In short, heat treatment is not a single, standalone industry. Instead, it is a critical manufacturing process used across numerous foundational sectors. Heat treatment involves a series of controlled heating and cooling operations applied to metals and alloys to achieve specific, enhanced properties like strength or hardness. It functions as a vital service or an in-house capability for major industries like aerospace, automotive, and energy that require high-performance materials.
Rather than being its own industry, think of heat treatment as a foundational industrial service—a crucial step in the manufacturing supply chain that enables other industries to create reliable, high-performance components from raw metals.

A Critical Process Across Multiple Sectors
Heat treatment is the hidden step that unlocks the full potential of metallic materials. Without it, the high-strength, durable components that define modern technology would not be possible.
The Core Function of Heat Treatment
The primary purpose is to alter the physical, and sometimes chemical, properties of a material. By precisely managing temperature and cooling rates, manufacturers can make a metal harder, tougher, or more resistant to corrosion. This process happens entirely in the metal's solid state and is distinct from simply heating it to be shaped.
Why a Controlled Atmosphere is Essential
For many advanced applications, heat treatment must occur in a controlled atmosphere. This prevents contamination from atmospheric gases like oxygen, which can compromise the material's integrity. This precision ensures the metal or special alloy retains its engineered properties, a non-negotiable requirement for critical components.
Key Industries Relying on Heat Treatment
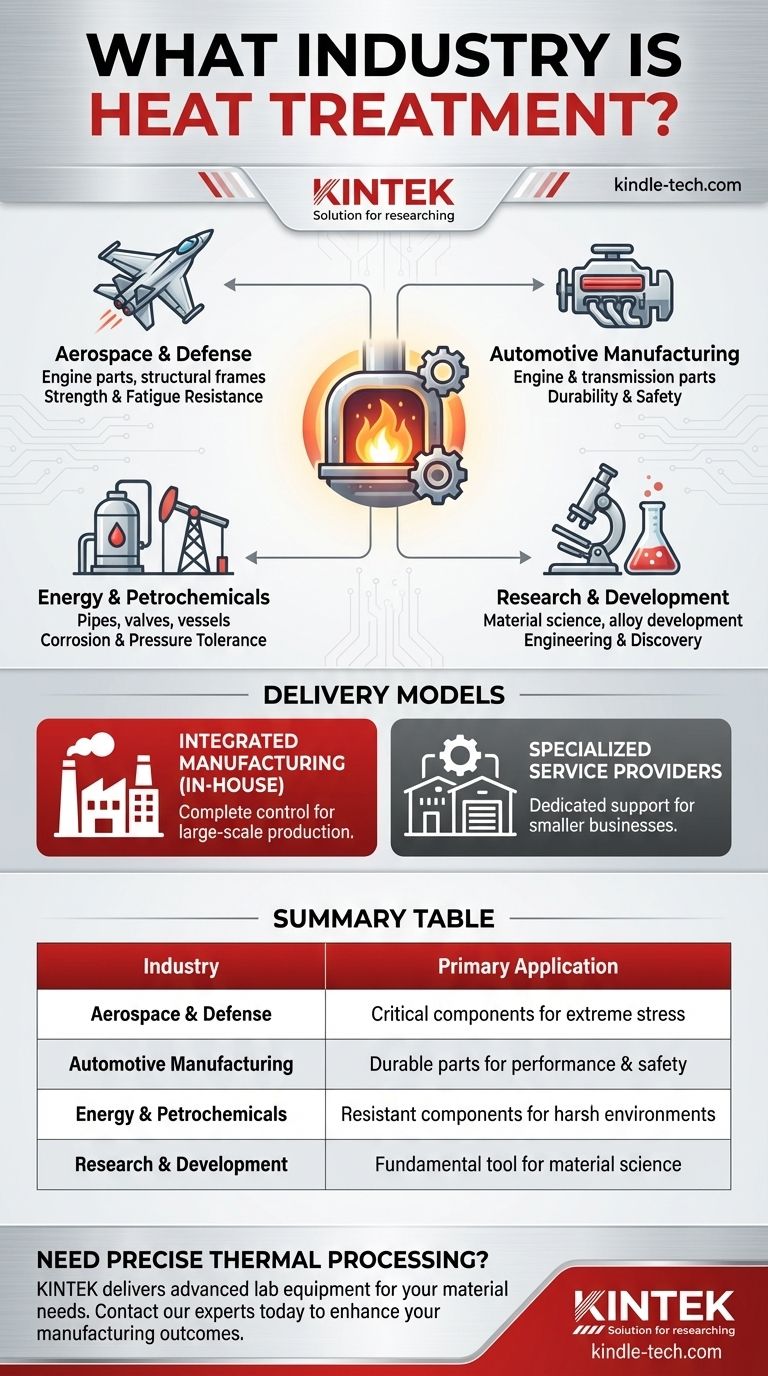
The need for materials with specific, reliable characteristics places heat treatment at the heart of many advanced manufacturing fields. Its applications are widespread and tailored to the unique demands of each sector.
Aerospace and Defense
This sector requires components that can withstand extreme stress and temperatures. Heat treatment is used on engine parts, landing gear, and structural frames to ensure maximum strength and fatigue resistance, which are critical for safety and performance.
Automotive Manufacturing
From engine components and transmissions to suspension parts, the automotive industry relies on heat treatment to create durable, long-lasting parts. This process ensures gears can handle immense torque and structural components can protect occupants in a collision.
Energy and Petrochemicals
Industries like nuclear power and oil refining use components exposed to high pressures, extreme temperatures, and corrosive environments. Heat treatment provides the necessary corrosion resistance and strength for parts like pipes, valves, and reactor vessels.
Research and Development
As noted in universities and laboratories, heat treatment is also a fundamental tool for material science. It is used to develop and test new alloys and to better understand the relationship between a material's internal structure and its physical properties.
Understanding the Trade-offs: In-House vs. Service Provider
A key point of clarification is that heat treatment doesn't operate as a single, monolithic industry. Its function is delivered through two primary models, each with its own context.
Integrated Manufacturing (In-House)
Large-scale manufacturers, such as a major automotive company or aerospace firm, often have their own in-house heat treatment facilities. This gives them complete control over the quality and production timeline for their most critical components.
Specialized Service Providers
Many other businesses operate specifically as heat treatment service providers. These specialized companies serve smaller manufacturers who lack the capital or expertise to run their own facilities. This creates a service sector dedicated entirely to supporting other manufacturing industries.
How to Classify Heat Treatment for Your Goal
Understanding heat treatment's role depends on your perspective. It can be seen as a process, a service, or a scientific field.
- If your primary focus is on manufacturing: View heat treatment as a critical, value-adding step in the production chain, essential for achieving final product specifications.
- If your primary focus is on business and economics: Classify it as a specialized industrial service sector that provides essential support to primary manufacturing industries.
- If your primary focus is on material science: See it as a fundamental tool for engineering and manipulating the properties of metals and alloys.
Ultimately, heat treatment is the invisible engineering process that gives modern, high-performance materials their strength and reliability.
Summary Table:
| Industry | Primary Application of Heat Treatment |
|---|---|
| Aerospace & Defense | Engine parts, landing gear, structural frames for strength & fatigue resistance |
| Automotive Manufacturing | Engine components, transmissions, suspension parts for durability & safety |
| Energy & Petrochemicals | Pipes, valves, reactor vessels for corrosion resistance & high-pressure tolerance |
| Research & Development | Material science research & new alloy development in laboratories |
Need precise thermal processing for your materials? Whether you're in aerospace, automotive, energy, or R&D, KINTEK's advanced lab equipment and consumables deliver the controlled heating solutions you need. Our expertise ensures your metals and alloys achieve the exact properties required for high-performance applications.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your heat treatment processes and enhance your manufacturing outcomes.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- How to vacuum out a furnace? A Step-by-Step Guide to Safe DIY Maintenance
- What materials are used in a vacuum furnace? Selecting the Right Hot Zone for Your Process
- What is vacuum heat treatment process? Achieve Superior Control, Cleanliness, and Quality
- What is a vacuum furnace used for? Unlock High-Purity Heat Treatment for Superior Materials
- What is the vacuum heat treatment cycle? Achieve Superior Material Purity and Precision



















