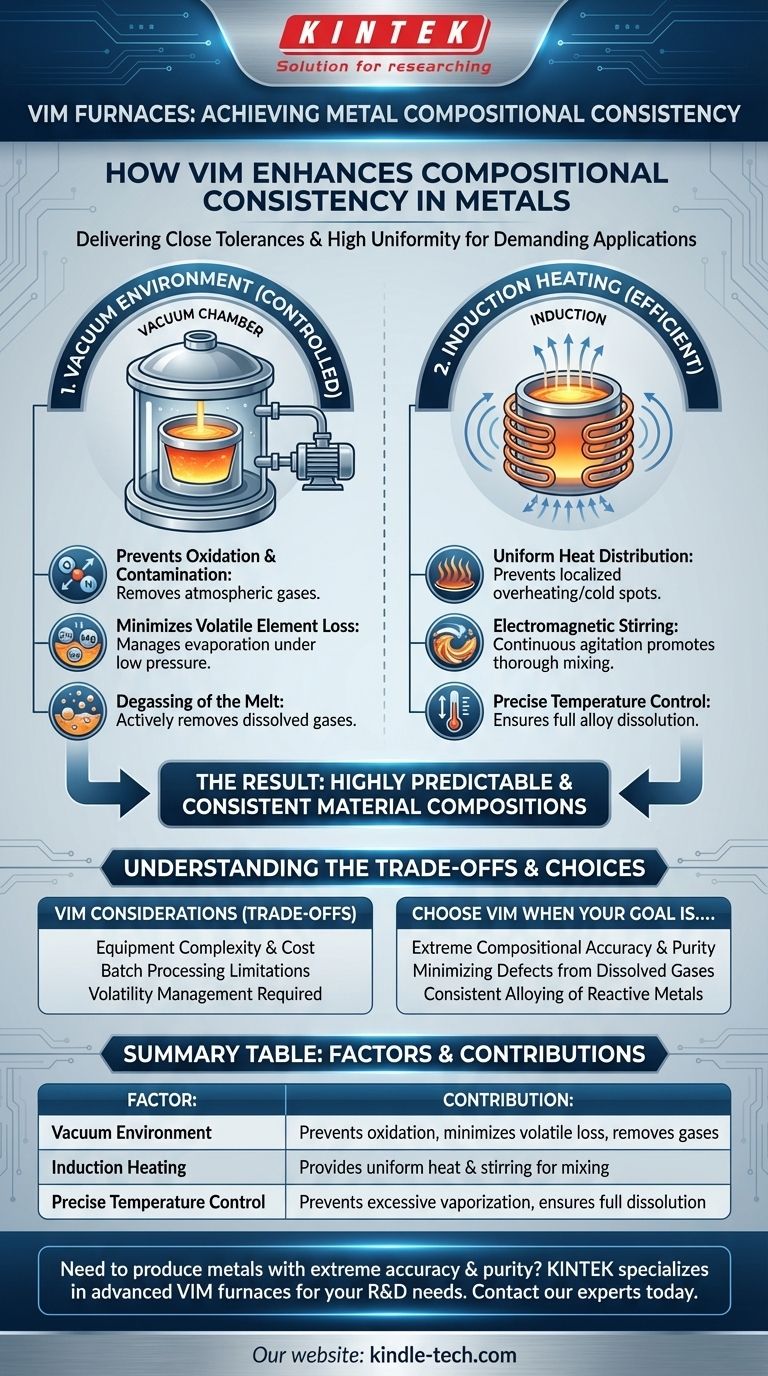
A vacuum induction melting (VIM) furnace significantly enhances the compositional consistency of metals, leading to very close tolerances in the final material. This process ensures that melted metals exhibit a high level of uniformity in their elemental makeup, which is critical for demanding applications.
The core advantage of vacuum induction melting in achieving compositional consistency lies in its ability to control the melting environment. By eliminating atmospheric interference and leveraging efficient electromagnetic heating, VIM minimizes volatile element loss and promotes uniform mixing, resulting in highly predictable and consistent material compositions.

The Mechanism of Compositional Consistency in VIM
Vacuum induction melting is specifically designed to control the melting process, directly impacting the final composition of the metal. This control is achieved through two primary factors: the vacuum environment and the induction heating method.
The Role of the Vacuum Environment
Operating under a vacuum is the most critical aspect for compositional control. It removes atmospheric gases that would otherwise react with the molten metal.
Preventing Oxidation and Contamination
In a vacuum, oxygen, nitrogen, and other reactive gases are largely absent. This prevents unwanted oxidation of reactive elements within the melt. Without a vacuum, these elements could form oxides, altering the intended composition.
Minimizing Volatile Element Loss
Many alloying elements have relatively low boiling points. In an atmospheric melt, these elements can vaporize and be lost from the melt due to their partial pressure. A vacuum environment, by lowering the total pressure, can help manage or even mitigate this loss, particularly for elements like manganese, zinc, or magnesium, allowing for more precise control over their concentration.
Degassing of the Melt
A vacuum actively removes dissolved gases (like hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen) from the molten metal. These gases, if present, can lead to porosity and other defects, indirectly affecting the material's structural consistency, which is linked to its overall performance derived from composition.
The Role of Induction Heating
Induction heating uses electromagnetic fields to generate heat directly within the metal charge, offering efficient and controllable melting. This method supports compositional consistency by ensuring thorough mixing.
Uniform Heat Distribution
The oscillating magnetic field induces eddy currents directly in the metal, generating heat throughout the material. This ensures uniform heating of the charge, preventing localized overheating or cold spots that could lead to uneven melting or segregation.
Electromagnetic Stirring
The nature of the induction field inherently creates an electromagnetic stirring effect in the molten metal. This continuous agitation promotes thorough mixing of all alloying elements. Such vigorous stirring helps achieve a homogeneous melt, ensuring that all constituents are uniformly distributed throughout the liquid phase before solidification.
Precise Temperature Control
Induction furnaces allow for very precise control over the melting temperature. Maintaining the desired temperature within tight limits helps prevent excessive vaporization of volatile elements and ensures that all intended alloying additions fully dissolve and homogenize.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While VIM offers significant advantages in compositional control, it also presents certain considerations.
Equipment Complexity and Cost
VIM furnaces are more complex and expensive to purchase and operate compared to air induction furnaces. This is due to the need for vacuum pumps, seals, and specialized power supplies.
Batch Processing Limitations
VIM is typically a batch process, meaning a specific quantity of metal is melted at one time. This can limit throughput compared to continuous casting methods, though it allows for precise control over each batch.
Volatility Management
While a vacuum minimizes volatile loss, extreme vacuum levels or prolonged exposure at high temperatures can still lead to some evaporation of highly volatile elements. Careful process control is required to balance these factors.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting a melting method should align with your specific material requirements and production goals.
- If your primary focus is extreme compositional accuracy and purity: VIM is the unequivocally superior choice due to its controlled environment and stirring capabilities.
- If your primary focus is minimizing defects from dissolved gases: VIM's degassing capability makes it ideal for producing high-integrity components.
- If your primary focus is consistent alloying of reactive metals: The absence of atmospheric oxygen in VIM is essential for preventing oxidation and maintaining the intended composition.
- If your primary focus is cost-effectiveness for less demanding applications: Air induction melting might be sufficient, accepting a potentially wider compositional tolerance.
The vacuum induction melting process stands as a cornerstone technology for producing metals with unparalleled compositional consistency, enabling the development of advanced materials with predictable and reliable properties.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Contribution to Consistency |
|---|---|
| Vacuum Environment | Prevents oxidation, minimizes volatile element loss, and removes dissolved gases. |
| Induction Heating | Provides uniform heat distribution and electromagnetic stirring for thorough mixing. |
| Precise Temperature Control | Prevents excessive vaporization and ensures full dissolution of alloying elements. |
Need to produce metals with extreme compositional accuracy and purity? KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment, including vacuum induction melting furnaces, to meet the demanding needs of laboratories and material scientists. Our solutions are designed to deliver the predictable and reliable material properties your research and development require. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your specific metal processing goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Arc Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the vacuum induction method? Master High-Purity Metal Melting for Advanced Alloys
- How does induction work in a vacuum? Achieve Ultra-Pure Metal Melting with VIM
- What is the principle of vacuum induction melting? Achieve Ultra-High Purity Metals
- What principle is used to generate heat in a vacuum induction melting furnace? Achieve Clean, Efficient Metal Melting
- What are the advantages of induction melting? Achieve Faster, Cleaner, and More Controlled Metal Melting



















