| Air Cooling | Moderate | Balanced Strength & Ductility | Normalizing |
| Liquid Quenching | Very Fast | High Hardness & Brittleness | Hardening |
Need to achieve maximum softness and stress relief in your materials?
KINTEK specializes in precision laboratory furnaces designed for controlled annealing processes. Our equipment ensures the slow, uniform cooling necessary to achieve your desired material properties, from stress-free metals to ductile alloys.
Contact our experts today to find the perfect furnace solution for your lab's annealing needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Pressure Sintering Furnace for High Temperature Applications
- 1200℃ Muffle Furnace Oven for Laboratory
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace Negative Material Graphitization Furnace
- Horizontal High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace Bottom Discharge Graphitization Furnace for Carbon Materials
People Also Ask
- What temperature does titanium vaporize at? Unlocking Its Extreme Heat Resistance for Aerospace
- What is sputtering technology? A Guide to Precision Thin Film Deposition
- What are the three most important factors in material heat treatment? Master Temperature, Time, and Cooling for Superior Properties
- What are the stages of sintering? A Guide to Mastering the Powder-to-Part Process
- How does a sputtering machine work? Achieve Atomic-Level Precision for Your Coatings



















