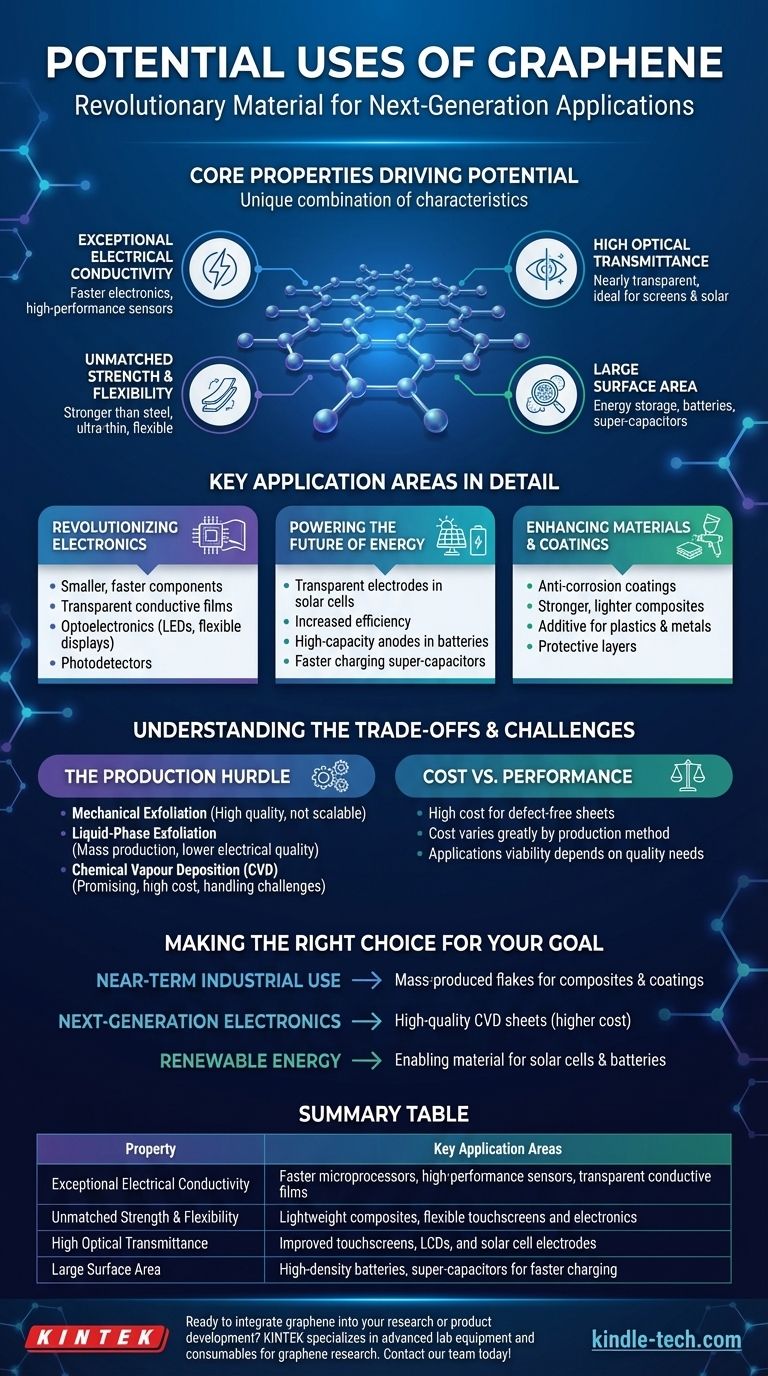
At its core, graphene is a revolutionary material with potential uses spanning nearly every industry. Its unique combination of properties—being the strongest material ever tested, highly conductive, transparent, and flexible—makes it a candidate for applications in next-generation electronics, renewable energy, advanced composites, and protective coatings.
Graphene is not a single solution but a foundational platform technology. Its practical applications are less about the material itself and more about how its extraordinary properties of strength, conductivity, and transparency can be harnessed to radically improve existing products and enable entirely new ones.

The Core Properties Driving Graphene's Potential
To understand graphene's applications, you must first understand its fundamental characteristics. Its uses are a direct result of a combination of properties not found together in any other material.
Exceptional Electrical Conductivity
Graphene is an exceptional conductor of electricity. This property is the foundation for its use in creating faster and more efficient electronics, from microprocessors to high-performance sensors.
Unmatched Strength and Flexibility
As a two-dimensional material, graphene is incredibly thin and flexible, yet it is also stronger than steel. This unique combination makes it an ideal additive for creating ultra-strong, lightweight composite materials and for building flexible touchscreens and electronics.
High Optical Transmittance
Graphene is almost completely transparent. This, combined with its conductivity, makes it a prime candidate to replace existing materials in touchscreens, liquid crystal displays (LCDs), and solar cells, where performance depends on letting light pass through a conductive layer.
Large Surface Area
Graphene's single-atom-thick structure provides an extremely large surface area relative to its volume. This is a critical advantage for applications in energy storage, such as in the anodes of batteries and within super-capacitors, where it can improve energy density and charging speeds.
Key Application Areas in Detail
Graphene's properties translate into specific, high-impact applications across several key sectors. While some are in early development, others are already entering the market.
Revolutionizing Electronics
Graphene's conductivity and thinness allow for the design of smaller, faster, and more efficient electronic components. It is a candidate for replacing silicon in some high-performance electronics and is crucial for developing transparent conductive films.
These films are essential for optoelectronics, including photodetectors, LEDs, and flexible displays that you can bend or roll.
Powering the Future of Energy
In the energy sector, graphene serves multiple roles. It is used as a transparent electrode in solar cells, improving efficiency by allowing more light to reach the active photovoltaic material.
It also acts as a highly conductive anode material in next-generation batteries and super-capacitors, promising faster charging and longer life cycles.
Enhancing Materials and Coatings
Because it can be deposited easily onto other materials, graphene is highly versatile as a coating. It can be mixed into paints to create highly effective anti-corrosion coatings.
When added to plastics, metals, or other materials, it creates composites that are significantly lighter and stronger than their traditional counterparts.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Challenges
Despite its immense potential, the widespread adoption of graphene is constrained by significant practical challenges. The hype often overlooks the realities of production and implementation.
The Production Hurdle
Not all graphene is created equal. The method of production determines its quality, cost, and suitability for a given application.
- Mechanical Exfoliation: Produces very high-quality graphene but is not scalable for industrial use.
- Liquid-Phase Exfoliation: Suitable for mass production of graphene flakes for use in composites and coatings, but the electrical quality is often low.
- Chemical Vapour Deposition (CVD): The most promising technique for producing the large, high-quality sheets needed for advanced electronics and transparent films. However, challenges related to cost, uniformity, and handling remain.
Cost vs. Performance
The high cost of producing top-tier, defect-free graphene makes it impractical for many applications today. The graphene used to strengthen a bicycle frame is far different—and far cheaper to produce—than the pristine sheet required for a microprocessor.
This cost-performance trade-off is the primary factor determining which applications are commercially viable right now versus which remain in the research and development phase.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding the different forms and grades of graphene is essential to applying it effectively. Your goal will determine which type of graphene is relevant.
- If your primary focus is on near-term industrial use: Look to graphene as an additive in composites and coatings, where lower-cost, mass-produced graphene flakes provide significant value.
- If your primary focus is next-generation electronics: High-quality, sheet-based graphene produced via CVD is essential, but be prepared for high costs and the challenges of a developing technology.
- If your primary focus is renewable energy: Graphene is a key enabling material for enhancing the performance of solar cells and batteries, acting as a critical component within a larger system.
Ultimately, graphene's true potential is unlocked by matching the right quality and form of the material to the specific problem you are trying to solve.
Summary Table:
| Property | Key Application Areas |
|---|---|
| Exceptional Electrical Conductivity | Faster microprocessors, high-performance sensors, transparent conductive films |
| Unmatched Strength & Flexibility | Lightweight composites, flexible touchscreens and electronics |
| High Optical Transmittance | Improved touchscreens, LCDs, and solar cell electrodes |
| Large Surface Area | High-density batteries, super-capacitors for faster charging |
Ready to integrate graphene into your research or product development? KINTEK specializes in providing the advanced lab equipment and consumables necessary for graphene research and application testing. Whether you are working on next-generation electronics, energy storage solutions, or advanced composite materials, our expertise can support your innovation. Contact our team today to discuss how we can help you achieve your materials science goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Large Vertical Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Vertical High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace IGBT Experimental Graphitization Furnace
- Ultra-High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the largest disadvantage of biomass as an energy source? The Hidden Costs of Low Energy Density
- Why does graphite have a high melting point? The Power of Its Giant Covalent Structure
- What are the challenges of large-scale biomass energy use? The Hidden Hurdles to a Green Energy Source
- What is a disadvantage of biomass energy? The Hidden Environmental and Economic Costs
- Is high ash content good? A Guide to Understanding Pet Food Mineral Levels



















