At its core, induction heating is a highly controlled method of generating heat directly within a material. It is used across a vast range of industrial and consumer applications, from melting high-temperature metals and hardening steel parts to advanced semiconductor manufacturing and everyday induction cooktops. This method is chosen for its unique ability to deliver fast, clean, and precise thermal energy without any physical contact.
The true value of induction heating lies not just in what it heats, but how. It offers unparalleled speed, precision, and efficiency by generating heat inside the target material, making it the superior choice for processes where absolute control is paramount.
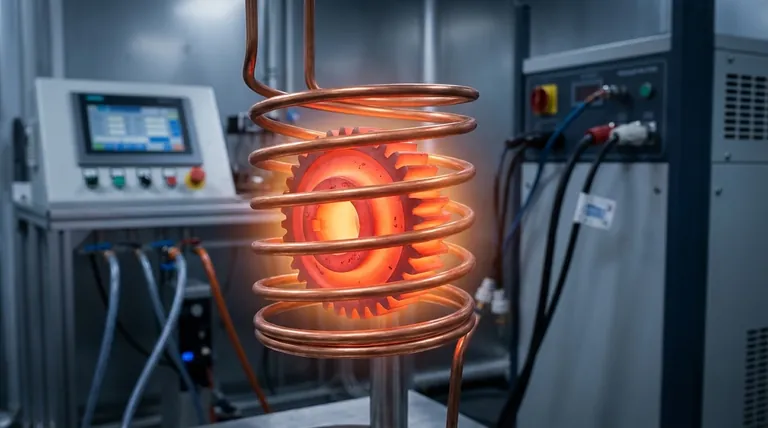
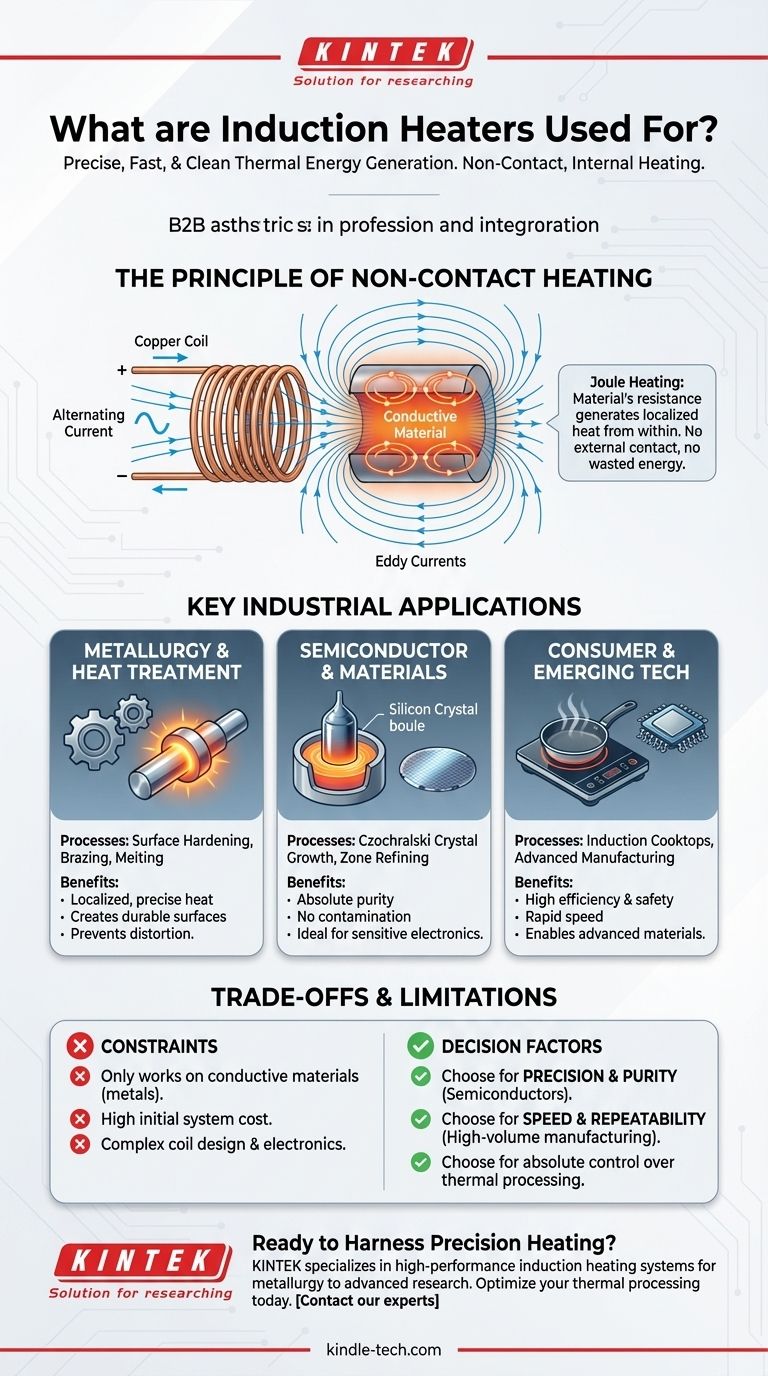
The Principle of Non-Contact Heating
To understand its applications, you must first understand its fundamental advantage over traditional methods. Unlike a furnace or a flame, an induction heater does not rely on external heat transfer.
How It Works: Electromagnetic Fields
An induction system uses an alternating electric current flowing through a copper coil. This creates a powerful, oscillating magnetic field around the coil.
When an electrically conductive material, like a piece of steel, is placed within this field, the field induces circulating electric currents (called eddy currents) inside the metal itself.
The Advantage of Internal Heat Generation
The material’s natural resistance to the flow of these eddy currents generates intense, localized heat—a principle known as Joule heating.
Because the heat originates within the part, the process is incredibly fast and efficient. There is no wasted energy heating the surrounding air or a furnace chamber, and the part heats from the inside out.
Key Industrial Applications and Their Rationale
The unique properties of induction heating make it the ideal solution for specific, high-value industrial processes where other methods fall short.
Metallurgy and Heat Treatment
This is the most common application space. In processes like surface hardening, induction allows you to heat just the outer layer of a steel gear or shaft to a precise depth. This creates a hard, wear-resistant surface while leaving the core of the part softer and more ductile, a combination that is mechanically superior.
For brazing and welding, the localized heat allows for strong, clean joints without distorting or weakening the surrounding material. For melting, the lack of contaminants from a flame or heating element ensures the purity of the final metal alloy.
Advanced Materials and Semiconductor Production
In highly sensitive processes, avoiding contamination is critical. Induction heating is essential for Czochralski crystal growth and zone refining, foundational techniques for producing the high-purity silicon used in all modern electronics.
Because there is no physical heating element, no impurities can be introduced into the molten material. This ensures the creation of perfect crystal structures necessary for semiconductor performance.
Consumer and Emerging Technologies
The most familiar application is the induction cooktop. Here, the benefits are efficiency and safety. The magnetic field heats the pan directly, so very little energy is wasted, and the glass cooktop itself remains cool to the touch.
Looking forward, induction is being leveraged for highly engineered materials and processes in alternative energy sectors, where its precision and efficiency are critical for manufacturing advanced components.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, induction heating is not a universal solution. Its effectiveness is governed by specific physical constraints that make it unsuitable for certain tasks.
Material Constraints
The primary limitation is that induction only works directly on electrically conductive materials. It cannot heat glass, plastics, ceramics, or other insulators without the use of a secondary conductive "susceptor" to transfer the heat.
Equipment and Coil Design
The initial capital cost for induction heating systems can be significant. Furthermore, the efficiency of the process is highly dependent on the induction coil design. The coil must be carefully shaped and positioned relative to the workpiece, often requiring custom engineering for each specific application.
Process Complexity
While the heating itself is precise, the overall system requires sophisticated power supplies and control electronics to manage the frequency and power output. This adds a layer of complexity compared to a simple gas-fired furnace.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
The decision to use induction heating depends entirely on whether its unique benefits align with your primary process requirements and justify its constraints.
- If your primary focus is precision and purity: Induction heating is often the only viable option, especially in semiconductor manufacturing or high-purity metallurgy.
- If your primary focus is speed and repeatability in manufacturing: The rapid, localized heating of induction is ideal for high-volume processes like surface hardening or brazing on an assembly line.
- If your primary focus is bulk heating of non-conductive materials: A conventional oven or resistive furnace will be a more direct and cost-effective solution.
Ultimately, adopting induction heating is a strategic choice for applications where precision control over the heating process directly translates to a higher quality final product.
Summary Table:
| Application Area | Key Processes | Primary Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Metallurgy & Heat Treatment | Surface Hardening, Brazing, Melting | Localized, precise heat; No part distortion |
| Semiconductor & Materials | Crystal Growth, Zone Refining | Absolute purity; No contamination |
| Consumer & Emerging Tech | Induction Cooktops, Advanced Manufacturing | High efficiency; Safety and speed |
Ready to harness the precision of induction heating in your lab or production line? At KINTEK, we specialize in high-performance lab equipment, including induction heating systems tailored for applications from metallurgy to advanced materials research. Our solutions deliver the speed, purity, and control your process demands. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can optimize your thermal processing.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Platinum Sheet Electrode for Laboratory and Industrial Applications
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- Ultra-High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the uses of silicon carbide rod? The Ultimate Heating Solution for Extreme Temperatures
- What is silicon carbide rod heated to high temperature used as? A Premier Heating Element for Extreme Environments
- What is a silicon carbide heating element? Unlock Extreme Heat for Industrial Processes
- What material is used for making heating element? Choose the Right Alloy for Your Application
- What is SiC elements? The Ultimate High-Temperature Heating Solution


















