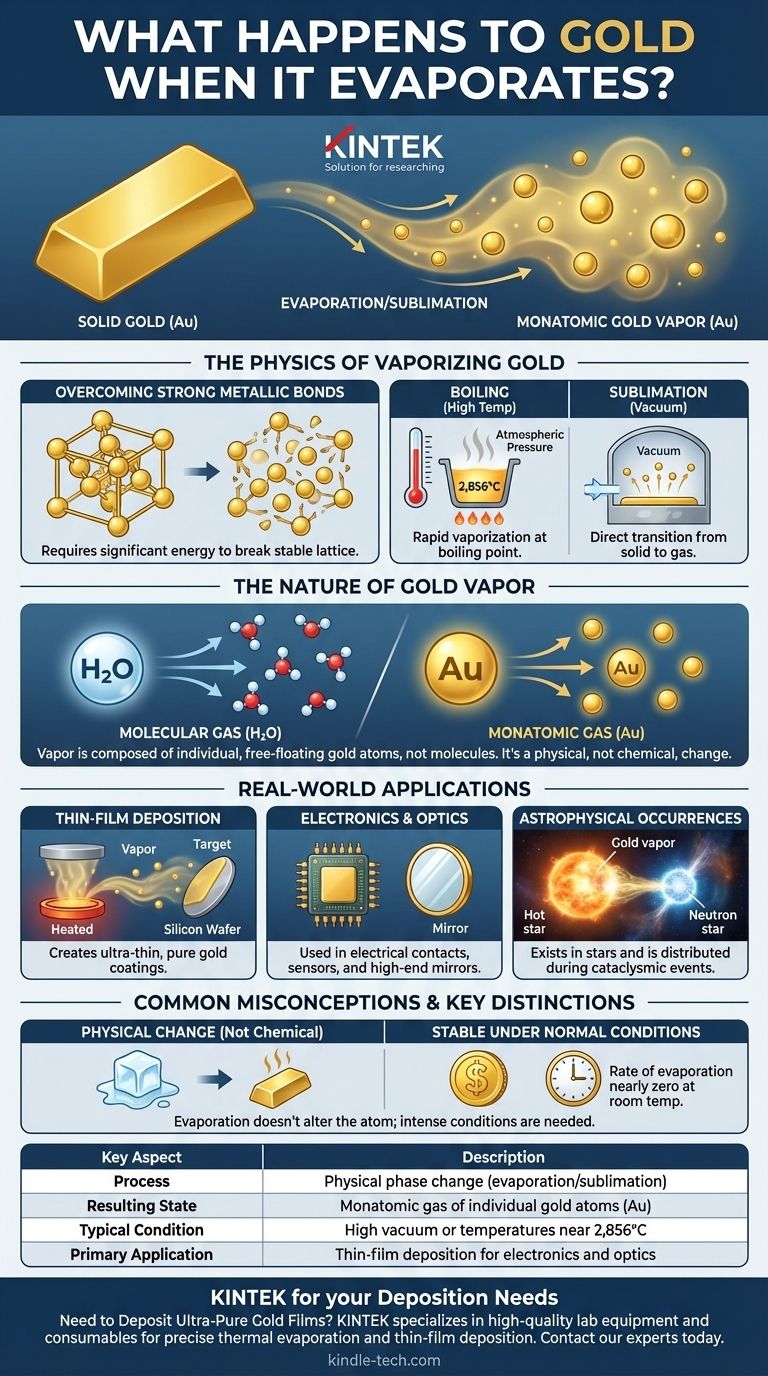
In short, when gold evaporates, it transforms into a monatomic gas. This means it becomes a vapor composed of individual, free-floating gold atoms (Au). This process requires extreme conditions, such as incredibly high temperatures or a near-perfect vacuum, to provide enough energy to break the powerful metallic bonds that hold the solid gold together.
The core principle is that evaporation is a physical change, not a chemical one. The gold atom itself remains unchanged; it simply transitions from being locked in a solid crystal lattice to moving freely as a gas, a state that is foundational to modern electronics and materials science.
The Physics of Vaporizing a Metal
Vaporizing a famously stable metal like gold requires overcoming significant physical barriers. The process hinges on providing enough energy to individual atoms so they can escape the collective pull of their neighbors.
Overcoming Strong Metallic Bonds
Gold atoms in their solid state are held together by strong metallic bonds. These bonds create a stable, dense crystal lattice structure. Evaporation is the process of supplying enough thermal energy to an atom to break it free from this structure entirely.
Boiling Point vs. Sublimation
Under standard atmospheric pressure, gold boils and turns to vapor at an extremely high temperature: 2,856°C (5,173°F). At this point, the vapor pressure of the gold equals the surrounding atmospheric pressure, allowing it to rapidly become a gas.
However, in the near-perfect vacuum of a deposition chamber, the process can happen at much lower temperatures. With virtually no air pressure to overcome, gold atoms can escape directly from the solid surface into a gaseous state in a process called sublimation.
The Nature of Gold Vapor
Unlike water, which evaporates to become a gas of H₂O molecules, gold vapor is monatomic. It consists of individual, electrically neutral gold atoms. There are no "gold molecules" in this gaseous state; it is the purest, most elemental form of gaseous gold.
Real-World Applications of Gold Vapor
The ability to turn gold into a vapor, while sounding exotic, is a critical process in advanced manufacturing and scientific research.
Thin-Film Deposition
The most common application is creating ultra-thin gold coatings. In a vacuum chamber, gold is heated until it evaporates. This gold vapor then travels and condenses on a cooler target surface, such as a silicon wafer or a piece of glass, forming a pure, microscopically thin gold film.
Electronics and Optics
These thin gold films are essential in modern technology. They are used as electrical contacts in microchips, as reflective coatings on high-end mirrors and visors, and in various sensors due to gold's high conductivity and resistance to corrosion.
Astrophysical Occurrences
On an astronomical scale, gold vapor exists in the atmospheres of very hot stars. Scientists also theorize that massive quantities of heavy elements like gold are vaporized and distributed across the cosmos during cataclysmic events like the merger of two neutron stars.
Common Misconceptions and Key Distinctions
It's crucial to distinguish this industrial process from everyday experience, as the conditions required are vastly different.
A Physical, Not Chemical, Change
Evaporation does not alter the gold atom. It is a physical phase transition, identical in principle to ice melting into water. The gold vapor, if cooled, will condense back into pure, solid gold.
Stability Under Normal Conditions
The immense energy required to break gold's metallic bonds is why it is so stable. At room temperature and normal pressure, the rate of evaporation is practically zero. A gold ring or coin will not lose any measurable mass to evaporation over a human lifetime.
Condensation is the Goal
In most technological applications, creating gold vapor is merely a means to an end. The ultimate goal is the controlled condensation of that vapor onto a surface to build precise, functional layers one atom at a time.
Key Insights Based on Your Interest
Understanding the state of evaporated gold depends on your underlying goal, whether it's academic curiosity or a practical application.
- If your primary focus is fundamental physics: The key takeaway is that gold vapor is a monatomic gas, formed when individual atoms gain sufficient energy to break their metallic bonds and escape into a gaseous phase.
- If your primary focus is technology: The critical concept is that gold can be evaporated or sublimated in a vacuum to create vapor, which is then condensed to deposit ultra-thin, high-purity films for electronics and optics.
- If your primary focus is everyday experience: The essential point is that gold's extremely high boiling point makes it exceptionally stable, ensuring it remains a solid under any conditions found naturally on Earth's surface.
Ultimately, even the most seemingly permanent materials like gold are subject to the fundamental laws of thermodynamics when conditions become extreme enough.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Process | Physical phase change (evaporation/sublimation) |
| Resulting State | Monatomic gas of individual gold atoms (Au) |
| Typical Condition | High vacuum or temperatures near 2,856°C (5,173°F) |
| Primary Application | Thin-film deposition for electronics and optics |
Need to Deposit Ultra-Pure Gold Films?
The process of gold evaporation is fundamental to creating the high-performance coatings essential for modern microchips, sensors, and optical devices. KINTEK specializes in providing the high-quality lab equipment and consumables required for precise thermal evaporation and thin-film deposition.
Our solutions help laboratories in the semiconductor, research, and advanced manufacturing sectors achieve reliable and consistent results. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your specific application with the right equipment and materials.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is PECVD in semiconductor? Enable Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition for ICs
- What are the steps of the CVD process? A Guide to Precision Thin Film Deposition
- What is the difference between PECVD and CVD? Unlock the Right Thin-Film Deposition Method
- How are thin films deposited? A Guide to PVD vs. CVD Methods for Your Application
- What is the process of vacuum vapor deposition? Mastering CVD and PVD Thin-Film Coating


















