At its core, a rotary kiln is a sophisticated thermal processing machine defined by its rotating cylindrical shell, precise temperature control, and customizable design. Its key features include a 360° heater placement for uniform heat transmission, advanced sealing mechanisms to ensure an airtight environment, and the ability to tailor heat patterns and components to the specific material being processed.
A rotary kiln is not merely a furnace; it's a dynamic reactor. Its defining feature is the use of rotation and inclination to continuously mix and move materials through a highly controlled thermal environment, making it indispensable for processes requiring uniform heat treatment at high temperatures.

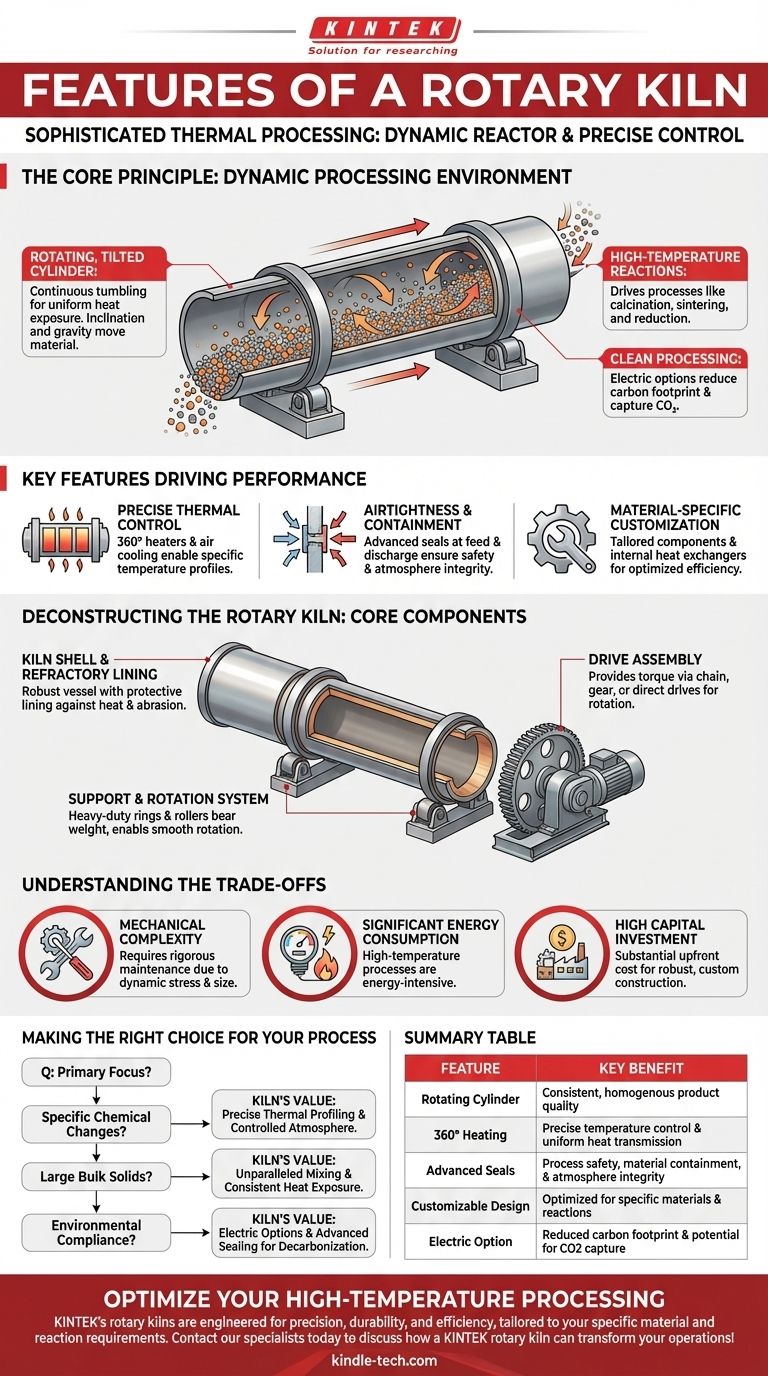
The Core Principle: A Dynamic Processing Environment
A rotary kiln's effectiveness comes from its fundamental design: a long, cylindrical vessel that is slightly inclined and rotates on its axis. This simple mechanical concept creates a powerful and highly controllable system for transforming materials.
The Rotating, Tilted Cylinder
The kiln shell is the heart of the system. Its slow rotation continuously tumbles the material inside, ensuring every particle is evenly exposed to the heat source. This tumbling action is critical for achieving a consistent and homogenous final product.
The slight tilt of the cylinder uses gravity to move material from the feed end to the discharge end at a controlled rate, ensuring a continuous process.
Driving High-Temperature Reactions
Rotary kilns are designed to achieve the high bed temperatures required to drive specific chemical reactions. They are used for demanding processes like calcination, sintering, reduction, and organic combustion that are kinetically or thermodynamically favored at extreme heat.
Clean Processing Alternatives
Modern electric rotary kilns offer a clean and efficient alternative to traditional fossil fuel-powered units. This feature enables industries to reduce their carbon footprint and even capture CO2 for reuse or sale, aligning industrial processes with environmental goals.
Key Features Driving Performance
While the rotating cylinder is the core concept, several other features are critical for a rotary kiln's performance, safety, and efficiency.
Precise Thermal Control
The ability to establish a specific heat pattern along the length of the kiln is a primary feature. This is often achieved with strategically placed 360° heaters and integrated air cooling mechanisms, allowing operators to create the exact temperature profile a product requires for its transformation.
Airtightness and Containment
Effective seals are placed at both the feed and discharge ends of the kiln. These seals are crucial for preventing the scattering of raw materials, ensuring process safety, and maintaining the integrity of the internal atmosphere, which is often critical for specific chemical reactions.
Material-Specific Customization
Rotary kilns are not one-size-fits-all. Key components are customized based on the material being processed. This can include options to suppress metal contamination from the kiln's internal surfaces or the addition of internal heat exchangers to improve thermal efficiency.
Deconstructing the Rotary Kiln: Core Components
A rotary kiln is a system of robust components working in concert to support and operate the main vessel.
The Kiln Shell and Refractory Lining
The shell is the main cylindrical body, often conically tapered at the ends, which must withstand significant torsion and flexural stress. Inside, a refractory lining protects the steel shell from extreme temperatures and abrasion.
The Support and Rotation System
Heavy-duty support tyres, also known as riding rings, are attached to the shell. These rings rest on trunnion wheels (rollers), which bear the entire weight of the kiln and allow it to rotate smoothly. Thrust rollers prevent the kiln from sliding downhill due to its inclination.
The Drive Assembly
This assembly provides the torque needed to rotate the massive kiln shell. Common types include chain and sprocket drives, gear drives, and direct drive systems, each selected based on the scale and demands of the operation.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, rotary kilns come with inherent complexities that require careful consideration.
Mechanical Complexity and Maintenance
A rotary kiln is a large, heavy, and dynamic piece of equipment. The constant rotation and thermal stress on components like the shell, support systems, and drive assembly necessitate a rigorous and proactive maintenance schedule to ensure reliability and safety.
Significant Energy Consumption
Achieving and maintaining the high temperatures required for processes like calcination is extremely energy-intensive. Whether using fossil fuels or electricity, the operational cost associated with energy is a primary consideration in any economic analysis.
High Capital Investment
The robust construction, specialized components, and process-specific customization make rotary kilns a significant capital investment. The upfront engineering and manufacturing costs are substantial, reflecting the system's complexity and long service life.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Selecting a rotary kiln depends entirely on the specific transformation your material needs to undergo.
- If your primary focus is achieving specific chemical changes (calcination, reduction): The kiln's precise thermal profiling and controlled atmosphere are its most valuable features.
- If your primary focus is processing large volumes of bulk solids uniformly: The tumbling action created by the rotating cylinder ensures unparalleled mixing and consistent heat exposure.
- If your primary focus is environmental compliance and process cleanliness: An electric rotary kiln with advanced sealing offers a path to decarbonization and prevents cross-contamination.
Ultimately, a rotary kiln is the definitive choice when you need to combine heat, mixing, and controlled residence time to fundamentally change the nature of a material.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Description | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Rotating Cylinder | Tumbles material for uniform exposure | Consistent, homogenous product quality |
| 360° Heating | Heaters placed around the kiln shell | Precise temperature control and uniform heat transmission |
| Advanced Seals | Airtight mechanisms at feed and discharge ends | Process safety, material containment, and atmosphere integrity |
| Customizable Design | Tailored components and heat patterns | Optimized for specific materials and reactions (e.g., calcination, reduction) |
| Electric Option | Clean alternative to fossil fuels | Reduced carbon footprint and potential for CO2 capture |
Ready to optimize your high-temperature processing? KINTEK's rotary kilns are engineered for precision, durability, and efficiency, tailored to your specific material and reaction requirements. Whether you need uniform calcination, sintering, or a cleaner electric solution, our expertise ensures your process achieves peak performance. Contact our specialists today to discuss how a KINTEK rotary kiln can transform your operations!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Three-dimensional electromagnetic sieving instrument
People Also Ask
- What is the purpose of a calciner? Boost Efficiency in High-Temperature Processing
- What is the difference between calcining and roasting? A Guide to High-Temperature Processing
- What is the principle of rotary kiln? Mastering Continuous Thermal Processing
- What equipment is used in pyrolysis? Choosing the Right Reactor for Your Feedstock and Products
- What biomass is used in pyrolysis? Selecting the Optimal Feedstock for Your Goals



















