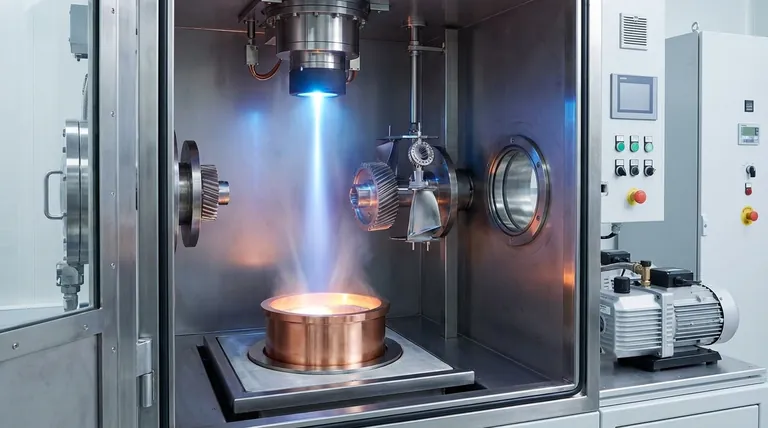
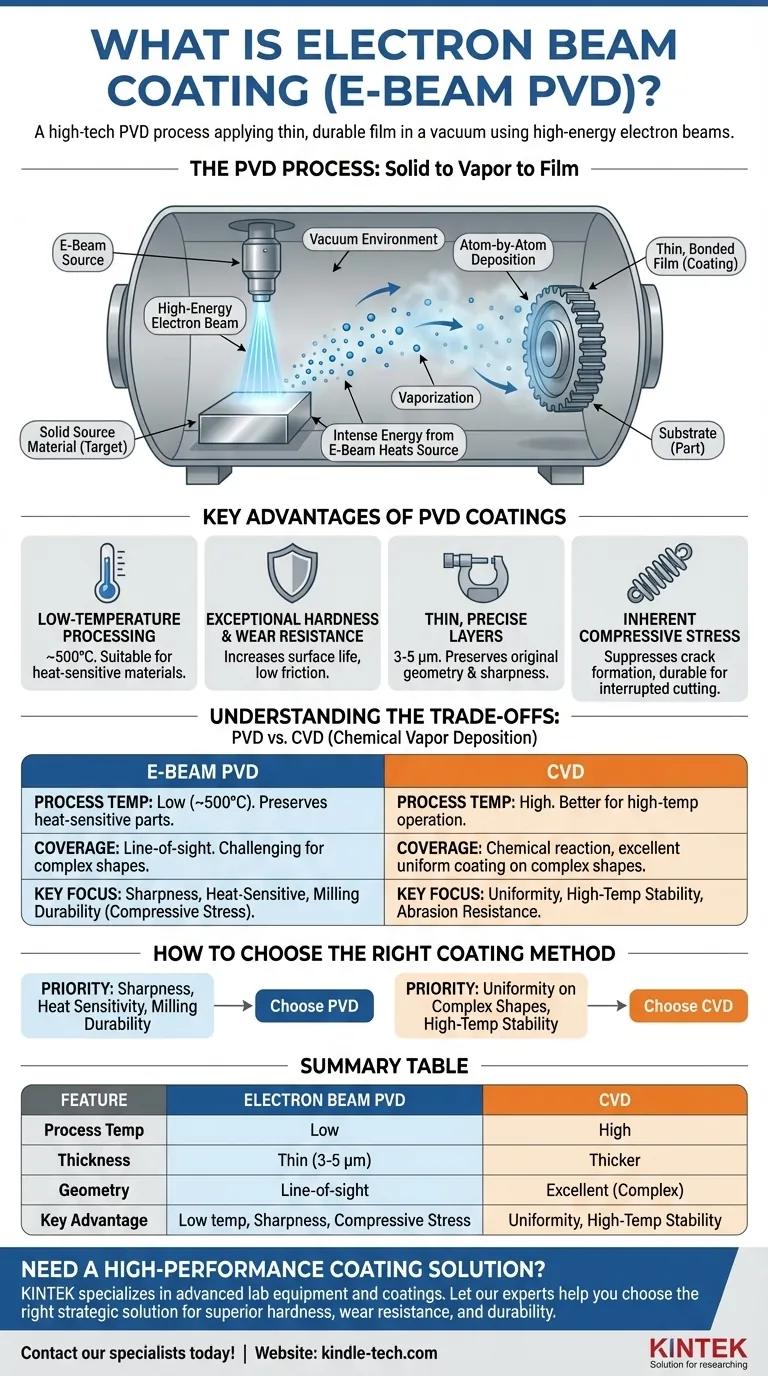
Electron beam coating is a specific type of Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD), a high-tech process used to apply a very thin, durable film onto a surface. In this method, a high-energy beam of electrons is fired at a solid source material inside a vacuum chamber, causing it to vaporize. This vapor then travels and condenses onto the target component, forming a bonded, atom-by-atom layer with superior properties.
The choice of a coating technology is not a question of which is "best," but a strategic decision based on trade-offs. The key is to match the unique properties of a coating process—like PVD or its alternative, CVD—to the specific demands of your component's final application.

Demystifying Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD)
PVD is not a single method but a family of vacuum deposition processes. Electron beam coating is one member of this family, alongside others like sputtering and arc discharge. They all share a fundamental principle.
The Core Principle: Solid to Vapor to Film
The PVD process involves three main steps, all conducted in a high-vacuum environment. First, a solid source material, often a pure metal like titanium or chromium known as a "target," is converted into a vapor.
This vaporization is the defining step where methods differ.
The Role of the Energy Source
To vaporize the solid target, a high-energy source is required. While some methods use arc discharges or ion bombardment (sputtering), electron beam PVD uses a precisely aimed beam of electrons.
The intense energy from the electron beam heats the source material until it evaporates.
Atom-by-Atom Deposition
Once vaporized, the material's atoms or molecules travel through the vacuum and strike the surface of the part being coated.
They condense on this surface to form a thin, dense, and highly adherent film. This layer can be a pure metal, a metallic alloy, or a ceramic compound if a reactive gas like nitrogen is introduced.
Key Advantages of PVD Coatings
PVD processes, including electron beam coating, are chosen for a distinct set of characteristics that make them ideal for high-performance applications.
Low-Temperature Processing
PVD coatings are typically applied at relatively low temperatures, often around 500°C. This makes the process suitable for coating materials that are sensitive to heat and could be damaged or warped by higher-temperature methods.
Exceptional Hardness and Wear Resistance
PVD films dramatically increase the surface hardness of a component. This creates a highly wear-resistant and low-friction surface, extending the life of parts like cutting tools.
Thin, Precise Layers
The resulting coatings are extremely thin, typically between 3 and 5 micrometers. This preserves the original geometry and sharpness of the underlying part, which is critical for precision blades and cutting tools.
Inherent Compressive Stress
During the cooling phase of the PVD process, a compressive stress is formed within the coating. This stress helps to suppress the formation and growth of cracks, making PVD-coated tools exceptionally durable for interrupted cutting tasks like milling.
Understanding the Trade-offs: PVD vs. CVD
The main alternative to PVD is Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD). Understanding their differences is key to making an informed decision.
The Temperature Divide
The most significant difference is temperature. CVD processes run much hotter than PVD, which can provide benefits for certain applications but risks thermal damage to the substrate. PVD's low processing temperature is its key advantage for heat-sensitive parts.
However, for a component that must operate in a very high-temperature environment, a CVD coating may offer superior stability.
Coverage on Complex Shapes
CVD is a chemical process where gas precursors react on all exposed surfaces. This gives it an advantage in creating a very uniform coating on parts with complex, irregular geometries like drill bits.
PVD is more of a "line-of-sight" process, where the vapor travels in a straight line from the source to the part, which can make uniform coverage on intricate shapes more challenging.
Abrasion and Wear Resistance
While both offer excellent protection, some sources suggest that CVD coatings can be more resistant to pure abrasion and wear than PVD coatings. The choice often depends on the specific type of wear a component will face.
How to Choose the Right Coating Method
Your decision should be driven entirely by the requirements of your project and the environment the part will operate in.
- If your primary focus is preserving the sharpness of precision cutting tools: PVD is the superior choice due to its thin layers and low processing temperature.
- If your primary focus is coating a heat-sensitive substrate: PVD is the only viable option, as it avoids the thermal damage associated with high-temperature CVD.
- If your primary focus is achieving a uniform coating on highly irregular shapes: CVD's gas-based deposition process generally offers better coverage and uniformity.
- If your primary focus is durability in interrupted cutting (e.g., milling): PVD's inherent compressive stress provides an advantage in preventing micro-cracking.
Ultimately, selecting the right coating is an engineering decision that balances the properties of the coating with the demands of the application.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Electron Beam PVD | CVD (Chemical Vapor Deposition) |
|---|---|---|
| Process Temperature | Low (~500°C) | High |
| Coating Thickness | Thin (3-5 μm) | Thicker |
| Geometry Suitability | Line-of-sight (complex shapes challenging) | Excellent for complex, irregular shapes |
| Key Advantage | Low temperature, preserves sharpness, compressive stress | Uniform coverage, high-temperature stability |
Need a High-Performance Coating Solution for Your Lab Equipment?
Choosing between PVD and CVD is critical for your component's performance and longevity. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing advanced lab equipment and consumables, including coating technologies tailored to your specific needs. Our experts can help you determine whether electron beam PVD or another method is the right strategic choice for your application, ensuring superior hardness, wear resistance, and durability.
Let KINTEK enhance your laboratory's capabilities. Contact our specialists today to discuss your project requirements and discover the ideal coating solution!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electron Beam Evaporation Coating Oxygen-Free Copper Crucible and Evaporation Boat
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- Evaporation Boat for Organic Matter
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
People Also Ask
- Can I solder copper to copper without flux? The Critical Role of Flux for a Strong Bond
- What is gold sputtered? A Guide to High-Purity Vacuum Coating for Electronics & SEM
- What is sputter coating used for? Achieve Superior Thin Films for Electronics, Optics, and Tools
- How is deposition time calculated? Mastering the Clock for Strategic Legal Advantage
- What are sputtering systems used for? A Guide to Advanced Thin-Film Deposition


















