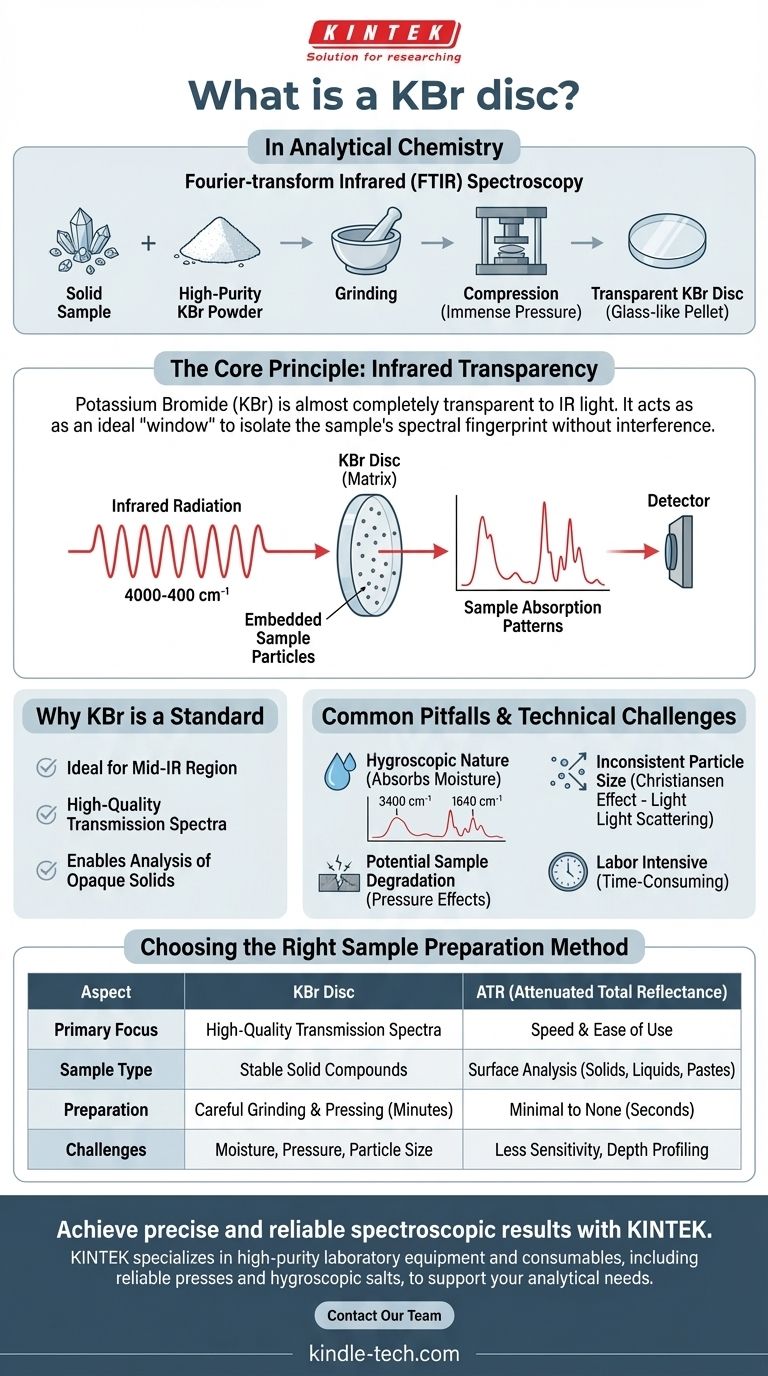
In analytical chemistry, a KBr disc is a solid, transparent pellet used to prepare solid samples for analysis via Fourier-transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy. It is created by finely grinding a small amount of the sample with high-purity potassium bromide (KBr) powder and then compressing the mixture under immense pressure to form a small, glass-like disc.
The core principle is straightforward: potassium bromide is almost completely transparent to infrared radiation. This allows it to act as an ideal matrix, or "window," holding the solid sample in the spectrometer's light path so that only the sample's unique chemical bonds absorb the infrared light.

Why KBr is a Standard for Solid Sample Analysis
Understanding why this specific salt became a laboratory staple reveals the fundamental requirements for infrared spectroscopy. The goal is to isolate the spectral "fingerprint" of your sample without any interference from the materials used to hold it.
The Principle of Infrared Transparency
The primary reason for using potassium bromide (KBr) is its lack of absorption in the mid-infrared region (4000-400 cm⁻¹), which is the most information-rich area for molecular analysis.
Because KBr itself does not absorb this light, any absorption detected by the spectrometer can be attributed directly to the sample embedded within it. This creates a clean, unobstructed view of the sample's molecular structure.
How the Disc Enables Measurement
FTIR spectroscopy works by passing a beam of infrared light through a sample, a technique known as transmission. For this to work with an opaque solid, the sample must be made extremely thin or dispersed in a non-absorbing medium.
The KBr disc effectively suspends microscopic particles of the sample in a solid, transparent matrix, allowing the IR beam to pass through and interact with the sample molecules.
The Goal: A Homogeneous Mixture
The quality of the final spectrum is directly dependent on the quality of the disc. The sample must be ground into extremely fine particles and distributed evenly throughout the KBr powder before pressing.
A good mixture ensures the light passes through the sample uniformly, producing a clear and accurate spectrum.
Common Pitfalls and Technical Challenges
While the KBr disc method can produce excellent spectra, it is a technique that requires care and is prone to specific errors. Understanding these challenges is key to producing reliable data.
The Problem of Moisture
Potassium bromide is highly hygroscopic, meaning it readily absorbs moisture from the air. This is the most common source of error.
Water has a very strong and broad absorption band in the infrared spectrum (around 3400 cm⁻¹ and 1640 cm⁻¹). If the KBr is not perfectly dry, these water peaks can obscure important features of your sample's spectrum.
Inconsistent Particle Size
If the sample particles are too large, they can scatter the infrared light instead of transmitting it. This phenomenon, known as the Christiansen effect, results in a distorted baseline that can make the spectrum difficult to interpret accurately.
Properly grinding the sample to a fine, flour-like consistency with an agate mortar and pestle is critical to minimize this scattering.
Potential for Sample Degradation
The immense pressure required to form the disc (typically several tons) can sometimes alter the sample. This is particularly true for polymorphic compounds, which can change their crystalline form under pressure, leading to a different spectrum.
Furthermore, the ionic nature of KBr can cause ion exchange with certain samples, such as halide salts, altering the very chemistry you are trying to measure.
Technique and Labor Intensity
Compared to modern alternatives like Attenuated Total Reflectance (ATR), the KBr disc method is significantly more time-consuming and requires more skill to perform correctly. The entire process of weighing, grinding, pressing, and cleaning can take several minutes per sample.
Choosing the Right Sample Preparation Method
The KBr disc is a classic and powerful technique, but it's not always the best choice. Your decision should be based on your sample's properties and your analytical goals.
- If your primary focus is high-quality transmission data for a stable solid compound: The KBr disc method, when done correctly, produces excellent, textbook-quality spectra.
- If your primary focus is speed and ease of use: ATR spectroscopy is a superior choice, as it requires almost no sample preparation and analyzes the surface of a solid directly.
- If your sample is sensitive to moisture, pressure, or is a liquid/paste: You should consider other methods like preparing a Nujol mull or using liquid cells.
Understanding the principles and limitations of the KBr disc technique is fundamental to generating accurate and reliable spectroscopic data.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Detail |
|---|---|
| Primary Use | Sample preparation for FTIR spectroscopy |
| Core Principle | KBr is transparent to IR light, acting as a matrix for the sample |
| Key Advantage | Produces high-quality transmission spectra |
| Main Challenge | Hygroscopic nature of KBr requires careful handling to avoid moisture |
| Common Alternative | ATR (Attenuated Total Reflectance) spectroscopy for faster analysis |
Achieve precise and reliable spectroscopic results with KINTEK.
The KBr disc method is a foundational technique for accurate FTIR analysis, but it requires the right equipment and consumables to avoid common pitfalls like moisture contamination. KINTEK specializes in high-purity laboratory equipment and consumables, including reliable presses and hygroscopic salts, to support your laboratory's analytical needs.
Let our expertise help you enhance your lab's efficiency and data quality. Contact our team today to find the perfect solution for your spectroscopy workflow.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- kbr pellet press 2t
- XRF & KBR plastic ring lab Powder Pellet Pressing Mold for FTIR
- Laboratory Disc Rotary Mixer for Efficient Sample Mixing and Homogenization
- Laboratory Hydraulic Pellet Press for XRF KBR FTIR Lab Applications
- Automatic Laboratory Hydraulic Pellet Press Machine for Lab Use
People Also Ask
- What is the purpose of using laboratory hydraulic presses for molecular sieve catalysts? Optimize Reactor Performance
- Why is KBr inactive in IR? The Key to Transparent Sample Analysis
- How much pressure should a hydraulic press have? Focus on Tonnage for Your Application
- What are the parts of a press forming machine? Understand the Core Components for Your Application
- Why is a laboratory hydraulic press essential for Cu-Mo alloy production? Maximize Green Body Strength and Density
- What role does a laboratory high-precision hydraulic press play in rare earth hydrogen storage? Optimize Pellet Density
- How accurate is the XRF measurement? Unlock the True Potential of Your Material Analysis
- How are laboratory hydraulic presses used in catalyst preparation? Key Steps for Pelletizing Heterogeneous Catalysts



















