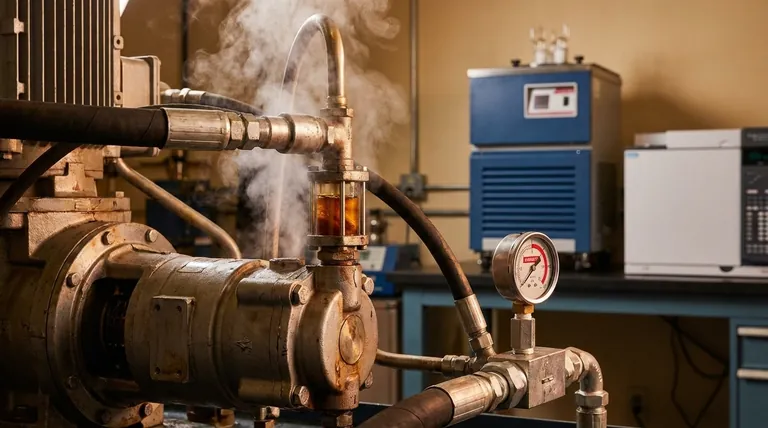
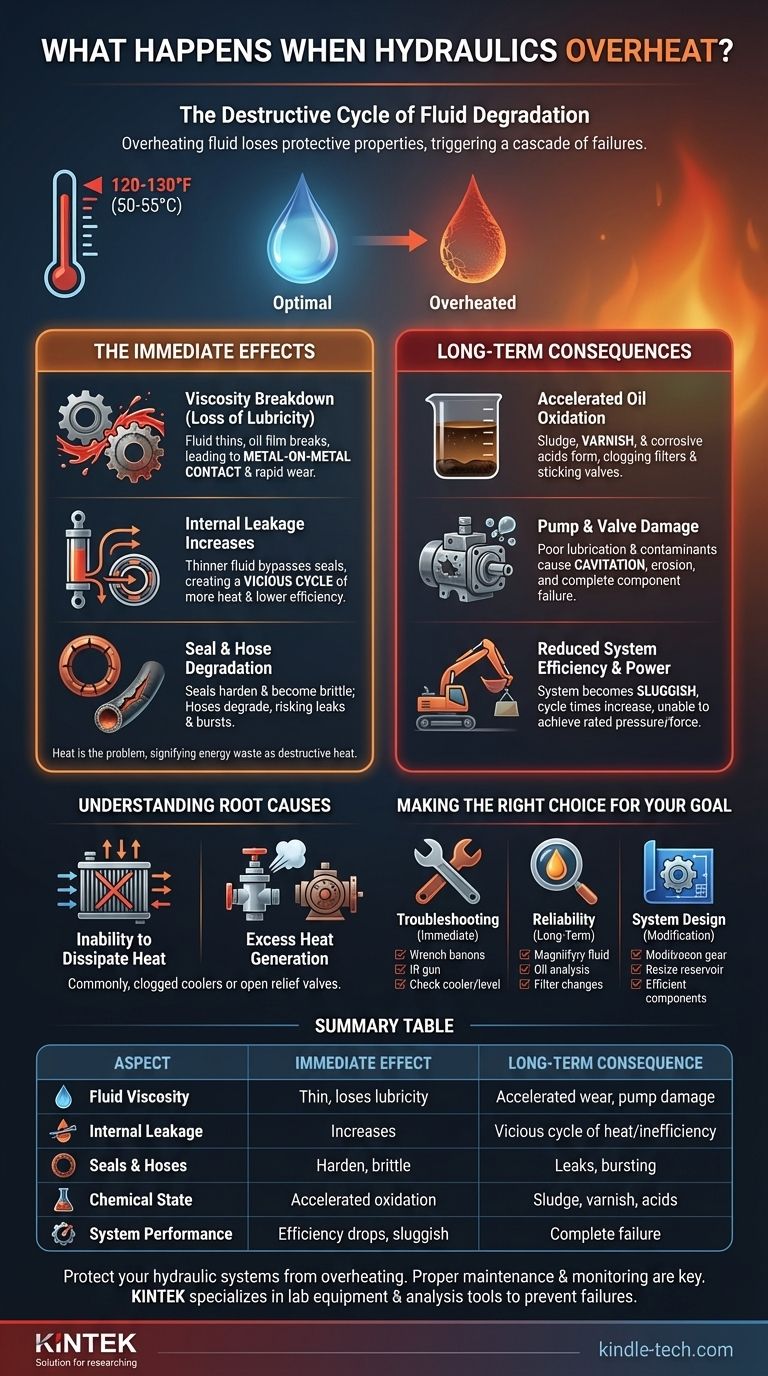
In short, overheating hydraulic fluid loses its ability to lubricate, protect, and transmit power effectively. When its temperature exceeds the optimal range (typically 120-130°F or 50-55°C), the fluid's viscosity drops, leading to accelerated wear on pumps and valves. This triggers a cascade of chemical breakdown, seal damage, and internal leakage that can culminate in catastrophic system failure.
Overheating in a hydraulic system is not merely a symptom; it is the problem itself. It signifies that energy is being converted into destructive heat instead of useful work, initiating a domino effect of fluid degradation and mechanical failure that compromises the entire system.

The Immediate Effects of High Temperature
When the temperature of hydraulic oil rises beyond its design limits, the physical and chemical properties that make it work begin to break down. This is not a slow process; the damage begins immediately.
Viscosity Breakdown: The Loss of Lubricity
The single most important property of hydraulic oil is its viscosity, or its resistance to flow. This property creates the strong oil film that separates moving metal parts.
As temperature increases, viscosity decreases exponentially. The oil becomes thin and watery, causing the protective oil film to break down. This leads to direct metal-on-metal contact inside pumps, motors, and cylinders, causing rapid and severe wear.
Internal Leakage Increases
A direct consequence of lower viscosity is an increase in internal leakage. The thinner oil more easily bypasses the tight clearances in pumps, valves, and actuators.
This leakage is a vicious cycle. The fluid slipping past these clearances generates even more heat due to friction, which further lowers viscosity, which in turn increases leakage. The system's efficiency plummets as more flow is wasted internally instead of performing work.
Seal and Hose Degradation
Hydraulic systems rely on elastomeric seals and flexible hoses. These components are designed to operate within a specific temperature range.
Excessive heat causes seals to harden and become brittle. They lose their ability to conform to surfaces, leading to external leaks and internal bypassing. Hoses can also degrade from the inside out, leading to delamination and eventual bursting.
The Long-Term Consequences of Overheating
If a system is allowed to run hot for extended periods, the immediate effects compound into long-term, irreversible damage that is far more costly to repair.
Accelerated Oil Oxidation
Heat is a powerful catalyst for oxidation, the chemical reaction between the oil and oxygen. For every 18°F (10°C) increase in temperature above 140°F (60°C), the rate of oxidation roughly doubles.
This process permanently degrades the oil, forming sludge, varnish, and corrosive acids. Varnish coats internal surfaces, causing critical components like servo and proportional valves to stick and malfunction. Sludge clogs filters, strainers, and small orifices, starving the system of lubrication.
Pump and Valve Damage
The combination of poor lubrication (low viscosity) and contaminants (sludge and varnish) is devastating to precision components.
Pumps may begin to cavitate as the hot, thin fluid fails to fill the pumping chambers properly. The fine tolerances within spool valves are quickly eroded, leading to persistent internal leakage and a loss of control. The eventual result is a complete failure of these expensive components.
Reduced System Efficiency and Power
A system that runs hot is an inefficient system. The energy that should be creating force and motion is instead being wasted as heat.
Operationally, this manifests as a sluggish and weak machine. Cycle times become longer, and the system may be unable to achieve its maximum rated pressure or force. This loss of performance directly impacts productivity and operational capability.
Understanding the Root Causes of Heat
Heat in a hydraulic system is generated whenever fluid flow is restricted or forced to do something other than produce useful work. Identifying the source is critical.
The System's Inability to Dissipate Heat
The most common cause is a failure in the cooling circuit. This can be a clogged or dirty heat exchanger (radiator), a malfunctioning fan, or insufficient airflow around the reservoir. The system generates a normal amount of heat but simply cannot get rid of it.
Excess Heat Generation
Alternatively, the system may be producing more heat than its cooling circuit was ever designed to handle. This points to an internal inefficiency or fault.
A classic example is a pressure-relief valve that is constantly open. If a relief valve is lifting, it means the full pump flow is being forced through a small orifice at high pressure, converting immense hydraulic power directly into heat. Other causes include worn pumps or motors with excessive internal leakage.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Effectively managing heat is fundamental to hydraulic system reliability. Your approach will depend on whether you are troubleshooting an immediate problem or focused on long-term prevention.
-
If your primary focus is immediate troubleshooting: Use an infrared temperature gun to identify hotspots. Check the heat exchanger for blockages and ensure the cooling fan is operational. Check the hydraulic oil level, as low levels reduce the system's ability to dissipate heat.
-
If your primary focus is long-term reliability: Institute a regular oil analysis program to monitor fluid condition and detect early signs of oxidation. Adhere to a strict schedule for changing filters and cleaning heat exchangers to prevent heat buildup.
-
If your primary focus is system design or modification: Ensure the reservoir is sized correctly (typically 3-5 times the pump flow rate) and the cooling system has an adequate margin of safety for the highest expected ambient temperatures. Consider using more efficient components, like variable displacement pumps, to reduce waste heat generation at the source.
Ultimately, managing temperature is managing the energy and extending the life of your entire hydraulic system.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Immediate Effect | Long-Term Consequence |
|---|---|---|
| Fluid Viscosity | Becomes thin, loses lubricity | Accelerated metal-on-metal wear, pump damage |
| Internal Leakage | Increases due to thin fluid | Vicious cycle of more heat and lower efficiency |
| Seals & Hoses | Harden, become brittle | External leaks, internal bypassing, bursting |
| Chemical State | Accelerated oxidation begins | Sludge, varnish, corrosive acids form |
| System Performance | Efficiency drops, becomes sluggish | Complete component failure, inability to perform work |
Protect your hydraulic systems from the destructive cycle of overheating. Proper maintenance and monitoring are key to preventing costly downtime and component failure. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, including analysis tools that help you monitor fluid condition and prevent system failures. Ensure your lab's hydraulic systems run efficiently and reliably—contact our experts today to find the right solutions for your needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Cold Trap Direct Cold Trap Chiller
- Automatic Laboratory Heat Press Machine
- Aluminized Ceramic Evaporation Boat for Thin Film Deposition
- Gold Electrochemical Sheet Electrode Gold Electrode
- Laboratory Disc Rotary Mixer for Efficient Sample Mixing and Homogenization
People Also Ask
- Why is a laboratory hydraulic press required for water vapor resistant sensor joints? Ensure High-Density Sealing
- Why is it difficult to scale up the volume of a cubic press? Understanding Force and Geometric Constraints
- What are the different types of mechanical presses? Choose the Right Press for Your Application
- How does a hydraulic press with two pistons work? Unlocking the Power of Force Multiplication
- What are the advantages of using a hydraulic press with precise pressure control for LPSCl0.3F0.7 electrolyte molding?
- Why is a hydraulic press required for all-solid-state batteries? Achieve Precision Layer Molding up to 200 MPa
- Why is a uniaxial hydraulic press used for LLZTO powder? Achieving High Green Density for Ceramic Success
- What is the pellet technique in IR? Master Solid Sample Preparation for Clear Spectroscopy














