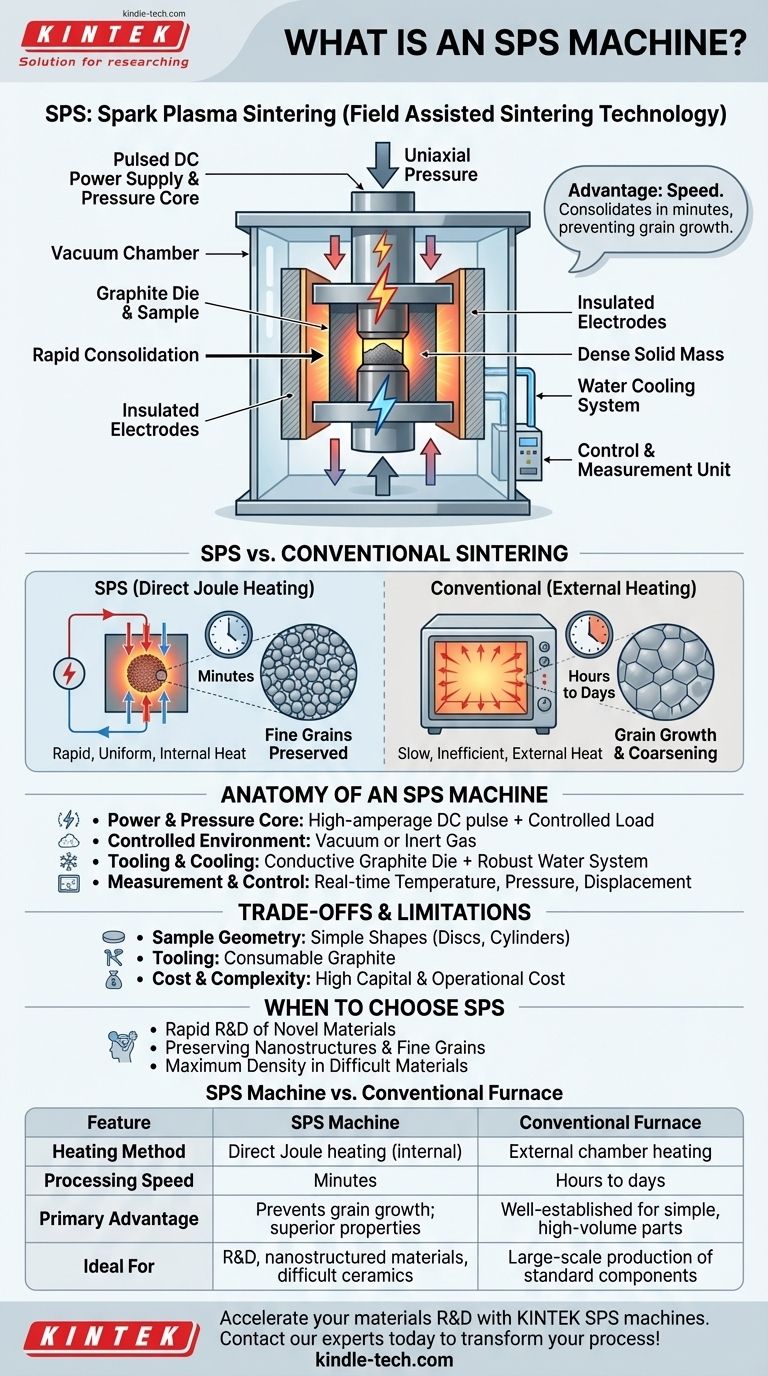
At its core, an SPS machine is a highly advanced furnace used for materials processing. The acronym stands for Spark Plasma Sintering, though the technology is also known as Field Assisted Sintering Technology (FAST). It uses a powerful, pulsed DC electric current combined with uniaxial pressure to rapidly consolidate powders into a dense, solid mass. Unlike a conventional furnace that heats from the outside in, an SPS machine passes the current directly through the conductive mold and the material itself, achieving incredibly high heating rates.
The central advantage of an SPS machine is its speed. By consolidating materials in minutes instead of hours, it prevents the unwanted grain growth that plagues slower, high-temperature methods, enabling the creation of advanced materials with superior properties that are often impossible to achieve conventionally.

How SPS Fundamentally Differs from Conventional Sintering
To understand the value of an SPS machine, it's essential to contrast it with traditional sintering furnaces, which have been the standard for decades. The difference lies in how energy is delivered to the material.
The Principle of Direct Joule Heating
A conventional furnace operates like an oven, slowly heating a chamber through radiation or convection. This process is inefficient and time-consuming.
An SPS machine uses Joule heating. The sample and its graphite mold become part of the electrical circuit. As a high-amperage current passes through them, their own electrical resistance causes them to heat up almost instantaneously and uniformly from within.
The Role of Uniaxial Pressure
While the sample is being heated, the SPS machine applies constant mechanical pressure through the electrodes. This force aids in particle rearrangement and plastic deformation, squeezing out porosity and accelerating the densification process significantly.
The "Spark Plasma" Effect
The name comes from a theorized phenomenon where electrical discharges, or sparks, are generated in the gaps between powder particles. This is thought to create a localized plasma that cleans particle surfaces of contaminants (like oxides), further promoting the bonding and densification of the material.
Anatomy of a Typical SPS Machine
While designs vary, all SPS machines are built around a few core systems that work in concert to achieve precise control over the sintering environment.
The Power and Pressure Core
This is the heart of the machine. It consists of a high-amperage DC pulse power supply capable of delivering thousands of amps of current and a hydraulic or electric pressure system that applies a controlled load to the sample.
The Controlled Environment
The entire process takes place inside a vacuum chamber. Removing air is critical to prevent the sample and the graphite tooling from oxidizing and combusting at the extremely high temperatures involved. The chamber can also be backfilled with an inert gas like argon.
The Tooling and Cooling System
The powdered material is loaded into a graphite die set (a mold and two punches). Graphite is used because it is both electrically conductive and can withstand very high temperatures. A robust water-cooling system is essential to protect the chamber, electrodes, and other machine components.
The Measurement and Control Unit
SPS is a precision process. Sophisticated sensors constantly monitor and control key parameters, including temperature (via pyrometers), applied pressure, and the displacement of the punch, which indicates how much the sample is shrinking or densifying in real-time.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, SPS technology is not a universal solution. Its unique mechanism comes with specific constraints that are critical to understand.
Sample Geometry and Size
The use of uniaxial pressure generally limits SPS to producing parts with relatively simple geometries, such as discs, cylinders, and squares. Creating complex, three-dimensional shapes is very difficult.
Material and Tooling Constraints
The standard process relies on an electrically conductive graphite mold. Sintering highly insulating ceramics can be more challenging, sometimes requiring alternative tooling setups. Furthermore, the graphite tooling is a consumable that degrades with each use, especially at extreme temperatures and pressures, adding to the operational cost.
Cost and Complexity
SPS machines are specialized, high-power instruments. They represent a significantly higher capital investment and have greater operational complexity than a standard industrial furnace.
When to Choose an SPS Machine
Selecting the right consolidation technology depends entirely on your material goals, production volume, and budget. SPS excels in specific, high-value applications.
- If your primary focus is rapid R&D of novel materials: The speed of the SPS process is unparalleled for quickly iterating on new compositions and creating property test coupons in a matter of hours.
- If your primary focus is preserving nanostructures or fine grains: The extremely short processing time and lower sintering temperatures of SPS are critical for preventing the grain growth that weakens many advanced materials.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum density in difficult-to-sinter materials: The combination of direct heat and pressure in an SPS machine often achieves theoretical densities in materials (like refractory metals or certain ceramics) that other methods cannot.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production of simple components: For many applications, traditional, slower methods like press-and-sinter or hot pressing may be more cost-effective at a large scale.
Ultimately, an SPS machine is a transformative tool for materials engineering, enabling the development of next-generation materials by fundamentally changing the dynamics of time, temperature, and pressure.
Summary Table:
| Feature | SPS Machine | Conventional Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Heating Method | Direct Joule heating (internal) | External chamber heating |
| Processing Speed | Minutes | Hours to days |
| Primary Advantage | Prevents grain growth; superior material properties | Well-established for simple, high-volume parts |
| Ideal For | R&D, nanostructured materials, difficult-to-sinter ceramics | Large-scale production of standard components |
Ready to accelerate your materials R&D with the precision of Spark Plasma Sintering?
KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment, including SPS machines, to help you develop next-generation materials with superior properties. Our expertise ensures you get the right solution for your specific laboratory needs, from rapid prototyping to achieving maximum density in challenging materials.
Contact our experts today to discuss how an SPS machine can transform your research and development process!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Spark Plasma Sintering Furnace SPS Furnace
- CF KF Flange Vacuum Electrode Feedthrough Lead Sealing Assembly for Vacuum Systems
- Single Punch Electric Tablet Press Machine TDP Tablet Punching Machine
- Small Injection Molding Machine for Lab Use
- Automatic Laboratory Heat Press Machine
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of SPS? Achieve Superior Material Density and Performance
- What are the different sintering methods? Choose the Right Technique for Your Material & Application
- What is the difference between hot press and SPS? Choose the Right Sintering Method for Your Lab
- Can aluminum be sintered? Overcome the Oxide Barrier for Complex, Lightweight Parts
- What is the vapor phase material? Unlock Faster, Denser Sintering with SPS Technology



















