In short, a vacuum is created in a furnace by using a specialized pumping system to mechanically remove the air and other gases from a sealed furnace chamber. This process lowers the internal pressure to a level far below the normal atmosphere, creating the vacuum environment required for processing.
A vacuum furnace doesn't create "vacuum" as a substance; it systematically removes atmospheric gases. This fundamental act prevents unwanted chemical reactions like oxidation at high temperatures, which is the core reason for its use in advanced material processing.

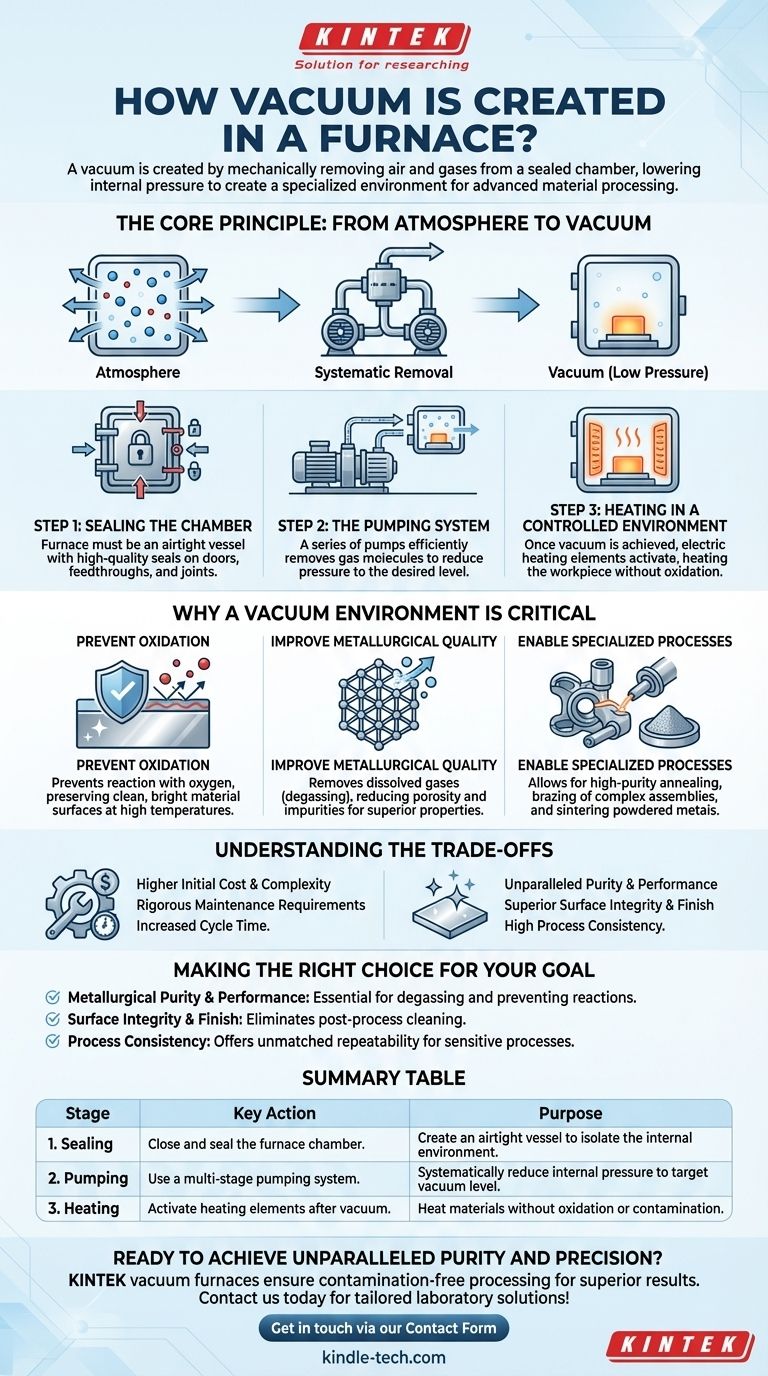
The Core Principle: From Atmosphere to Vacuum
Creating a vacuum is a process of subtraction. A vacuum furnace is engineered to be an isolated system where the internal atmosphere can be precisely controlled by removing almost all of the air that would normally be present.
Step 1: Sealing the Chamber
Before a vacuum can be created, the furnace must be a completely airtight vessel. The furnace door, feedthroughs for power and sensors, and all joints are fitted with high-quality seals to prevent outside air from leaking back into the chamber once pumping begins.
Step 2: The Pumping System
A vacuum system, not a single pump, evacuates the chamber. This typically involves a series of pumps working in stages to efficiently remove gas molecules and reduce the internal pressure to the desired level.
Step 3: Heating in a Controlled Environment
Once the target vacuum level is reached, electric heating elements inside the furnace are activated. Because the oxygen and other reactive gases have been removed, the workpiece can be heated to very high temperatures without oxidizing, decarburizing, or becoming contaminated.
Why a Vacuum Environment is Critical
Operating under vacuum isn't just an alternative method; for many applications, it is the only way to achieve the required material properties and finish. It solves fundamental problems that occur when heating metals in the presence of air.
To Prevent Oxidation
Heating metals in air causes them to react with oxygen, forming a layer of oxide scale on the surface. A vacuum environment is virtually free of oxygen, which preserves the clean, bright surface of the material even at extreme temperatures.
To Improve Metallurgical Quality
A vacuum helps pull dissolved gases, like hydrogen and nitrogen, out of the metal itself—a process called degassing. This reduces internal porosity and impurities, leading to a final product with superior density, strength, and overall mechanical properties.
To Enable Specialized Processes
Certain advanced processes are only possible in a vacuum. These include high-purity annealing, the brazing of complex assemblies with filler metals that would otherwise oxidize, and sintering powdered metals into a solid mass.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, vacuum furnaces introduce their own set of operational complexities that must be managed. They are not a universal replacement for all heating applications.
Higher Initial Cost and Complexity
A vacuum furnace is inherently more complex than a standard atmospheric furnace. The vacuum pumps, sophisticated control systems, and the need for a perfectly sealed chamber result in higher initial equipment and installation costs.
Rigorous Maintenance Requirements
Maintaining the integrity of the vacuum system is critical. This involves regular checks of seals, pumps, and gauges to prevent leaks and ensure consistent performance. As the references note, strong operational discipline and detailed record-keeping are essential.
Increased Cycle Time
The process of pumping down the furnace chamber to the required vacuum level adds time to every cycle. This "pump-down time" must be factored into production scheduling and can impact overall throughput compared to simpler atmospheric furnaces.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use a vacuum furnace should be driven by the specific technical requirements of your process and material.
- If your primary focus is metallurgical purity and performance: A vacuum furnace is non-negotiable for degassing materials and preventing reactions that compromise mechanical integrity.
- If your primary focus is surface integrity and finish: The vacuum environment eliminates the need for post-process acid cleaning or abrasive blasting by preventing oxidation from ever occurring.
- If your primary focus is process consistency for high-value components: The tightly controlled, low-pressure environment offers unmatched repeatability for sensitive processes like brazing and heat treatment.
Ultimately, choosing a vacuum furnace is a strategic decision to control the process environment with the highest possible precision.
Summary Table:
| Stage | Key Action | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Sealing | Close and seal the furnace chamber. | Create an airtight vessel to isolate the internal environment. |
| 2. Pumping | Use a multi-stage pumping system to evacuate air and gases. | Systematically reduce internal pressure to the target vacuum level. |
| 3. Heating | Activate heating elements once vacuum is achieved. | Heat materials without oxidation, decarburization, or contamination. |
Ready to achieve unparalleled purity and precision in your heat treatment processes?
A vacuum furnace from KINTEK ensures your high-value materials are processed in a contamination-free environment, preventing oxidation and improving mechanical properties. Our expertise in lab equipment and consumables means we provide solutions tailored to your specific laboratory needs—from advanced brazing and sintering to high-purity annealing.
Contact us today to discuss how a KINTEK vacuum furnace can enhance your results and efficiency.
Get in touch via our Contact Form
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is a vacuum furnace used for? Unlock High-Purity Heat Treatment for Superior Materials
- What are the applications of vacuum evaporation? Unlock Thin Film Deposition & Wastewater Purification
- Why is a Laboratory Vacuum Drying Oven recommended for PBAT microspheres? Protect Sensitive Polymer Integrity
- What are the benefits of tempering? Achieve the Perfect Balance of Hardness and Toughness
- Is it better to weld or braze aluminum? Maximize Strength or Minimize Distortion
- What is the primary function of large-scale resistance furnaces in the Acheson process? Powering SiC Synthesis
- What are the methods of sintering? Choose the Right Technique for Your Materials
- What are the various types of heat treatment processes? Master Annealing, Hardening, Tempering & Case Hardening



















