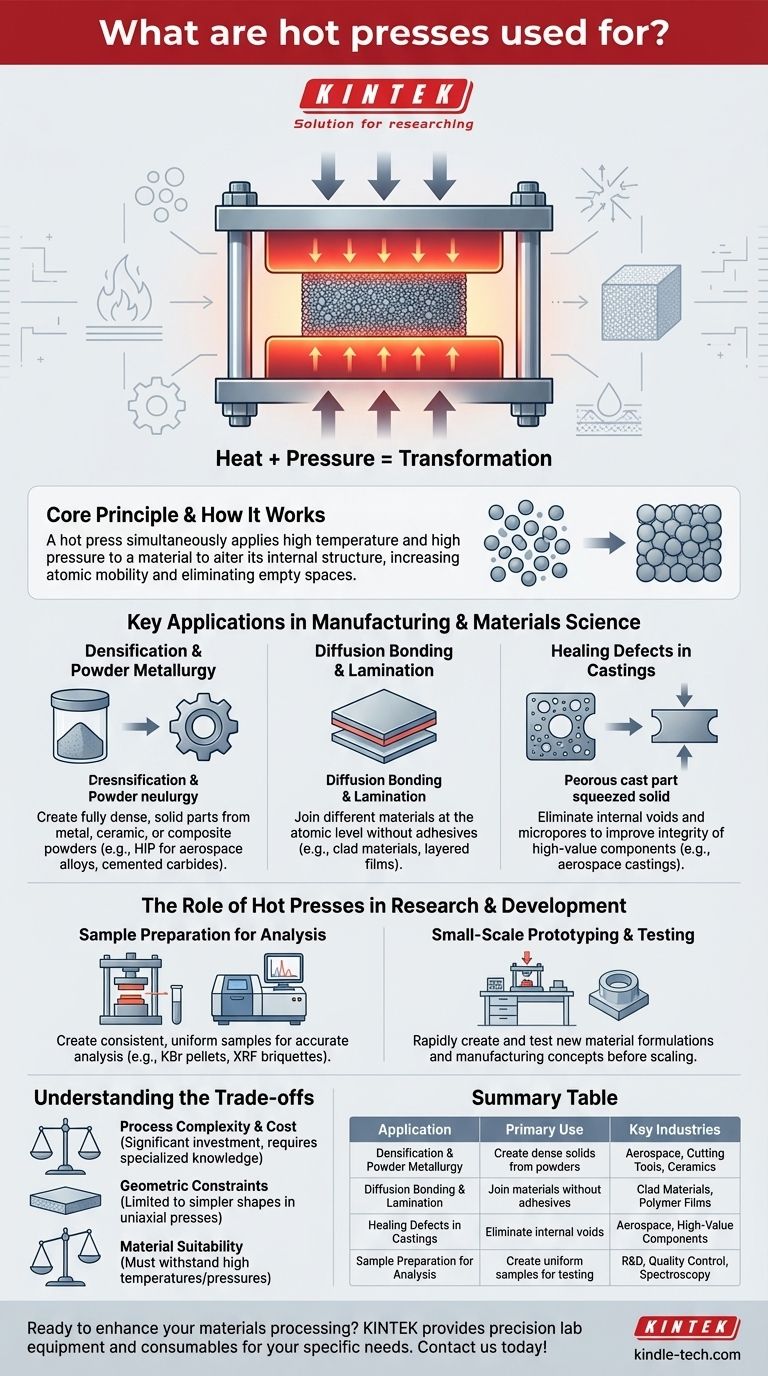
At its core, a hot press is a specialized machine that simultaneously applies high temperature and high pressure to a material. This combined action is used to consolidate powders into dense solids, bond different materials together, eliminate internal defects in components, or prepare highly uniform samples for scientific analysis.
The fundamental purpose of a hot press is not merely to shape an object, but to fundamentally alter its internal structure. By controlling heat and force, you can transform loose powders, flawed castings, or separate layers into a single, high-performance, engineered material.

The Core Principle: Heat + Pressure = Transformation
How It Works
A hot press operates on a simple but powerful principle. Heating a material softens it and increases atomic mobility, while the immense pressure forces particles or surfaces together, eliminating empty space and encouraging atomic bonds to form.
Think of it like forging metal, but with more precise control and the ability to work with materials like ceramics and powdered metals that can't be worked in traditional ways.
Key Applications in Manufacturing and Materials Science
Densification and Powder Metallurgy
This is a primary use of hot pressing, especially a variant called Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP). The goal is to turn metal, ceramic, or composite powders into a fully dense, solid part with superior mechanical properties.
Applications include creating high-performance ceramics, cemented carbides for cutting tools, and net-shape components from nickel-base superalloys and titanium powders for the aerospace industry.
Diffusion Bonding and Lamination
Hot pressing enables the joining of different materials without melting or using adhesives. At high temperatures and pressures, atoms from each material migrate across the boundary, creating a strong, continuous bond at the atomic level.
This is critical for creating clad materials or joining dissimilar metals and alloys. On a smaller scale, it is also used for laminating documents or creating layered polymer films.
Healing Defects in Castings
High-value components, especially for aerospace, are often created through casting. However, this process can leave behind microscopic voids or pores that compromise the part's integrity.
A hot press, particularly a HIP system, can subject these castings to immense pressure and heat, effectively squeezing these internal voids shut and healing the defects.
The Role of Hot Presses in Research & Development
Sample Preparation for Analysis
In a laboratory setting, hot presses are indispensable for preparing materials for analysis. Consistent, uniform samples are required for accurate results.
For example, a lab press is used to create KBr pellets for infrared (IR) spectroscopy or to press thin polymer films for transmission analysis. It is also used to form briquettes for X-ray fluorescence (XRF) spectroscopy.
Small-Scale Prototyping and Testing
Laboratory presses are perfect for R&D, small production runs, and materials testing. They allow researchers and engineers to quickly create and test new material formulations or manufacturing concepts before scaling up.
This is common in cell manufacturing and lean manufacturing environments where rapid iteration and testing are key.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Process Complexity and Cost
Industrial hot presses, especially HIP units, are significant capital investments. They are complex machines that require specialized knowledge to operate and maintain, making them unsuitable for simple forming tasks.
Geometric Constraints
While HIP technology allows for complex "net-shape" forming, traditional uniaxial hot presses are generally limited to simpler geometries like cylinders, discs, and blocks. The shape of the final part is dictated by the die it is pressed in.
Material Suitability
The process is only suitable for materials that can withstand high temperatures and pressures without degrading. The specific temperature, pressure, and time cycle must be carefully developed for each material to achieve the desired outcome without causing damage.
How to Apply This to Your Goal
Before selecting a process, clarify your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is large-scale industrial production: You need a production-grade hot press or HIP unit for densifying powders, healing casting defects, or net-shape forming of high-performance parts.
- If your primary focus is materials research and development: A versatile laboratory press with heated platens is essential for creating novel materials, testing new formulations, and small-scale prototyping.
- If your primary focus is routine quality control or analysis: A small, dedicated laboratory press is the right tool for consistently preparing samples for spectroscopic or other analytical techniques.
Ultimately, a hot press provides you with precise control over a material's density, structure, and integrity.
Summary Table:
| Application | Primary Use | Key Industries |
|---|---|---|
| Densification & Powder Metallurgy | Create dense solids from powders | Aerospace, Cutting Tools, Ceramics |
| Diffusion Bonding & Lamination | Join materials without adhesives | Clad Materials, Polymer Films |
| Healing Defects in Castings | Eliminate internal voids | Aerospace, High-Value Components |
| Sample Preparation for Analysis | Create uniform samples for testing | R&D, Quality Control, Spectroscopy |
Ready to enhance your materials processing? Whether you're in large-scale manufacturing or cutting-edge R&D, KINTEK's lab equipment and consumables are designed to meet your specific needs. From industrial hot presses for high-performance part production to versatile laboratory presses for prototyping and sample preparation, we provide the precision and reliability you require. Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can transform your workflow and deliver superior results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Heated Vacuum Press Machine Tube Furnace
- Electric Heated Hydraulic Vacuum Heat Press for Lab
- Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Vacuum Box Laboratory Hot Press
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is the significance of precise temperature control in melt infiltration? Achieve High-Performance Li-Alloy Electrodes
- How does the uniaxial pressing function of a vacuum hot press furnace influence the microstructure of ZrC-SiC ceramics?
- What are the primary advantages of using a vacuum hot pressing sintering furnace? Maximize Density in B4C-CeB6 Ceramics
- What advantages does hot pressing sintering equipment provide for NASICON? Achieve 100% Dense Solid Electrolyte Plates
- What are the advantages of using a vacuum hot press sintering furnace? Achieve 99.1% Density in CuW30 Composites



















