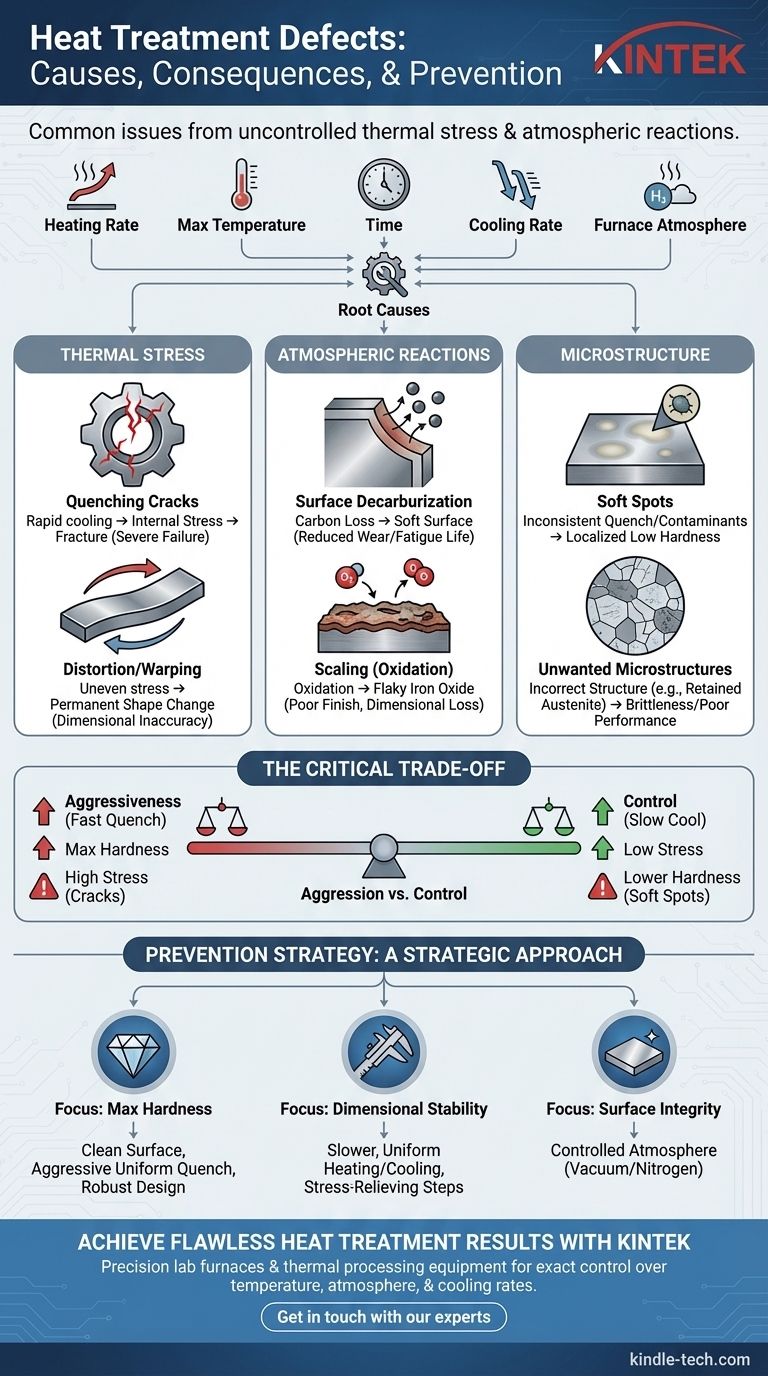
The most common defects in heat treatment include quenching cracks, distortion, decarburization, soft spots, and surface scaling. These issues arise from improper control over the core variables of the process: the rate of heating, the maximum temperature, the duration of heating, the rate of cooling, and the composition of the furnace atmosphere.
Heat treatment defects are not random failures. They are predictable consequences of an imbalance between the material, its geometry, and the thermal process applied, with the most critical issues stemming from uncontrolled thermal stress and atmospheric reactions.

Defects Caused by Thermal Stress
The rapid temperature changes inherent to heat treatment create immense internal stress within a material. If not managed, this stress is the primary source of catastrophic failure.
Quenching Cracks
Quenching cracks are the most severe heat treatment defect. They occur when a part is cooled too rapidly, causing different sections of the material to contract at different rates.
This differential shrinkage creates internal stresses that exceed the material's tensile strength, resulting in fractures. Sharp corners or abrupt changes in section thickness are common initiation points for these cracks.
Distortion and Warping
Distortion, including warping and changes in shape (ovality), is a less severe result of the same thermal stresses that cause cracking.
When internal stresses from heating and cooling are relieved, the part permanently changes shape. This is particularly common in long, thin parts or components with non-symmetrical geometry.
Defects from Surface and Atmospheric Reactions
The environment inside the furnace plays a critical role. Reactions between the heated metal surface and the surrounding atmosphere can degrade the material's properties from the outside in.
Surface Decarburization
Decarburization is the loss of carbon content from the surface of steel. At high temperatures, carbon atoms can react with gases in the furnace atmosphere (like oxygen or water vapor) and diffuse out of the part.
This leaves a soft, low-carbon layer on the surface, which drastically reduces wear resistance and fatigue life, even if the core of the part is properly hardened.
Scaling (Oxidation)
Scaling is the formation of a thick, flaky layer of iron oxide on the surface of the part. It occurs when the heated steel reacts directly with oxygen in an ordinary atmosphere furnace.
While some light scaling is expected, heavy scale can ruin surface finish, interfere with subsequent machining processes, and lead to a loss of dimensional accuracy.
Defects in Material Microstructure
The entire purpose of heat treatment is to achieve a specific, desirable crystalline structure (microstructure) within the material. When the process is flawed, an undesirable or inconsistent structure results.
Soft Spots
Soft spots are localized areas on the surface of a quenched part that failed to achieve the specified hardness.
This is often caused by contaminants on the surface (like scale or oil) that insulate the part from the quenching medium, or by inconsistencies in the quenching process itself, such as vapor bubbles.
Unwanted Microstructures
A successful heat treatment creates a uniform, intended microstructure (e.g., martensite for high hardness). Microstructural defects include the presence of retained austenite or large, coarse grains.
These incorrect structures can lead to brittleness, poor wear resistance, or a failure to meet hardness specifications, even if no visible cracks or soft spots are present.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The core challenge in heat treatment is managing the fundamental trade-off between achieving high hardness and introducing excessive brittleness and internal stress.
Aggressiveness vs. Control
A very aggressive (fast) quench is needed to achieve maximum hardness, but it also generates the most thermal stress, increasing the risk of cracks and distortion.
Conversely, a slower, more controlled cooling process reduces stress but may not cool the part quickly enough to achieve the desired hardened microstructure, resulting in soft spots or poor overall hardness.
The Role of Design
Part geometry is a critical factor. Designs with sharp internal corners, deep holes, or drastic changes in thickness create stress concentrations. These features are highly susceptible to cracking during quenching, forcing a compromise on the aggressiveness of the heat treatment process.
Preventing Defects: A Strategic Approach
Controlling heat treatment outcomes requires a focus on the specific goal for the component. Your strategy should be tailored to the most critical property you need to achieve.
- If your primary focus is maximum hardness: Ensure a clean part surface and an aggressive, uniform quench while considering a more robust material or design modifications to prevent cracking.
- If your primary focus is dimensional stability: Prioritize slower, more uniform heating and cooling rates, and consider adding pre-treatment stress-relieving steps for complex geometries.
- If your primary focus is surface integrity: You must use a controlled furnace atmosphere (such as vacuum or nitrogen) to prevent decarburization and scaling.
Ultimately, preventing defects is about establishing precise control over every stage of the thermal process.
Summary Table:
| Defect Type | Primary Cause | Key Consequence |
|---|---|---|
| Quenching Cracks | Rapid cooling causing high internal stress | Catastrophic part failure |
| Distortion/Warping | Uneven heating/cooling creating stress | Dimensional inaccuracy |
| Decarburization | Carbon loss from surface due to furnace atmosphere | Reduced surface hardness and fatigue life |
| Scaling | Surface oxidation in an uncontrolled atmosphere | Poor surface finish, dimensional loss |
| Soft Spots | Inconsistent quenching or surface contaminants | Localized areas of low hardness |
Achieve flawless heat treatment results for your laboratory components.
Defects like cracking, warping, and decarburization can compromise your research and development, leading to costly delays and unreliable data. KINTEK specializes in precision lab furnaces and thermal processing equipment designed to deliver the exact control over temperature, atmosphere, and cooling rates that is essential for preventing these common issues.
Whether you are hardening tools, annealing samples, or processing advanced materials, our solutions help you achieve consistent, high-quality results by minimizing thermal stress and atmospheric reactions.
Contact us today to discuss your specific application and how we can help you optimize your heat treatment process for superior outcomes.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of a vacuum furnace? Achieve Superior Purity and Control in Heat Treatment
- Is heat Cannot travel in a vacuum True or false? Discover How Heat Crosses the Void of Space
- What is a vacuum furnace used for? Unlock High-Purity Heat Treatment for Superior Materials
- What does a vacuum furnace do? Achieve High-Purity Heat Treatment for Superior Components
- What is the standard thickness of plating? Optimize Durability, Corrosion & Cost



















