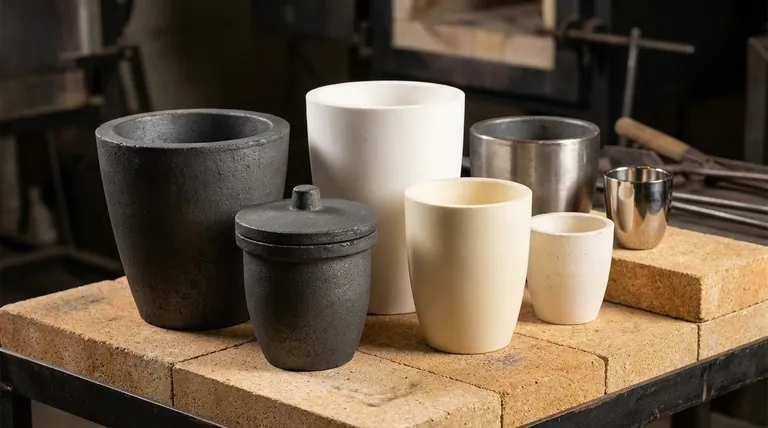
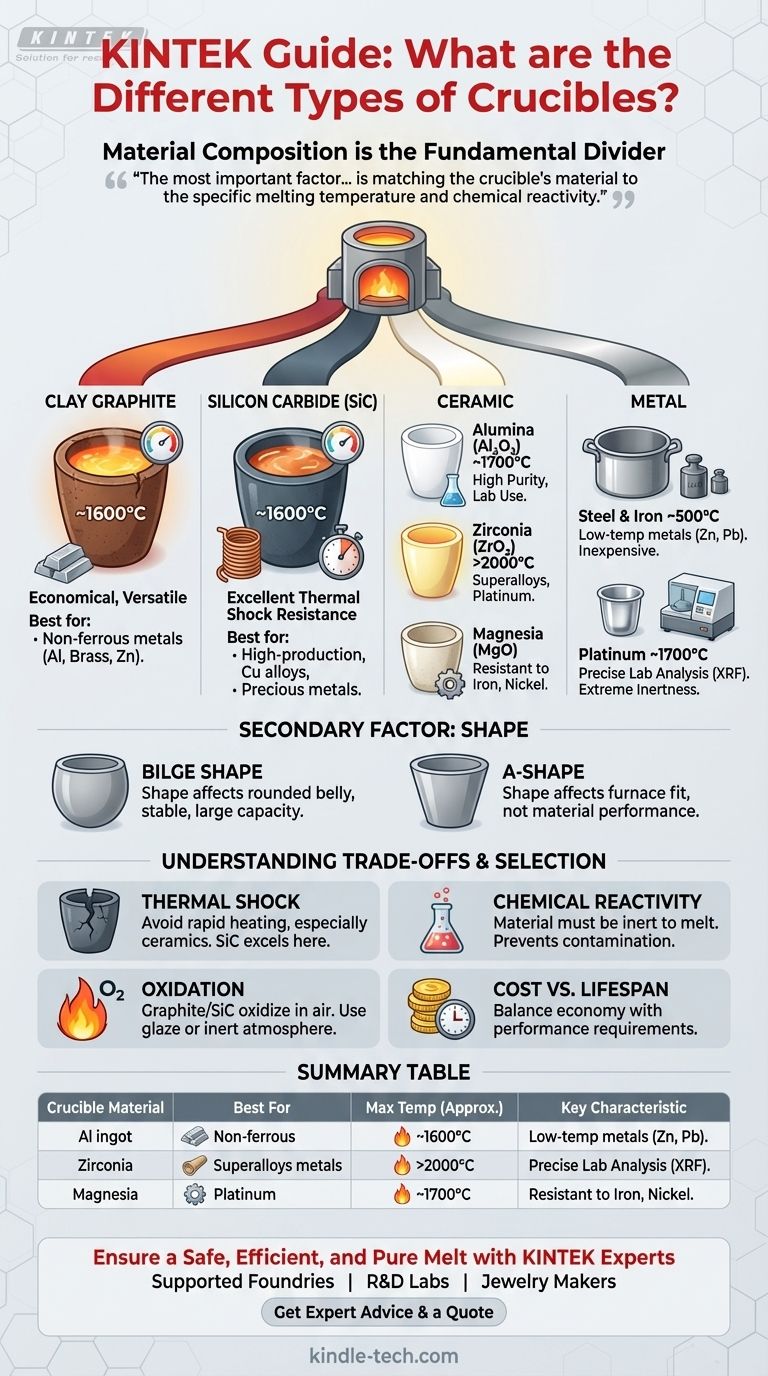
Crucibles are primarily categorized by their material composition, which dictates their performance at high temperatures and their compatibility with different molten substances. While physical shapes like the 'A' shape or bilge shape exist, the crucial distinction lies in the material—such as clay graphite, silicon carbide, pure ceramics like alumina, or various metals—as each is engineered for a specific range of temperatures and chemical environments.
The most important factor in choosing a crucible is not finding the "best" type, but matching the crucible's material to the specific melting temperature and chemical reactivity of the substance you are working with. The material defines its capabilities, while the shape is a secondary factor related to the furnace and process.

The Fundamental Divider: Material Composition
The single most critical property of a crucible is the material it is made from. This determines its maximum operating temperature, its resistance to chemical attack, and its ability to withstand rapid temperature changes.
Clay Graphite Crucibles
Clay graphite is a common, versatile, and economical choice. A bonded mixture of clay and graphite creates a crucible with good thermal conductivity and mechanical strength.
These are the workhorses for melting most non-ferrous metals, including aluminum, brass, and zinc alloys.
Silicon Carbide (SiC) Crucibles
Silicon carbide crucibles offer superior performance to clay graphite, featuring excellent thermal conductivity and exceptional resistance to thermal shock. This allows for faster melting cycles and a longer service life.
They are widely used for melting copper-based alloys, precious metals, and aluminum in high-production foundries.
Ceramic Crucibles
Ceramic crucibles are used for applications requiring very high temperatures, high purity, or resistance to extremely reactive materials.
- Alumina (Al₂O₃): A high-purity, widely used ceramic that can handle temperatures up to 1700°C (3092°F). It is relatively inert, making it suitable for melting a wide range of materials.
- Zirconia (ZrO₂): Used for even higher temperatures, often exceeding 2000°C (3632°F). It is ideal for melting platinum-group metals and specialty superalloys that would react with alumina.
- Magnesia (MgO): This material is chosen for its superior resistance to basic slags and specific metals like iron, nickel, and their alloys.
Metal Crucibles
In some cases, crucibles are made from metal. Their use is typically limited by their own melting points and reactivity.
- Steel & Iron: Inexpensive and suitable for lower-temperature applications like melting zinc or lead. They are not suitable for melting higher-temperature metals like aluminum or copper.
- Platinum: Extremely expensive and used almost exclusively in laboratory settings for sample analysis (e.g., XRF prep). Its very high melting point and extreme chemical inertness prevent sample contamination.
Secondary Factor: Crucible Shape
While material is paramount, shape affects how the crucible fits into a furnace and interacts with the heat source. The earliest crucibles were wide, shallow clay vessels for smelting, but modern metallurgy uses more standardized forms.
Bilge vs. 'A' Shape
The bilge shape is a classic pot-like form with a rounded belly. This design is very stable and provides a large capacity, making it one of the most common shapes for foundry work.
The 'A' shape is more conical. As noted in historical contexts, these may have a coarser surface finish, but this does not negatively impact their melting performance. The shape is simply a different standard for fitting specific types of furnaces or tongs.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting a crucible involves balancing performance against risk and cost. Understanding these trade-offs is key to preventing catastrophic failures and ensuring a pure melt.
Thermal Shock Resistance
Heating a crucible too quickly, especially a ceramic one, can cause it to crack from thermal shock. Materials like silicon carbide excel in this area, while certain high-purity ceramics may require a slower, more controlled heating cycle.
Chemical Reactivity and Contamination
The crucible material must be inert to the substance being melted. Using a graphite crucible to melt steel, for example, will cause carbon to dissolve into the iron, altering the alloy's properties. Similarly, aggressive fluxes can rapidly degrade an incompatible crucible wall.
Oxidation and Atmosphere
At high temperatures, carbon-based materials like graphite and silicon carbide will oxidize (burn away) in the presence of air. For this reason, they are often manufactured with a protective glaze. For very high-temperature work or when using pure graphite, melting must be done in a vacuum or inert gas atmosphere.
Cost vs. Lifespan
There is a direct correlation between cost and performance. A clay graphite crucible is economical for general-purpose melting, while a high-purity zirconia crucible can cost orders of magnitude more. The goal is to choose the most cost-effective option that meets the technical requirements of the job without failing.
How to Select the Right Crucible
Base your decision on your specific application and the material you intend to melt.
- If your primary focus is melting non-ferrous metals like aluminum, brass, or bronze: A clay graphite or silicon carbide crucible offers the best balance of performance and cost.
- If your primary focus is high-purity melts or very high-temperature alloys: A specialized ceramic crucible, such as alumina for general purity or zirconia for reactive superalloys, is necessary.
- If your primary focus is low-temperature metals like zinc or lead: An inexpensive steel crucible is a viable and practical option.
- If your primary focus is precise laboratory analysis: A platinum or high-purity alumina crucible is required to ensure sample integrity.
By understanding these core principles of material science and application, you can confidently select a crucible that ensures the safety, efficiency, and purity of your work.
Summary Table:
| Crucible Material | Best For | Max Temp (Approx.) | Key Characteristic |
|---|---|---|---|
| Clay Graphite | Non-ferrous metals (Al, Brass, Zn) | ~1600°C | Economical, versatile workhorse |
| Silicon Carbide (SiC) | High-production (Cu alloys, Precious metals) | ~1600°C | Excellent thermal shock resistance |
| Ceramic (Alumina) | High-purity melts, general lab use | ~1700°C | Chemically inert, high purity |
| Ceramic (Zirconia) | Superalloys, platinum-group metals | >2000°C | Extreme temperature resistance |
| Metal (Steel) | Low-temp metals (Zn, Pb) | ~500°C | Inexpensive, practical |
| Platinum | Precise lab analysis (XRF) | ~1700°C | Extreme inertness, prevents contamination |
Ensure a Safe, Efficient, and Pure Melt
Choosing the wrong crucible can lead to equipment failure, contaminated materials, and safety hazards. Let KINTEK's experts guide you to the perfect solution for your specific application, temperature, and material compatibility needs.
We provide high-performance crucibles and expert support for:
- Foundries & Metal Producers: Maximize melt efficiency and crucible lifespan.
- Research & Development Labs: Ensure sample integrity with high-purity materials.
- Jewelry Makers: Achieve consistent, high-quality results with precious metals.
Contact us today for a personalized recommendation and discover how the right crucible can enhance your process's safety, efficiency, and output quality.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- High Purity Pure Graphite Crucible for Electron Beam Evaporation
- Arc-Shaped Alumina Ceramic Crucible High Temperature Resistant for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Al2O3 Crucible With Lid Cylindrical Laboratory Crucible
- High Purity Pure Graphite Crucible for Evaporation
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Crucibles (Al2O3) for Thermal Analysis TGA DTA
People Also Ask
- What is difference between crucible and furnace? Understand the Heat Source vs. Containment Vessel
- What is the function of a crucible? A Guide to Safe, High-Temperature Material Processing
- What are the advantages of graphite crucibles? Achieve Superior High-Temperature Performance
- Why is the use of high-performance alumina crucibles necessary when melting alloys with high nickel content?
- Why are Platinum/Gold (Pt/Au) crucibles selected for silver phosphate glass? Ensure Maximum Purity in Glass Synthesis
- What material is used to make a crucible? The Ultimate Guide to Choosing the Right One
- What is the temperature range of a crucible furnace? From Hobbyist to Industrial Melting
- Can porcelain be used as a crucible? A Guide to Its High-Temperature Strengths & Limits



















