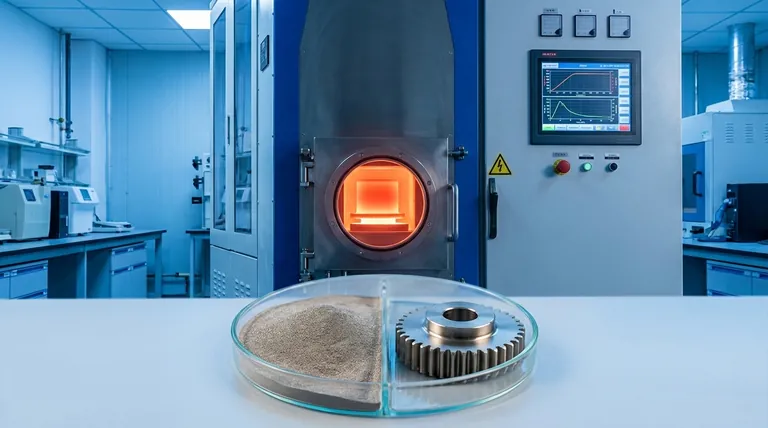
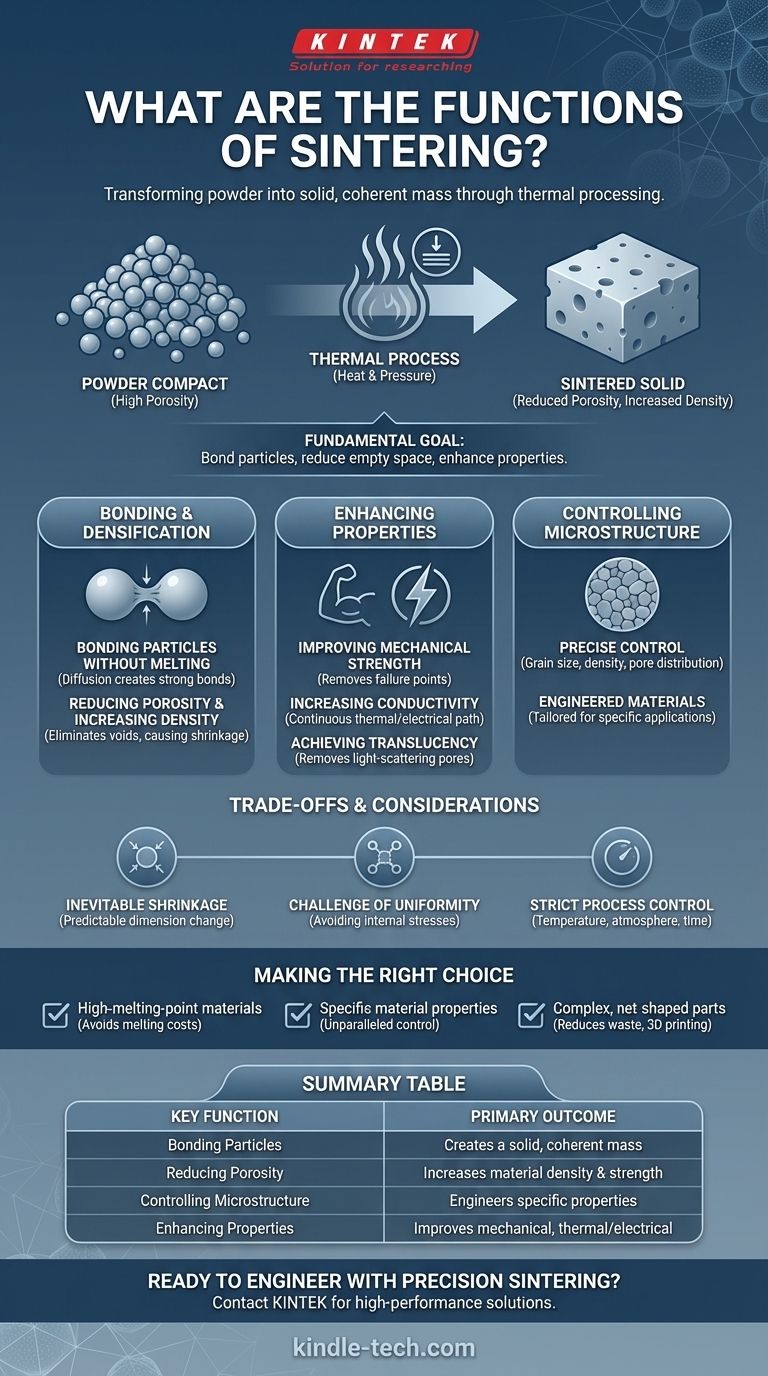
At its core, sintering is a thermal process that transforms a powder compact into a solid, coherent mass without fully melting it. Its primary functions are to bond individual particles, reduce the empty space (porosity) between them to increase density, and ultimately enhance the material's physical properties like strength and conductivity.
Sintering is not about melting; it's about using heat and sometimes pressure to make individual particles fuse together. This fundamental process allows us to create strong, dense objects from powders, giving us precise control over the final material's structure and properties in a way that melting often cannot.

The Fundamental Goal: From Powder to Solid
The central purpose of sintering is to consolidate loose or lightly-pressed powder into a durable, solid block. This is achieved through several interconnected functions that occur at a microscopic level.
Bonding Particles Without Melting
The most basic function of sintering is to create strong bonds between adjacent particles. Heat provides the energy for atoms to diffuse across the boundaries where particles touch, effectively welding them together into a solid structure.
This is especially critical for materials with extremely high melting points, like tungsten or many ceramics, where melting them is impractical or prohibitively expensive.
Reducing Porosity and Increasing Density
A collection of powder, even when compressed, contains a significant volume of empty space, or pores. Sintering eliminates many of these voids, causing the material to shrink and become denser.
This densification is directly responsible for many of the improvements in a material's performance after sintering.
Controlling the Final Microstructure
Expert use of sintering allows for the precise control of a material's internal structure. By managing variables like temperature, time, and atmosphere, engineers can design the final grain size, pore distribution, and density.
This means a material can be intentionally engineered for a specific application, such as having a particular strength or thermal performance.
Enhancing Key Material Properties
By changing the microstructure, sintering directly improves the functional characteristics of the finished part. The reduction of porosity is the primary driver behind these enhancements.
Improving Mechanical Strength and Integrity
A denser material is almost always a stronger material. By removing pores, which act as microscopic points of failure, sintering dramatically increases the overall strength and durability of the component.
This is why it's used to create high-performance parts like jet engine turbine blades.
Increasing Thermal and Electrical Conductivity
The voids between unsintered particles act as insulators, impeding the flow of heat and electricity. As sintering eliminates these pores, it creates a more continuous path, significantly boosting both thermal and electrical conductivity.
Achieving Translucency
In certain advanced ceramics, sintering can remove pores to the point that they no longer scatter light. This highly specialized function allows for the creation of translucent materials used in applications like transparent armor or high-intensity lamps.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Considerations
While powerful, sintering is a complex process with critical variables that must be managed. Understanding its limitations is key to using it effectively.
The Inevitability of Shrinkage
Because sintering eliminates porosity and increases density, the part will shrink during the process. This dimensional change is predictable but must be precisely accounted for in the initial design of the powdered form.
The Challenge of Uniformity
Achieving perfectly uniform density and microstructure throughout a complex part can be difficult. Uneven heating or pressure can lead to internal stresses, warping, or weak spots in the final product.
The Need for Strict Process Control
Sintering is highly sensitive to its parameters. Temperature, heating rate, time, and the composition of the furnace atmosphere must all be tightly controlled to produce consistent, repeatable results.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Sintering is not a single process but a versatile tool used to achieve different outcomes. Your primary objective will determine how you approach it.
- If your primary focus is creating parts from high-melting-point materials: Sintering is the essential method, as it avoids the extreme energy costs and technical challenges of melting.
- If your primary focus is achieving specific material properties: Sintering offers unparalleled control over microstructure, allowing you to engineer density, strength, and conductivity.
- If your primary focus is manufacturing complex, nearly net-shaped parts: Powder metallurgy and 3D printing via sintering reduce material waste and minimize the need for post-processing machining.
Ultimately, sintering provides a powerful pathway to engineer advanced materials with properties that are simply unattainable through conventional melting and casting.
Summary Table:
| Key Function | Primary Outcome |
|---|---|
| Bonding Particles | Creates a solid, coherent mass from powder |
| Reducing Porosity | Increases material density and strength |
| Controlling Microstructure | Engineers specific properties like conductivity |
| Enhancing Properties | Improves mechanical strength, thermal/electrical conductivity |
Ready to engineer advanced materials with precision sintering?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the high-performance lab equipment and consumables you need to master the sintering process. Whether you're working with high-melting-point metals, advanced ceramics, or complex geometries, our solutions deliver the strict temperature control and uniform heating essential for repeatable, high-quality results.
Contact our experts today to discuss how KINTEK can support your laboratory's specific sintering applications and help you achieve your material property goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Spark Plasma Sintering Furnace SPS Furnace
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Furnace Chairside with Transformer
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is the difference between hot press and SPS? Choose the Right Sintering Method for Your Lab
- What are the steps in spark plasma sintering? Achieve Rapid, Low-Temperature Densification
- What are the advantages of SPS? Achieve Superior Material Density and Performance
- What are the different sintering methods? Choose the Right Technique for Your Material & Application
- What is the SPS process of spark plasma sintering? A Guide to Rapid, Low-Temperature Densification



















