At its core, Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is a manufacturing process for growing extremely thin, high-quality solid films on a surface. In semiconductor fabrication, this involves introducing carefully selected reactive gases into a vacuum chamber containing silicon wafers. These gases undergo a controlled chemical reaction, depositing a new, solid layer that becomes a fundamental building block of the final microchip.
Understanding Chemical Vapor Deposition is not just about coating a surface; it's about understanding how the microscopic, multi-layered cities inside a computer chip are constructed, layer by precise layer, by transforming gas into solid material.
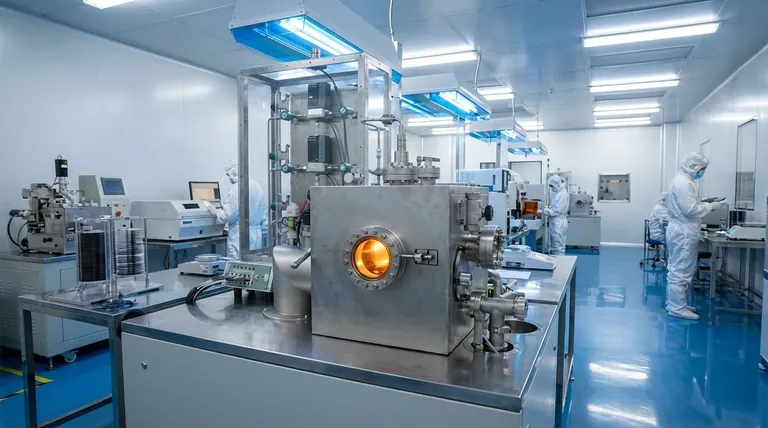

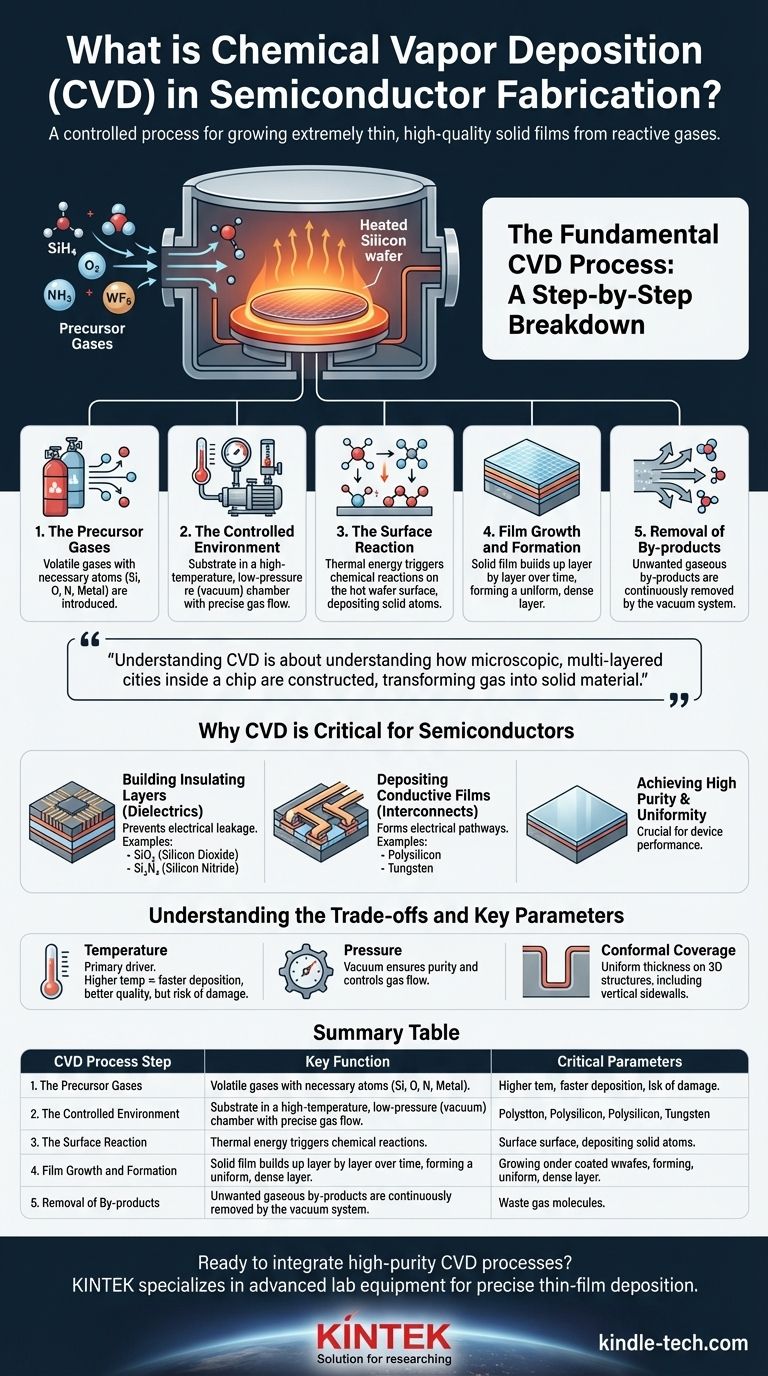
The Fundamental CVD Process: A Step-by-Step Breakdown
To truly grasp CVD, it's best to visualize it as a controlled, high-temperature construction process where the building materials arrive as a gas.
The Precursor Gases
The process begins with one or more volatile gases, known as precursors. These gases are specifically chosen because they contain the atoms needed for the final film (e.g., silicon, oxygen, nitrogen, or a metal).
The Controlled Environment
The silicon wafer, or substrate, is placed inside a reaction chamber. This chamber's environment is tightly controlled for three key variables: high temperature, low pressure (vacuum), and a precise gas flow rate.
The Surface Reaction
When the precursor gases flow over the heated substrate, the thermal energy triggers a chemical reaction. The gases decompose or react with each other directly on the hot surface of the wafer.
This reaction causes the desired atoms to "precipitate" out of their gaseous state and bond firmly to the substrate, forming a new solid layer.
Film Growth and Formation
This deposition process is not instantaneous. The solid film builds up over time, often atom by atom, growing into a uniform, dense layer across the entire wafer. The thickness is controlled by the duration of the process.
Removal of By-products
The chemical reaction almost always creates unwanted gaseous by-products. These volatile waste products are continuously removed from the chamber by the vacuum system's gas flow, leaving only the pure, solid film behind.
Why CVD is Critical for Semiconductors
CVD isn't just one of many options; it is an essential technique used repeatedly during the fabrication of a single chip to build different parts of its intricate circuitry.
Building Insulating Layers
Circuits require insulators to prevent electrical current from leaking between wires. CVD is the primary method for depositing high-purity insulating films, such as silicon dioxide (SiO₂) and silicon nitride (Si₃N₄).
Depositing Conductive Films
The "wires" that connect transistors are also often created using CVD. It is used to deposit films of polysilicon (a form of silicon) and various metals like tungsten, which serve as conductive pathways in the integrated circuit.
Achieving High Purity and Uniformity
The performance of a semiconductor device is critically dependent on the quality of its layers. CVD allows for exceptional control over the purity and thickness of the deposited film, ensuring consistent performance across the entire wafer.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Key Parameters
The success of a CVD process depends on a delicate balance of competing factors. Engineers must manage these variables to achieve the desired outcome.
The Role of Temperature
Temperature is the primary driver of the chemical reaction. Higher temperatures generally lead to faster deposition rates and higher quality films. However, excessive heat can damage the delicate structures already built on the chip in previous steps.
The Impact of Pressure
Operating under a vacuum is non-negotiable. The vacuum environment ensures purity by removing unwanted air molecules and helps control the flow of the precursor gases. Different pressures are used to influence the film's final properties and how evenly it coats the surface.
The Challenge of Conformal Coverage
As chips become more three-dimensional, a key challenge is ensuring the deposited film is equally thick on vertical sidewalls as it is on horizontal surfaces. This property, known as conformality, is a critical parameter that CVD is uniquely capable of controlling.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The specific goals of your fabrication step dictate the ideal approach to CVD.
- If your primary focus is creating a flawless insulating layer (dielectric): You need a process that guarantees exceptional uniformity and purity, as even microscopic defects can cause circuit failure.
- If your primary focus is forming conductive pathways (interconnects): Your priority is achieving excellent adhesion to the underlying layer and the precise electrical properties required for the circuit.
- If your primary focus is coating complex, three-dimensional structures: You must prioritize a CVD variant known for high conformality, ensuring the film is equally thick on all exposed surfaces.
Ultimately, mastering CVD is mastering the ability to construct the intricate, multi-layered architecture that defines modern electronics.
Summary Table:
| CVD Process Step | Key Function | Critical Parameters |
|---|---|---|
| Precursor Gases | Supply atoms (e.g., Si, O, N) for the film | Gas composition, purity |
| Controlled Environment | Enable the chemical reaction | Temperature, pressure, gas flow rate |
| Surface Reaction | Decompose gases to deposit solid film | Substrate temperature |
| Film Growth | Build a uniform, dense layer | Process duration |
| By-product Removal | Maintain film purity | Vacuum system efficiency |
Ready to integrate high-purity CVD processes into your semiconductor fabrication? KINTEK specializes in providing the advanced lab equipment and consumables essential for precise thin-film deposition. Our solutions help you achieve the uniform, conformal coatings critical for next-generation microchips. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's specific semiconductor manufacturing goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the process capabilities of ICPCVD systems? Achieve Low-Damage Film Deposition at Ultra-Low Temperatures
- What is the difference between PECVD and APCVD? Choose the Right CVD Method for Your Application
- What is the process of PECVD in semiconductor? Enabling Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- How are thin films deposited? A Guide to PVD vs. CVD Methods for Your Application
- What is the difference between plasma CVD and thermal CVD? Choose the Right Method for Your Substrate



















