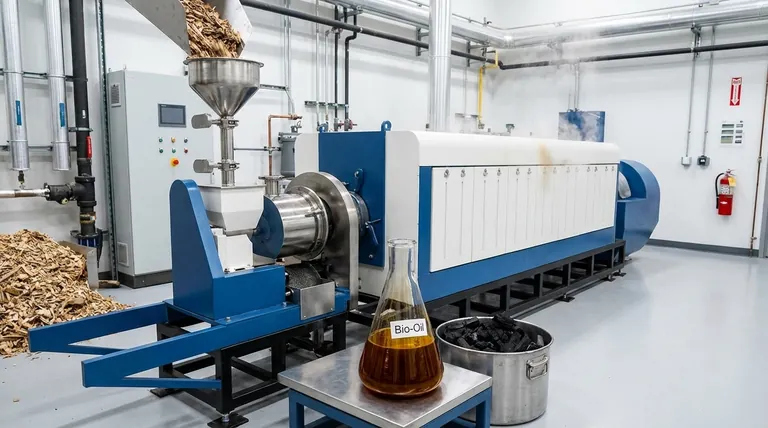
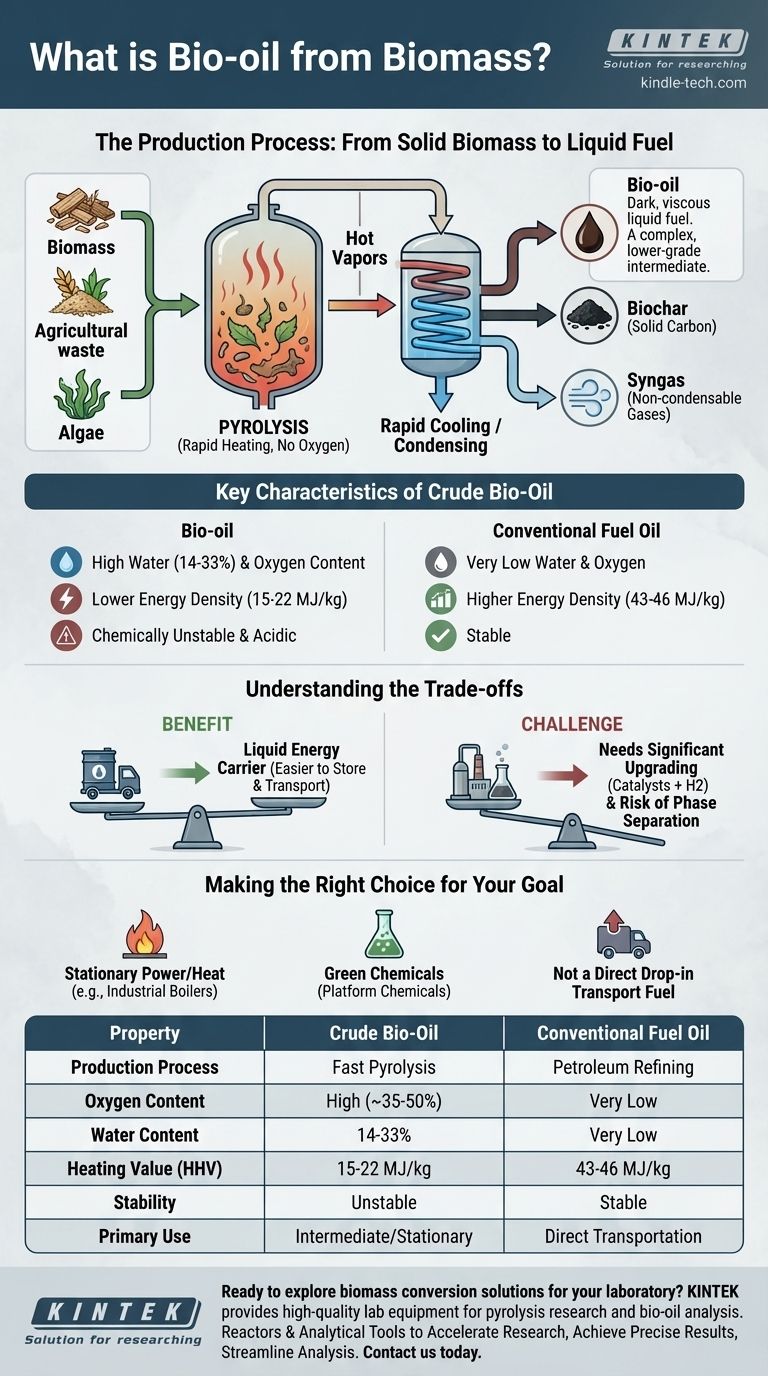
At its core, bio-oil is a dark, viscous liquid fuel derived from the thermal decomposition of biomass. It is produced through a process called pyrolysis, which involves rapidly heating organic matter like wood, agricultural waste, or algae in an environment without oxygen. The resulting hot vapors are then quickly cooled and condensed to form this liquid, which is sometimes referred to as pyrolysis oil.
Bio-oil represents a direct method for converting solid, bulky biomass into a liquid energy carrier. However, its inherent chemical properties—notably high water and oxygen content—make it a complex, lower-grade intermediate that requires significant upgrading to compete with conventional fossil fuels.

The Production Process: From Solid Biomass to Liquid Fuel
To understand bio-oil, you must first understand the process that creates it. It is fundamentally different from other common biofuels like ethanol or biodiesel.
The Role of Pyrolysis
The entire process hinges on pyrolysis. This is the thermal decomposition of a material at high temperatures in the complete absence of oxygen.
By preventing oxygen from entering the system, the biomass does not combust (burn). Instead, its complex organic polymers break down into smaller, volatile molecules, forming a hot gas.
Condensing Vapors into Oil
This hot gas is then cooled rapidly. This cooling, or quenching, causes the volatile components to condense into a liquid.
This condensed liquid is bio-oil. The process also yields two other byproducts: non-condensable gases (syngas) and a solid, carbon-rich charcoal (biochar).
Distinguishing from Other Biofuels
It is critical to distinguish pyrolysis from the processes used to make other biofuels.
Biofuels like ethanol are made through a biochemical process of fermentation. Biodiesel is created via a chemical process called transesterification. Bio-oil, in contrast, is the product of a purely thermo-chemical conversion.
Key Characteristics of Crude Bio-Oil
Raw bio-oil is chemically very different from petroleum-based crude oil. These differences define its limitations and potential applications.
High Water and Oxygen Content
Bio-oil contains a significant amount of water, typically 14% to 33% by weight, which is emulsified within the oil and difficult to remove.
It also has a high oxygen content, inherited from the original biomass. This makes it fundamentally different from hydrocarbons like crude oil, which contain almost no oxygen.
Lower Energy Density
The presence of water and oxygenated organic compounds dramatically lowers its energy content.
The higher heating value (HHV) of bio-oil decisões between 15–22 MJ/kg. This is roughly half the value of conventional fuel oil, which is in the range of 43–46 MJ/kg. You get less energy per kilogram of fuel.
Chemical Instability and Acidity
The oxygenated compounds, such as organic acids, make bio-oil acidic and corrosive. They also make the oil chemically unstable, causing it to thicken and polymerize over time, which complicates storage and handling.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Bio-oil is not a perfect solution, but a technology with specific benefits and clear challenges. Acknowledging these trade-offs is key to evaluating its role.
The Benefit: A Liquid Energy Carrier
The primary advantage of pyrolysis is its ability to convert low-density, difficult-to-handle solid biomass into a high-density, transportable liquid. This liquid can be stored and used more easily than the original raw material.
The Challenge: The Need for Upgrading
Due to its high oxygen content, acidity, and instability, crude bio-oil is not a "drop-in" fuel for modern engines. It cannot be directly mixed with or used in place of gasoline or diesel.
To be used as a transportation fuel, it must undergo intensive upgrading—a process that uses catalysts and hydrogen to remove oxygen. This adds significant cost and complexity.
The Risk: Phase Separation
As noted, bio-oil contains a large amount of water. If the water content becomes too high, or if more water is introduced, the oil can separate into two phases: an aqueous phase and a heavy organic phase. This ruins its consistency as a fuel.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
How you view bio-oil depends entirely on your intended application. It is not a one-size-fits-all solution.
- If your primary focus is direct transportation fuel: Recognize that crude bio-oil is not a viable option and requires extensive, costly upgrading to become a usable hydrocarbon fuel.
- If your primary focus is stationary power or heat: Bio-oil can be a more practical substitute for heavy fuel oil in industrial boilers, furnaces, and certain stationary engines designed to handle its properties.
- If your primary focus is producing green chemicals: The oxygenated compounds, पुलिस a problem for fuel, can be isolated and used as valuable platform chemicals for the bio-based economy.
Ultimately, it is best to view bio-oil not as a final product, but as a chemically complex intermediate on the path from raw biomass to refined energy and materials.
Summary Table:
| Property | Crude Bio-Oil | Conventional Fuel Oil |
|---|---|---|
| Production Process | Fast Pyrolysis | Petroleum Refining |
| Oxygen Content | High (~35-50%) | Very Low |
| Water Content | 14-33% | Very Low |
| Heating Value (HHV) | 15-22 MJ/kg | 43-46 MJ/kg |
| Stability | Unstable, thickens over time | Stable |
| Primary Use | Intermediate for upgrading, stationary heat/power | Direct transportation fuel |
Ready to explore biomass conversion solutions for your laboratory?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-quality lab equipment for pyrolysis research and bio-oil analysis. Whether you are developing new biofuels, studying catalyst performance, or analyzing biomass feedstocks, our reactors and analytical tools are designed to meet your precise needs.
We help you:
- Accelerate your biofuel and green chemical research.
- Achieve precise and reliable pyrolysis results.
- Streamline your analysis of complex bio-oils.
Contact us today using the form below to discuss how KINTEK's expertise in lab equipment can support your biomass conversion projects.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
People Also Ask
- What are the products of pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock Bio-Char, Bio-Oil, and Syngas
- What are the reactions involved in pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock the Chemistry for Tailored Bio-Products
- How is energy converted into biomass? Harnessing Nature's Solar Power for Renewable Energy
- What are the conditions for biomass pyrolysis? Optimize Temperature, Heating Rate & Time
- Is pyrolysis viable? A Guide to Economic, Technological, and Environmental Success



















