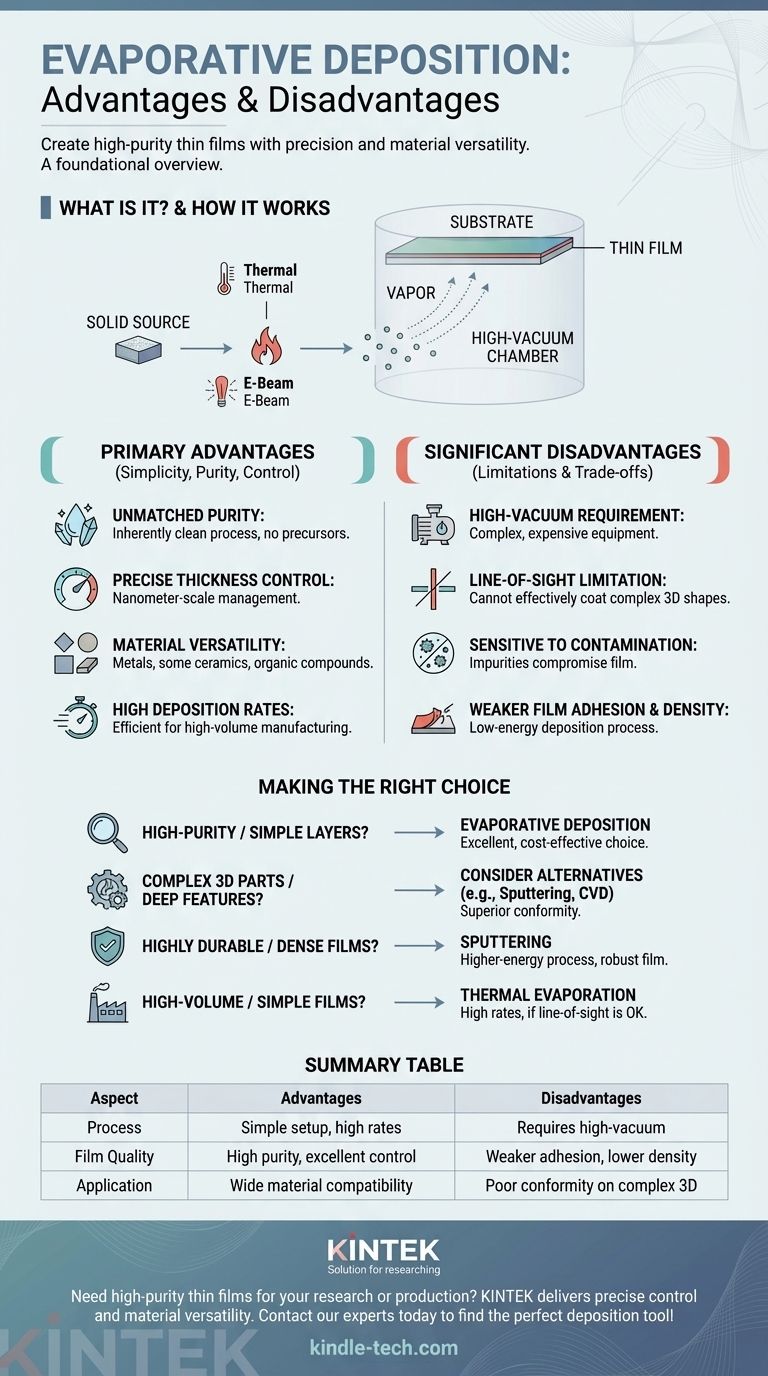
At its core, evaporative deposition is a highly effective method for creating pure, simple thin films with excellent thickness control. Its main advantages are its precision and material versatility, while its primary disadvantages stem from its requirement for a high-vacuum environment and its difficulty in coating complex shapes.
The decision to use evaporative deposition hinges on a fundamental trade-off: it provides exceptional purity and control in a simple setup, but this comes at the cost of environmental sensitivity and limitations in coating geometry.
What is Evaporative Deposition? A Foundational Overview
Evaporative deposition is a type of Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) used to apply a thin layer of material onto a surface, known as a substrate. The process is straightforward but requires a carefully controlled environment.
The Core Principle: From Solid to Vapor to Film
The source material is heated in a high-vacuum chamber until it evaporates, turning from a solid into a gas. These vaporized atoms travel in a straight line through the vacuum until they strike the cooler substrate, where they condense back into a solid, forming a thin, uniform film.
Key Techniques: Thermal vs. E-Beam
Two common methods are used to heat the source material.
- Thermal Evaporation: A current is passed through a resistive "boat" or filament holding the source material, heating it until it evaporates. This is simple and cost-effective.
- Electron Beam (E-Beam) Evaporation: A high-energy beam of electrons is fired at the source material, causing localized heating and evaporation. This allows for higher temperatures and the deposition of a wider range of materials.
The Critical Role of High Vacuum
The entire process must occur in a high-vacuum environment. This is non-negotiable for two reasons: it prevents vaporized atoms from colliding with air molecules, and it minimizes contamination from atmospheric gases, ensuring the purity of the final film.
The Primary Advantages of Evaporative Deposition
Engineers and researchers choose this method for its unique combination of simplicity, purity, and control.
Unmatched Purity and Simplicity
Because the process simply involves heating a source material in a vacuum, it is inherently clean. Unlike chemical processes, there are no precursor gases or byproducts that can become trapped in the film, resulting in exceptionally high-purity layers.
Precise Control Over Thickness
By carefully monitoring and controlling the temperature of the source, you can precisely manage its evaporation rate. This, combined with the deposition time, gives you fine-grained control over the final film thickness, often down to the nanometer scale.
Versatility Across Materials
Evaporative deposition is compatible with a vast array of materials, including most metals, some ceramics, and various organic compounds. If a material can be vaporized by heat without decomposing, it can likely be deposited.
High Deposition Rates
Compared to more complex methods like sputtering or atomic layer deposition, thermal evaporation can achieve very high deposition rates. This makes it efficient and suitable for high-volume manufacturing where speed is a factor.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Disadvantages
Despite its benefits, evaporative deposition has significant limitations that make it unsuitable for certain applications.
The High-Vacuum Requirement
Achieving and maintaining a high vacuum requires expensive and complex equipment, including vacuum chambers, pumps, and gauges. This adds to the initial cost and operational complexity of the system.
The "Line-of-Sight" Limitation
Vaporized atoms travel in straight lines from the source to the substrate. This means the process can only coat surfaces that are in the direct line of sight of the source. It cannot effectively coat complex 3D objects, undercuts, or the inside of deep trenches.
Sensitivity to Contamination
While the vacuum provides a clean environment, the process is extremely sensitive to any impurities. A small leak in the vacuum chamber or an impure source material can easily contaminate the entire film, compromising its performance.
Weaker Film Adhesion and Density
The atoms in evaporative deposition arrive at the substrate with relatively low energy. This can result in films that are less dense and have weaker adhesion compared to those produced by sputtering, where atoms are bombarded onto the surface with high kinetic energy.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right deposition method requires aligning the process capabilities with your primary goal.
- If your primary focus is high-purity optical coatings or simple metallic layers: Evaporative deposition is an excellent, cost-effective choice due to its simplicity and the clean films it produces.
- If your primary focus is coating complex 3D parts or deep features: You must consider alternatives like sputtering or chemical vapor deposition (CVD), which offer superior conformity and step coverage.
- If your primary focus is creating highly durable, dense, or wear-resistant films: Sputtering is often a better choice because the higher-energy deposition process creates a more robust film structure.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production of simple films: The high deposition rates of thermal evaporation make it a very strong candidate, provided its line-of-sight limitation is not an issue.
Understanding these fundamental trade-offs empowers you to select the most effective tool for your specific engineering challenge.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Process | Simple setup, high deposition rates | Requires expensive high-vacuum equipment |
| Film Quality | High purity, excellent thickness control | Weaker adhesion and lower film density |
| Application | Wide material compatibility | Poor conformity on complex 3D shapes |
Need to deposit high-purity thin films for your research or production? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, including advanced evaporative deposition systems. Our solutions deliver the precise control and material versatility your laboratory requires. Contact our experts today to find the perfect deposition tool for your specific application!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Tungsten Tantalum Evaporation Boat for High Temperature Applications
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- Aluminized Ceramic Evaporation Boat for Thin Film Deposition
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
People Also Ask
- What is the meaning of thermal evaporation? A Guide to Simple, Cost-Effective Thin Film Coating
- What is vacuum thermal evaporation? A Guide to High-Purity Thin Film Deposition
- What is thermal evaporation technique thin film deposition? A Guide to Simple, Cost-Effective PVD
- What is the thermal evaporation technique? A Guide to Thin-Film Deposition for Your Lab
- What is the process of thermal evaporation in PVD? A Step-by-Step Guide to Thin Film Deposition



















