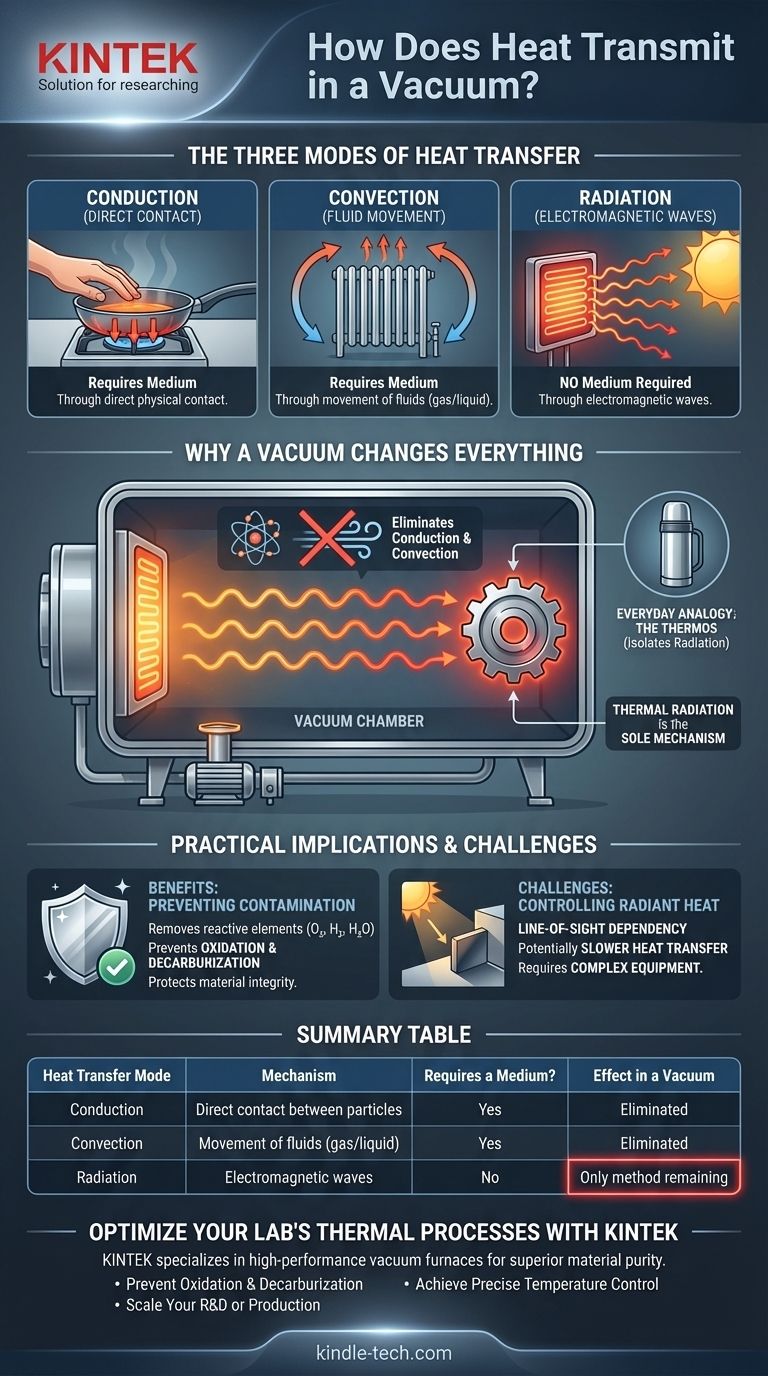
In a vacuum, heat is transmitted exclusively through a process called thermal radiation. Unlike conduction or convection, which require a physical medium of atoms or molecules to transfer energy, radiation moves heat in the form of electromagnetic waves. This is the same fundamental principle that allows the sun's energy to travel through the vacuum of space to reach Earth.
A vacuum does not stop heat transfer; it fundamentally changes the rules. By eliminating heat transfer from physical contact (conduction) and fluid movement (convection), it forces all energy exchange to occur through thermal radiation, which has profound implications for industrial processes.

The Three Modes of Heat Transfer
To understand why a vacuum is unique, we must first recognize the three ways heat can move from one place to another.
Conduction: Heat Through Direct Contact
Conduction is the transfer of heat through direct physical contact. When you touch a hot pan, the energy moves directly from the metal atoms into the atoms of your hand. This process requires a medium; it cannot happen in a true vacuum.
Convection: Heat Through Fluid Movement
Convection transfers heat through the movement of fluids (liquids or gases). A furnace heating a room is a classic example: air is heated, becomes less dense, rises, and is replaced by cooler, denser air, creating a circulating current that distributes heat. This, too, requires a medium.
Radiation: Heat Through Electromagnetic Waves
Thermal radiation is the transfer of energy via electromagnetic waves, primarily in the infrared spectrum. Every object with a temperature above absolute zero emits thermal radiation. This process requires no medium and can travel through the vacuum of space.
Why a Vacuum Changes Everything
By removing the air and other gases, a vacuum fundamentally alters the environment for heat transfer.
Eliminating Conduction and Convection
The primary effect of creating a vacuum is removing the particles needed for conduction and convection. With very few molecules present, there is no effective medium to transfer heat through physical contact or fluid currents.
Isolating Thermal Radiation
This leaves thermal radiation as the sole mechanism for heat transfer. In a vacuum furnace, for example, heat moves from a hot heating element to a cooler metal part only because the element radiates energy, and the part absorbs it.
An Everyday Analogy: The Thermos
A thermos (or vacuum flask) is a perfect real-world example. It has an inner and outer wall separated by a vacuum. The vacuum stops heat from moving via conduction and convection. The shiny, reflective coating on the inner wall minimizes heat transfer by radiation, reflecting it back to the liquid.
Practical Implications: Vacuum Heat Treating
The unique properties of heat transfer in a vacuum are not just a scientific curiosity; they are essential for high-tech manufacturing.
The Core Benefit: Preventing Contamination
Many industrial processes, like annealing or brazing specialty metals, are performed in a vacuum. The primary reason is to protect the material's surface.
By removing air, you eliminate reactive elements like oxygen, hydrogen, and water vapor. This prevents unwanted chemical reactions such as oxidation (rust) or decarburization (loss of carbon from steel), which can degrade the metal's properties and create a weak surface "skin."
The Challenge: Controlling Radiant Heat
Because radiation is the only method of heat transfer, the entire process hinges on managing it effectively. Engineers must select heating elements that radiate energy efficiently at the target temperature.
The material's surface finish, color, and chemical characteristics also become critical, as they determine how well it absorbs that radiated energy.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, operating in a vacuum presents unique challenges.
Line-of-Sight Dependency
Radiant heat travels in straight lines, just like light. If one part of a component is in the "shadow" of another, it will not heat up at the same rate. This requires careful positioning of parts relative to the heating elements to ensure uniform heating.
Potentially Slower Heat Transfer
While radiation is very effective at high temperatures, it can be less efficient than forced convection at lower temperatures. This can sometimes lead to longer heating and cooling cycles compared to processes in atmospheric furnaces.
Equipment Complexity
Vacuum furnaces are inherently more complex and expensive than their atmospheric counterparts. They require robust pumping systems, sealed chambers, and sophisticated controls to maintain the vacuum environment.
How to Apply This to Your Process
Your approach should be dictated by the primary goal of your thermal process.
- If your primary focus is surface purity and material integrity: A vacuum is the superior choice, as it provides the ultimate protection against atmospheric contamination.
- If your primary focus is uniform heating of complex shapes: You must prioritize furnace design and part arrangement to mitigate the line-of-sight limitations of thermal radiation.
- If your primary focus is cost and high throughput: Carefully evaluate if the material benefits of vacuum processing justify the higher equipment cost and potentially longer cycle times.
Understanding that a vacuum isolates thermal radiation is the key to mastering high-performance material processing.
Summary Table:
| Heat Transfer Mode | Mechanism | Requires a Medium? | Effect in a Vacuum |
|---|---|---|---|
| Conduction | Direct contact between particles | Yes | Eliminated |
| Convection | Movement of fluids (gas/liquid) | Yes | Eliminated |
| Radiation | Electromagnetic waves (e.g., infrared) | No | Only method remaining |
Optimize Your Lab's Thermal Processes with KINTEK
Understanding heat transfer in a vacuum is critical for achieving contamination-free results in applications like annealing, brazing, and heat treating. KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment, including vacuum furnaces designed to leverage thermal radiation for superior material purity and integrity.
We help you:
- Prevent Oxidation & Decarburization: Our vacuum solutions eliminate reactive gases, protecting sensitive materials.
- Achieve Precise Temperature Control: Engineered for efficient radiant heat management.
- Scale Your R&D or Production: From benchtop to industrial systems, we have the right equipment for your needs.
Ready to enhance your process with reliable vacuum technology? Contact our experts today to discuss your specific application and discover the right solution for your laboratory.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Heated Vacuum Press Machine Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is environmental control within a vacuum furnace important for diffusion bonding? Master Titanium Alloy Laminates
- What does a vacuum furnace do? Achieve High-Purity Heat Treatment for Superior Components
- What is the standard thickness of plating? Optimize Durability, Corrosion & Cost
- What is the vacuum heat treatment cycle? Achieve Superior Material Purity and Precision
- What are the uses of vacuum furnace? Achieve Unmatched Material Purity and Performance



















