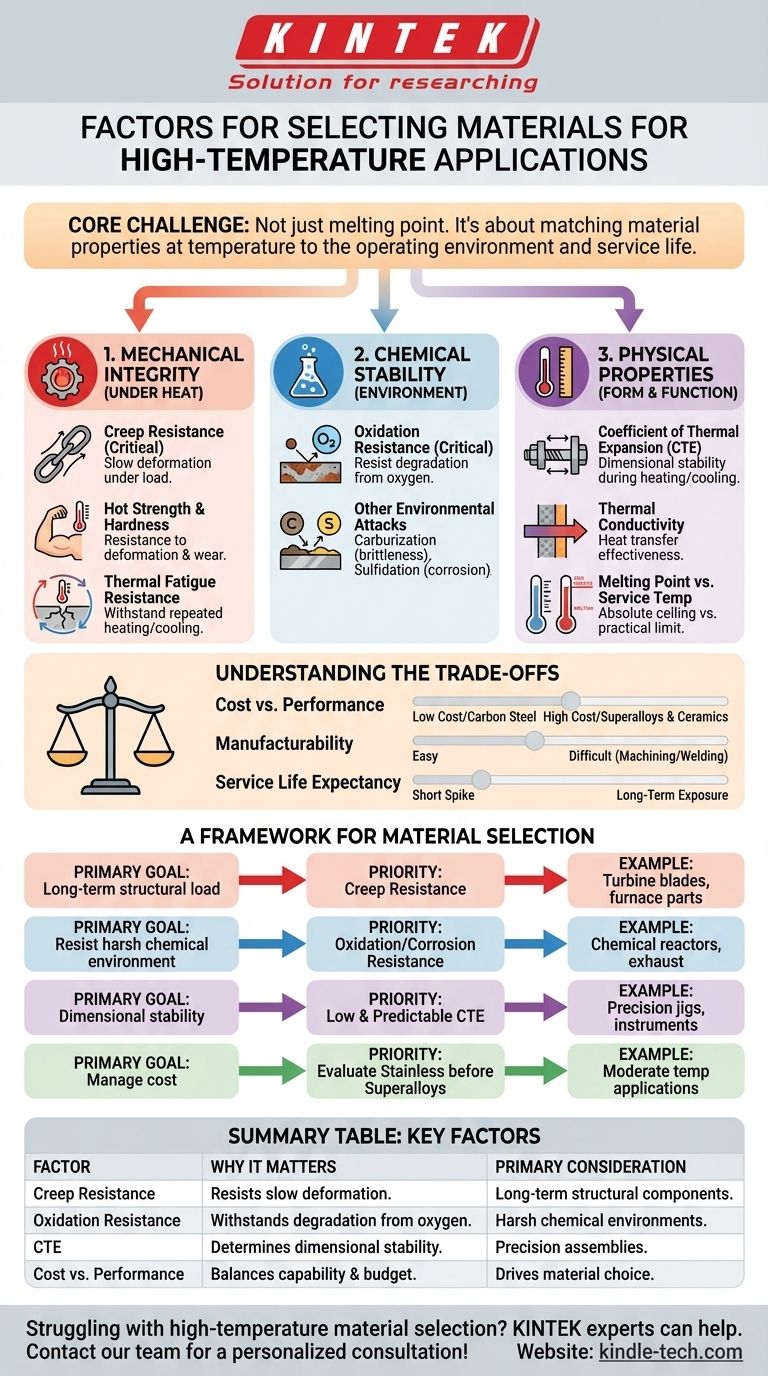
In short, selecting a material for high-temperature applications requires you to evaluate its mechanical strength at the target temperature, its chemical stability in the service environment, and its physical properties like thermal expansion. The most critical factors are typically creep resistance, which is the material's ability to resist slow deformation under load, and oxidation resistance, its ability to withstand degradation from the surrounding atmosphere.
The core challenge is not finding the material with the highest melting point. It is about understanding that a material's properties degrade significantly under heat, and a successful choice depends entirely on matching its specific performance profile at temperature to the demands of its operating environment and service life.

The Foundation: Mechanical Integrity Under Heat
A material's strength at room temperature is often a poor indicator of its performance under heat. High temperatures fundamentally alter a material's internal structure, directly impacting its ability to carry a load.
Creep Resistance
Creep is the slow, continuous deformation of a material under a constant stress at high temperatures, often well below its yield strength. It is a primary cause of failure in components like turbine blades and furnace structures.
A material's ability to resist this phenomenon is known as its creep strength. This is arguably the single most important mechanical property for any load-bearing, high-temperature application.
Hot Strength and Hardness
Materials invariably soften as they get hotter. Hot strength (or elevated-temperature tensile strength) and hot hardness measure a material's ability to resist deformation and wear at its service temperature.
You must review data that specifically tests these properties at a temperature relevant to your application, not at room temperature. Another key metric is stress rupture strength, which defines the stress a material can withstand for a given time at temperature before it breaks.
Thermal Fatigue Resistance
Components that undergo repeated heating and cooling cycles are subject to thermal fatigue. The constant expansion and contraction create internal stresses that can lead to crack initiation and failure over time, even with no external load.
Surviving the Environment: Chemical Stability
High temperatures act as a catalyst, dramatically accelerating chemical reactions between a material and its environment. A mechanically sound material can fail rapidly if it cannot withstand chemical attack.
Oxidation Resistance
For most applications, the primary environmental threat is oxygen. Oxidation resistance is a material's ability to resist chemical degradation from reacting with oxygen at high temperatures.
Many high-temperature alloys, like stainless steels and nickel-based superalloys, achieve this by forming a stable, protective oxide layer (a "passive film") on their surface that prevents further attack. The stability of this layer determines the material's upper service temperature.
Other Environmental Attacks
Depending on the specific environment, other forms of chemical attack can be dominant. Carburization (absorption of carbon) can make materials brittle, while sulfidation (reaction with sulfur compounds) can cause rapid corrosion, especially in fuel-burning applications.
Maintaining Form and Function: Physical Properties
Beyond strength and stability, a material's physical response to heat is critical for the function and integrity of the entire assembly.
Coefficient of Thermal Expansion (CTE)
This property defines how much a material expands when heated and contracts when cooled. In an assembly of multiple materials, a mismatched CTE is a major source of failure.
If a bolt and a flange expand at different rates, immense internal stresses can build up, leading to distortion, yielding, or fracture. Low-expansion alloys are often chosen for applications requiring high dimensional stability.
Thermal Conductivity
Thermal conductivity measures how effectively a material transfers heat. The ideal choice depends on the component's function.
A turbine blade may require high conductivity to dissipate heat away from the hottest points, while a furnace lining requires low conductivity to act as an insulator.
Melting Point
A material's melting point represents an absolute ceiling, not a practical operating limit. The maximum service temperature is always significantly lower, limited by the onset of creep, rapid oxidation, or loss of strength.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting a material is an exercise in balancing competing factors. The theoretically "best" material is often impractical or too expensive.
Cost vs. Performance
There is a direct and steep correlation between temperature capability and cost. Carbon steels are inexpensive but have low-temperature limits. Stainless steels offer a moderate improvement. For the most demanding applications, nickel or cobalt-based superalloys and ceramics offer the highest performance but at a substantial cost premium.
The goal is to select the most economical material that safely meets all design requirements for the intended service life of the component.
Manufacturability and Weldability
A superior material is useless if you cannot form it into the required part. Many high-performance superalloys are notoriously difficult to machine, cast, or weld.
These fabrication challenges add significant cost and complexity to a project and must be considered early in the material selection process.
Service Life Expectancy
The required lifetime of the component is a critical variable. A material that can survive a brief, high-temperature spike in a rocket nozzle is very different from one that must endure the same temperature for tens of thousands of hours inside a power plant. Long-term exposure makes properties like creep and oxidation far more dominant.
A Framework for Material Selection
To make the right choice, you must first define your primary engineering goal.
- If your primary focus is long-term structural load at high heat (e.g., turbine blades, furnace parts): Prioritize creep resistance and stress rupture strength above all other factors.
- If your primary focus is resisting a harsh chemical environment (e.g., chemical reactors, exhaust components): Focus on oxidation, sulfidation, or corrosion resistance specific to your operating atmosphere.
- If your primary focus is dimensional stability in a precision assembly (e.g., jigs, fixtures, scientific instruments): Pay closest attention to a low and predictable Coefficient of Thermal Expansion (CTE).
- If your primary focus is managing cost for moderately high-temperature applications: Thoroughly evaluate the many grades of stainless steel before moving to more expensive nickel-based alloys.
A successful high-temperature design is achieved by matching a material's complete thermal behavior, not just its melting point, to the specific demands of the application.
Summary Table:
| Key Selection Factor | Why It Matters | Primary Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Creep Resistance | Resists slow deformation under load at temperature. | Critical for long-term structural components (e.g., furnace parts). |
| Oxidation Resistance | Withstands degradation from oxygen/atmosphere. | Essential for harsh chemical environments (e.g., reactors). |
| Coefficient of Thermal Expansion (CTE) | Determines dimensional stability during heating/cooling. | Key for precision assemblies and multi-material systems. |
| Cost vs. Performance | Balances material capability with project budget. | Drives the choice between steel, superalloys, and ceramics. |
Struggling to select the right high-temperature material for your lab equipment? The wrong choice can lead to premature failure, costly downtime, and compromised results. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratory needs. Our experts can help you navigate the complexities of material science to ensure your furnaces, reactors, and components are built for performance and longevity. Let's discuss your specific application and environment — contact our team today for a personalized consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) Thermal Elements Electric Furnace Heating Element
- Zirconia Ceramic Gasket Insulating Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- High-Purity Titanium Foil and Sheet for Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer PTFE Beaker and Lids
- Hexagonal Boron Nitride HBN Ceramic Ring
People Also Ask
- What is molybdenum disilicide used for? Powering High-Temperature Furnaces Up to 1800°C
- Is molybdenum disulfide a heating element? Discover the best material for high-temperature applications.
- What is the temperature range of a MoSi2 heating element? Unlock 1900°C Performance for Your Lab
- What function do molybdenum disilicide heating elements perform? Precision Heat for Pulverized Coal Research
- What material is used for furnace heating? Select the Right Element for Your Process



















