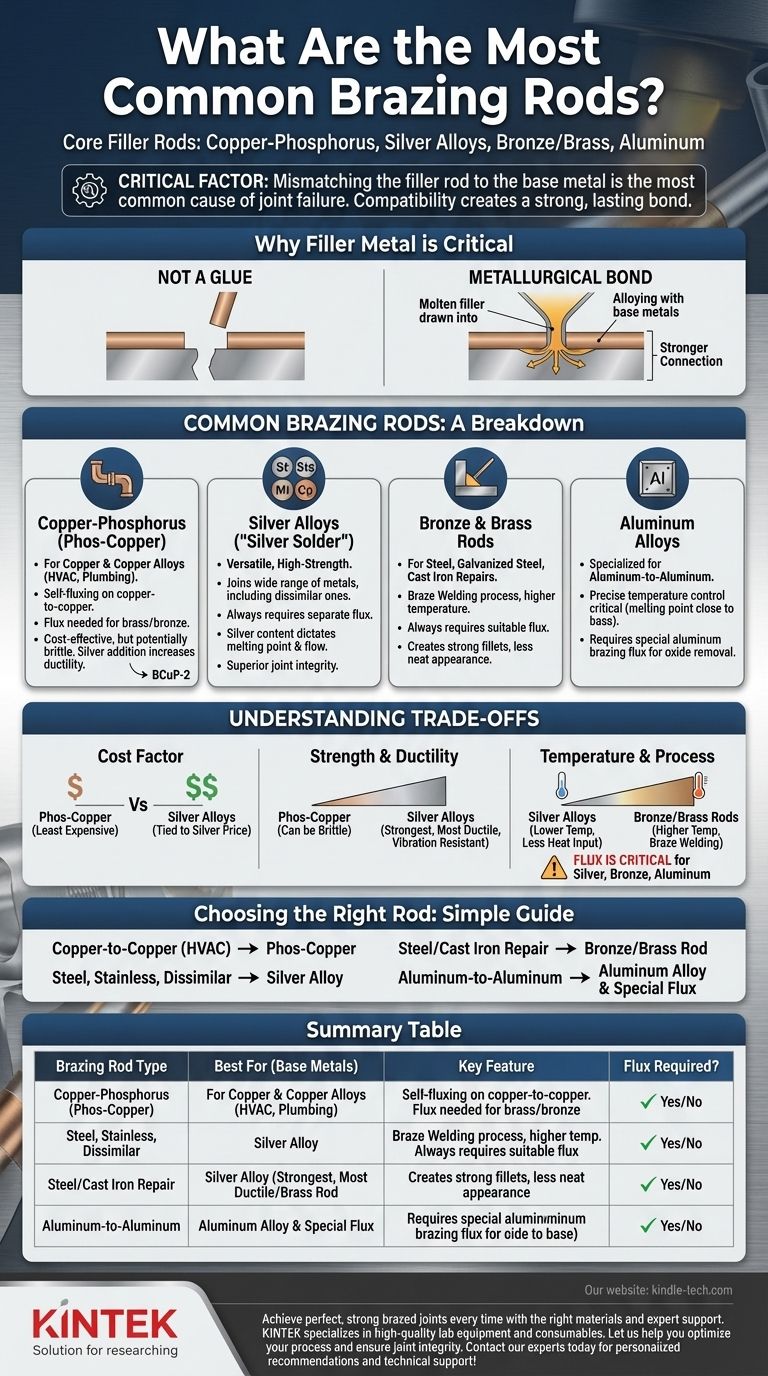
At its core, brazing relies on a few key types of filler rods. The most common you will encounter are copper-phosphorus alloys, versatile silver alloys, and bronze or brass rods. Each is designed for specific base metals and applications, from plumbing and HVAC to high-strength industrial fabrication.
The single most important factor in choosing a brazing rod is the material of the parts you are joining. Mismatching the filler rod to the base metal is the most common cause of joint failure, as the chemical and metallurgical compatibility is what creates a strong, lasting bond.
Why the Filler Metal is Critical
The brazing rod, or filler metal, is not merely a "glue" that holds parts together. It forms a metallurgical bond with the base metals.
The right filler metal melts at a temperature lower than the base metals, is drawn into the joint by capillary action, and then alloys with the surfaces of the parts to create a connection that can be stronger than the base metals themselves.
A Breakdown of Common Brazing Rods
Your choice of brazing rod will be dictated by the materials you need to join, the required strength of the joint, and your operating environment.
Copper-Phosphorus (Phos-Copper)
This is the go-to filler metal for joining copper and copper alloys like brass and bronze. It is extremely common in the HVAC and plumbing industries.
Its key feature is that the phosphorus acts as a fluxing agent when joining copper to copper, meaning no separate flux is required. However, you must use a separate flux when joining copper to brass or bronze with this rod.
These alloys, such as BCuP-2, are cost-effective but can be more brittle than silver-bearing alloys. Adding a small amount of silver (e.g., 5% or 15%) increases the rod's ductility and lowers its melting point.
Silver Alloys ("Silver Solder")
Silver alloys are the most versatile and high-strength brazing fillers. They can join a wide range of metals, including steel, stainless steel, copper, brass, and combinations of these (dissimilar metals).
The silver content, which can range from 20% to over 70%, determines the alloy's melting point and flow characteristics. Higher silver content generally provides a lower melting temperature and better wetting action.
These fillers always require the use of a separate brazing flux. Due to their strength and ductility, they are used in applications where joint integrity is critical.
Bronze and Brass Rods
These rods are typically used for braze welding, a process that often creates a fillet at the joint rather than relying purely on capillary action. They are excellent for joining steel, galvanized steel, and repairing cast iron.
Braze welding with a bronze or brass rod requires a higher temperature than silver brazing and always necessitates a suitable flux. The resulting joints are strong but may not have the same neat, low-profile appearance as a true brazed joint.
Aluminum Alloys
Brazing aluminum requires a specialized filler metal. These aluminum-silicon alloys have a melting point that is very close to the base aluminum, making precise temperature control absolutely critical.
These fillers are used exclusively for joining aluminum to aluminum and require a special aluminum brazing flux to remove the tough oxide layer that forms on the metal's surface.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a brazing rod involves balancing cost, performance, and process requirements.
The Cost Factor
Phos-copper is generally the least expensive option, making it ideal for high-volume copper-to-copper work. Silver alloy prices are directly tied to the commodity price of silver, making them significantly more expensive.
Strength and Ductility
Silver alloys typically produce the strongest, most ductile joints, especially on ferrous metals like steel. They are superior at withstanding vibration and thermal cycling. Low-silver or no-silver phos-copper alloys can be brittle.
Temperature and Process Requirements
Each alloy family has a different working temperature range. Silver alloys often have lower melting points than bronze rods, requiring less heat input and reducing the risk of overheating the base metals. Forgetting to use flux with silver, bronze, or aluminum alloys will guarantee a failed joint.
Choosing the Right Rod for Your Application
Use this as a simple guide to make your selection.
- If your primary focus is joining copper to copper (e.g., HVAC lines): Use a copper-phosphorus (phos-copper) alloy for its cost-effectiveness and self-fluxing properties.
- If your primary focus is joining steel, stainless steel, or dissimilar metals: Use a silver alloy for its superior strength, versatility, and ability to join nearly any common metal combination.
- If your primary focus is general repair on steel or cast iron: A bronze or brass rod for braze welding is a robust and reliable choice.
- If your primary focus is joining aluminum: You must use a dedicated aluminum brazing alloy and its corresponding specialized flux.
Ultimately, successful brazing is achieved by precisely matching the filler metal to the base material and the demands of the application.
Summary Table:
| Brazing Rod Type | Best For (Base Metals) | Key Feature | Flux Required? |
|---|---|---|---|
| Copper-Phosphorus | Copper to Copper | Self-fluxing on copper | No (for copper-copper) |
| Silver Alloys | Steel, Stainless, Dissimilar Metals | High strength & versatility | Yes |
| Bronze/Brass Rods | Steel, Cast Iron (Repairs) | Braze welding, strong fillets | Yes |
| Aluminum Alloys | Aluminum to Aluminum | Specialized for aluminum | Yes (special flux) |
Achieve perfect, strong brazed joints every time with the right materials and expert support.
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables for all your brazing and fabrication needs. Whether you're in HVAC, industrial manufacturing, or laboratory research, our team can help you select the ideal brazing rods and fluxes for your specific base metals and application requirements.
Let us help you optimize your process and ensure joint integrity. Contact our experts today for personalized recommendations and technical support!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Engineering Advanced Fine Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Rod Insulated for Industrial Applications
- Precision Machined Yttrium Stabilized Zirconia Ceramic Rod for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Boron Nitride (BN) Ceramic Rod for High Temperature Applications
- High Purity Zinc Foil for Battery Lab Applications
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- Is ceramic chemically inert? Unlock the Power of Ultimate Chemical Resistance
- What is the process of alumina tube manufacturing? From Powder to High-Performance Ceramic
- What is the advantage of ceramic over metal? Unlock Superior Performance in Extreme Conditions
- Which of the following is used in furnace to withstand high temperature? Key Materials for Extreme Heat
- What is the maximum temperature for alumina tube? Unlock Its Full Potential with High Purity









