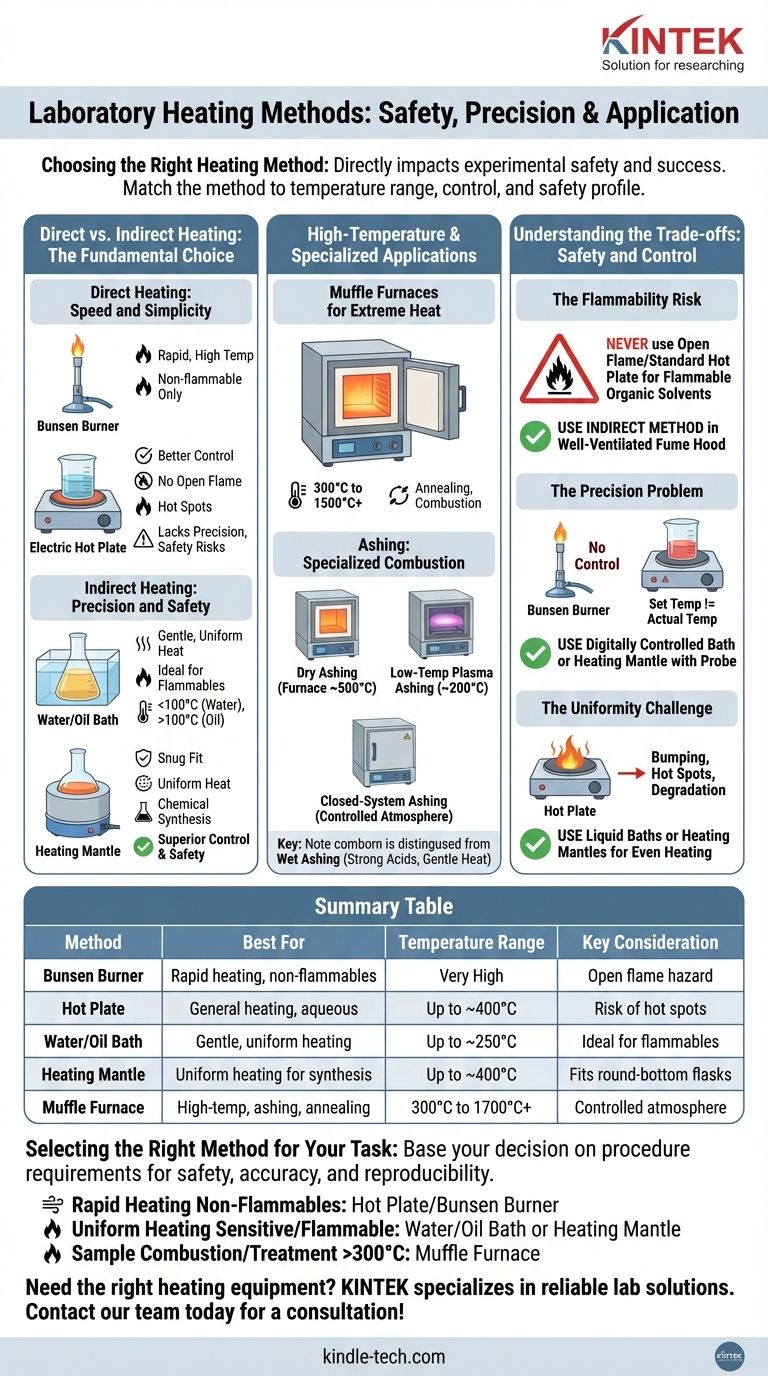
Choosing the right laboratory heating method is a fundamental decision that directly impacts experimental safety and success. The most common methods include open-flame Bunsen burners, electric hot plates, heating mantles, water and oil baths, and high-temperature furnaces. The best choice depends entirely on the required temperature, the flammability of your materials, and the need for precise, uniform heat.
The core challenge is not simply knowing what heating tools exist, but understanding how to match the method's temperature range, control, and safety profile to the specific chemical and procedural requirements of your work.

Direct vs. Indirect Heating: The Fundamental Choice
The first decision point is whether to apply heat directly to your vessel or to use an intermediary medium for more gentle and uniform temperature control.
Direct Heating: Speed and Simplicity
Direct heating methods are fast and straightforward but often lack precision and can introduce safety hazards.
A Bunsen burner provides an open flame for rapid, high-temperature heating. It is best used for non-flammable substances, such as heating water in a beaker, or for tasks like sterilizing equipment.
An electric hot plate offers better temperature control than a flame and removes the ignition risk of the flame itself. However, they can create "hot spots" on the bottom of glassware, leading to uneven heating or bumping.
Indirect Heating: Precision and Safety
Indirect methods use a liquid or a conforming solid surface to transfer heat evenly to the entire vessel, providing superior temperature control and safety.
A water bath is ideal for gently and uniformly heating samples to temperatures at or below 100°C. It is the standard method for temperature-sensitive biological reactions.
For temperatures above 100°C, an oil bath (using silicone or mineral oil) functions on the same principle as a water bath, offering excellent thermal stability.
A heating mantle is a flexible fiberglass blanket with embedded heating elements. It is specifically designed to fit snugly around round-bottom flasks, providing extremely uniform heat for chemical synthesis.
High-Temperature and Specialized Applications
When temperatures exceed 250-300°C or when the atmosphere must be controlled, standard benchtops tools are insufficient.
Muffle Furnaces for Extreme Heat
A muffle furnace is an insulated chamber capable of reaching temperatures from 300°C to over 1500°C. It is used for high-temperature applications like annealing metals, analyzing material properties, or completely combusting samples.
Ashing: A Specialized Combustion Technique
Ashing is a specific application of furnace heating used to determine the inorganic, non-combustible content of a sample. The organic material is burned away, leaving only the mineral ash.
Techniques include dry ashing in a furnace around 500°C and low-temperature plasma ashing around 200°C. Closed-system ashing may be used when the surrounding atmosphere must be precisely controlled.
It is important to distinguish these from wet ashing, which is a chemical digestion process using strong acids and often gentle heat, rather than a high-temperature combustion method.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Safety and Control
Choosing incorrectly can lead to failed experiments or, worse, a laboratory accident. Always consider the following trade-offs.
The Flammability Risk
Never use an open flame or a standard (non-spark-proof) hot plate to heat flammable organic solvents like ethanol or ether. The vapors can easily ignite. For these materials, always use an indirect method like a water bath or a heating mantle in a well-ventilated fume hood.
The Precision Problem
A Bunsen burner offers almost no temperature control. A hot plate is better, but the set temperature rarely matches the actual temperature of the liquid inside the flask. For reactions requiring precise thermal management, a digitally controlled water bath or a heating mantle connected to a probe thermometer is essential.
The Uniformity Challenge
A hot spot from a hot plate can cause localized boiling ("bumping") or degrade sensitive compounds at the bottom of a flask while the rest of the liquid remains too cool. Liquid baths and heating mantles eliminate this problem by heating the vessel's surface evenly.
Selecting the Right Method for Your Task
Base your decision on the specific requirements of your procedure to ensure safety, accuracy, and reproducibility.
- If your primary focus is rapidly heating non-flammable aqueous solutions: A hot plate or Bunsen burner is often sufficient.
- If your primary focus is uniformly heating a temperature-sensitive or flammable reaction: Use a water bath, oil bath, or heating mantle for superior safety and precision.
- If your primary focus is sample combustion or material treatment above 300°C: A muffle furnace is the required tool.
Matching the heating method to the task is a cornerstone of safe and effective laboratory science.
Summary Table:
| Method | Best For | Temperature Range | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bunsen Burner | Rapid heating of non-flammables | Very High | Open flame hazard |
| Hot Plate | General heating, aqueous solutions | Up to ~400°C | Risk of hot spots |
| Water/Oil Bath | Gentle, uniform heating | Up to ~250°C | Ideal for flammables |
| Heating Mantle | Uniform heating for synthesis | Up to ~400°C | Fits round-bottom flasks |
| Muffle Furnace | High-temp applications (ashing, annealing) | 300°C to 1700°C+ | Controlled atmosphere |
Need the right heating equipment for your lab's specific challenges? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, providing reliable solutions from precise hot plates and heating mantles to high-temperature muffle furnaces. Let our experts help you select the perfect tool for safety, precision, and reproducibility in your work. Contact our team today for a consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the meaning of debinding? Master the Critical Step to High-Performance Parts
- What temperature is required for calcination? Master Material-Specific Thermal Decomposition
- How do you perform calcination? Master Precise Thermal Treatment for Your Materials
- What is the effect of calcination temperature on the properties of nanoparticles? Master the Trade-Off for Optimal Performance
- What is the theory of calcination? Master Precise Thermal Decomposition for Your Materials



















