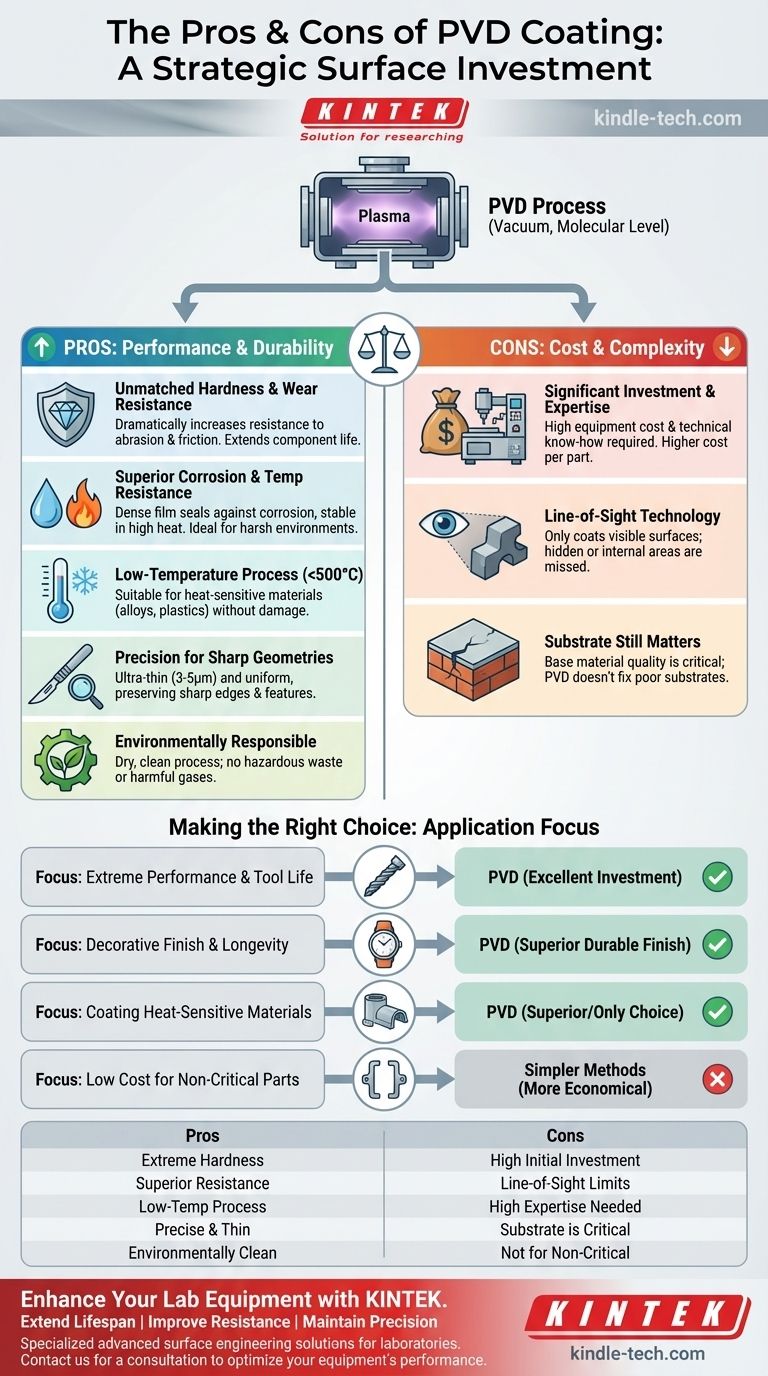
At its core, Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) coating is a process that enhances a material's surface, not a material in itself. Its primary advantage is a dramatic increase in hardness, wear resistance, and durability, while its main disadvantage is the significant cost and technical complexity of the application process, which requires a vacuum and specialized equipment.
PVD is not a simple upgrade; it is a strategic investment in surface engineering. The central trade-off is between achieving superior performance and durability versus the higher cost and process limitations compared to more traditional coating methods.

The Core Advantages of PVD
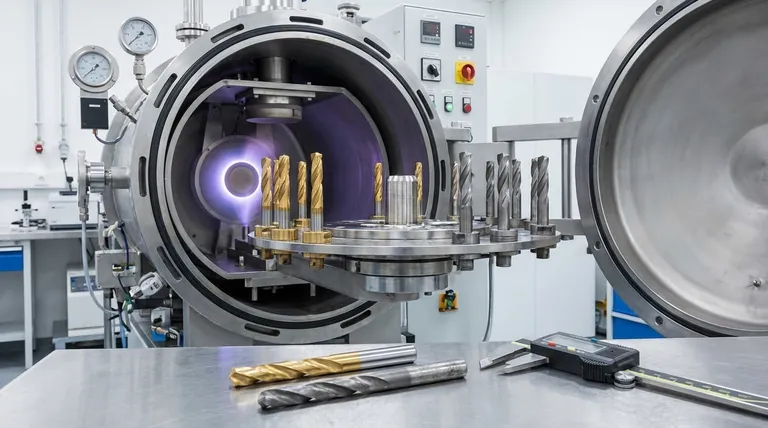
PVD coatings are applied in a vacuum at a molecular level, resulting in a thin film that is extremely well-bonded to the base material, or substrate. This process imparts several significant performance benefits.
Unmatched Hardness and Wear Resistance
PVD can deposit ceramic or composite films with exceptionally high hardness. This coating acts as a protective barrier that dramatically increases the surface's resistance to abrasion, friction, and wear.
This extends the operational life of components, especially cutting tools, by maintaining their sharpness and reducing the heat generated during use.
Superior Corrosion and Temperature Resistance
The dense, non-porous film created by PVD is highly effective at preventing corrosion. It seals the substrate from environmental factors like moisture and oxidation.
Many PVD coatings also exhibit excellent stability at high temperatures, making them ideal for high-performance applications where both heat and wear are significant factors.
A Low-Temperature Process
PVD operates at relatively low temperatures (typically below 500°C). This is a critical advantage over other methods like Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD), which require much higher temperatures.
This makes PVD suitable for coating heat-sensitive materials, such as certain steel alloys or plastics, without the risk of altering their fundamental properties or causing thermal damage.
Precision for Sharp and Complex Geometries
PVD coatings are extremely thin, often just a few micrometers (3-5μm). This ensures that the process provides a uniform coating that conforms precisely to the substrate's surface features.
This is essential for applications like razor blades, surgical instruments, and cutting tools, where preserving a sharp edge is non-negotiable.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, PVD is not a universal solution. Its benefits must be weighed against its inherent constraints and costs, which can make it unsuitable for certain applications.
Significant Initial Investment and Expertise
The primary barrier to PVD is the cost and complexity of the equipment. The process requires a large vacuum chamber and sophisticated machinery.
Operating this equipment effectively demands a high level of expertise to manage the variables and ensure a consistent, high-quality coating. This translates to higher costs per part compared to simpler methods.
It's a Line-of-Sight Technology
In a PVD process, the coating material travels in a straight line from the source to the substrate. This means the process can only coat surfaces that it can "see."
Complex internal geometries, deep crevices, or hidden surfaces cannot be effectively coated. This is a fundamental physical limitation that must be considered during the design phase.
The Substrate Still Matters
A PVD coating enhances a part's surface, but it does not fix a poor-quality base material. The final performance of a coated component is a function of both the coating and the substrate it's applied to.
The hardness and integrity of the underlying material are critical for supporting the coating and achieving the desired durability.
PVD is an Environmentally Responsible Choice
Unlike traditional electroplating, which involves wet chemistry and produces hazardous waste, PVD is a dry, environmentally clean process.
It produces no harmful gases or waste products and does not alter the recyclable value of the base material, such as stainless steel.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right coating requires aligning the process capabilities with your primary goal.
- If your primary focus is extreme performance and tool life: PVD is an excellent investment for cutting tools and wear components due to its unmatched hardness and low-friction properties.
- If your primary focus is decorative finish and longevity: PVD offers a durable, brilliant finish for products like watches or architectural hardware, far superior to paint or traditional plating.
- If your primary focus is coating heat-sensitive materials: PVD's low processing temperature makes it the superior—and sometimes only—choice for adding a high-performance coating without damaging the substrate.
- If your primary focus is low cost for non-critical parts: The high cost and complexity of PVD make simpler methods like painting or basic electroplating more economical for general-purpose applications.
By understanding these fundamental trade-offs, you can confidently determine if PVD's advanced capabilities align with your project's specific demands.
Summary Table:
| Pros of PVD Coating | Cons of PVD Coating |
|---|---|
| Extreme hardness & wear resistance | High initial investment & operational cost |
| Superior corrosion & temperature resistance | Line-of-sight process limits complex geometries |
| Low-temperature process for sensitive materials | Requires high expertise and specialized equipment |
| Thin, precise coating for sharp edges | Substrate quality is critical for performance |
| Environmentally clean, dry process | Not cost-effective for non-critical applications |
Need to enhance your lab equipment's durability and performance?
At KINTEK, we specialize in advanced surface engineering solutions for laboratories. Our expertise in PVD coating can help you:
- Extend the lifespan of critical lab tools and components.
- Improve resistance to corrosion, wear, and high temperatures.
- Maintain precision for sensitive instruments without thermal damage.
Whether you're working with cutting tools, sample holders, or specialized lab equipment, our team can help you determine if PVD coating is the right strategic investment for your needs.
Contact KINTEK today for a consultation and discover how our lab-focused coating solutions can optimize your equipment's performance and reliability.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- Anti-Cracking Press Mold for Lab Use
People Also Ask
- What is the hot filament chemical vapour deposition of diamond? A Guide to Synthetic Diamond Coating
- What is microwave plasma CVD? A Guide to High-Purity Diamond and Material Synthesis
- How do CVD diamonds grow? A Step-by-Step Guide to Lab-Grown Diamond Creation
- How is diamond coating made? A Guide to CVD and PVD Methods
- What is direct current DC magnetron sputtering? A Guide to High-Quality Thin Film Deposition



















