In materials science and manufacturing, the hot press method is a fabrication technique that simultaneously applies high temperature and high pressure to a material. This combination reduces the material's porosity and fuses its constituent particles together, forming a solid, dense object. This process is fundamental for creating high-performance components from powders, especially with non-oxide materials like hexaborides.
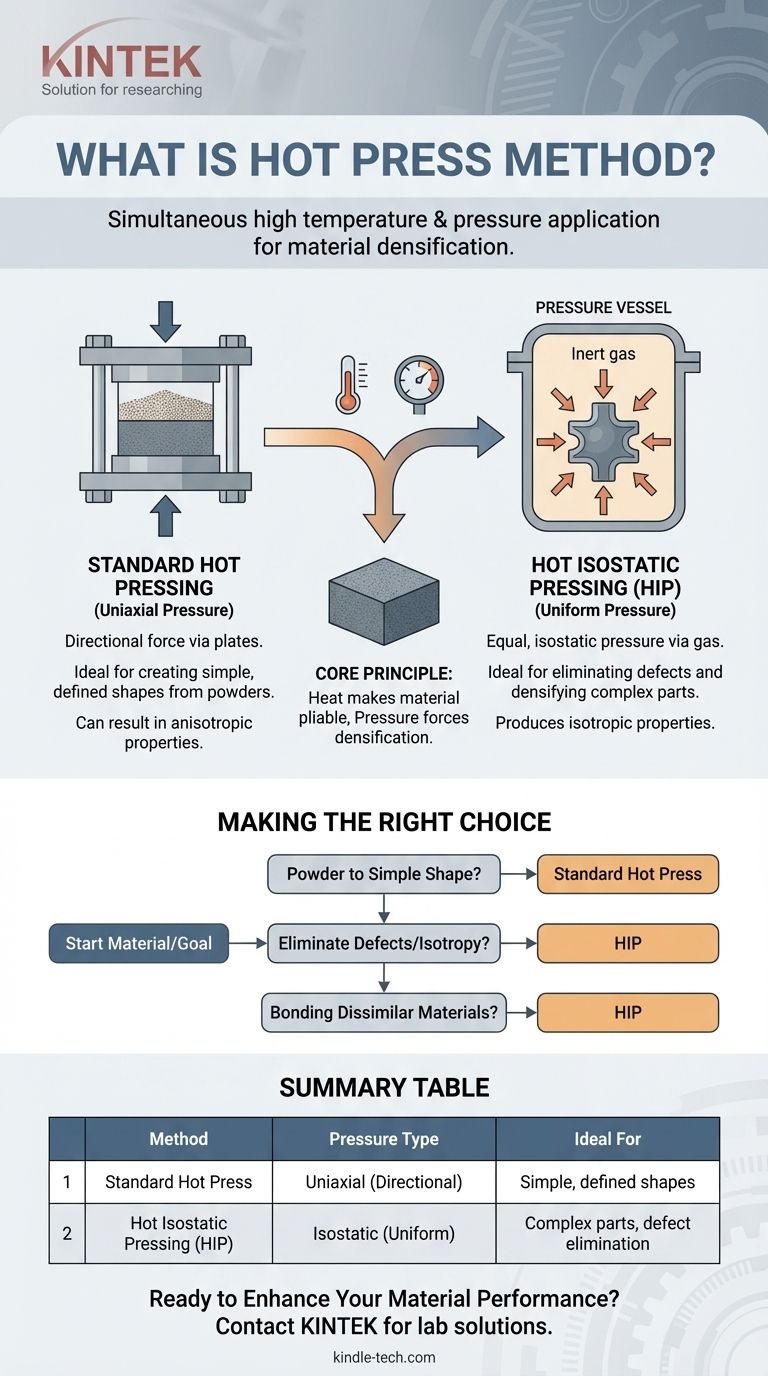
The core concept of hot pressing is using heat to make a material pliable and pressure to force it into a dense, solid state. The critical distinction lies in how that pressure is applied: directionally with plates in a standard hot press, or uniformly with gas in Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP).

How a Hot Press System Works
A hot press is not a single device but a system of integrated components designed for precise control over the manufacturing environment.
The Core Principle: Heat and Pressure
The fundamental goal is densification. Heating the material, typically a powder, lowers its yield strength and increases atomic diffusion. Applying immense pressure then forces the particles together, eliminating the empty spaces (voids) between them.
Applying Controlled Pressure
Modern hot presses typically use a hydraulic system to generate and apply force. This ensures the pressure is high, stable, and can be precisely controlled. The machine can be programmed to maintain a set pressure, automatically compensating for any minor fluctuations during the process.
Achieving Precise Temperatures
Temperature control is equally critical. Advanced systems use pulse heating technology and multi-stage controllers to manage the heating and cooling cycles with extreme accuracy. This prevents thermal shock and ensures the material achieves the desired properties without being damaged.
Differentiating the Methods: Hot Pressing vs. Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP)
While often discussed together, it's crucial to understand the difference between standard (uniaxial) hot pressing and Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP). The distinction is in the direction of the applied pressure.
Standard Hot Pressing: Uniaxial Pressure
This is the traditional method. The material is placed in a die, and pressure is applied from one or two directions by moving plates or rams. This is highly effective for consolidating powders into a specific, predefined shape like a disc or block.
Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP): Uniform Pressure
In the HIP process, parts are placed inside a sealed, high-pressure vessel. The vessel is filled with an inert gas (commonly Argon), which is then heated and pressurized. This applies an equal, isostatic pressure to the part from all directions simultaneously.
Key Applications and Use Cases
The choice between methods depends entirely on the desired outcome.
Consolidating Powders
Both methods are used to turn powders into solid parts. Standard hot pressing is a direct way to form a shape, while HIP is often used to further densify a part that has already been pre-formed.
Eliminating Internal Defects
Hot Isostatic Pressing is the premier technology for eliminating microscopic voids in castings. The uniform pressure collapses internal porosity (like microshrinkage) without changing the part's overall shape, dramatically improving its mechanical strength and fatigue life.
Diffusion Bonding and Cladding
HIP can also be used to bond or clad two or more different materials together. The high heat and pressure promote atomic diffusion across the boundary of the materials, creating a true metallurgical bond that is as strong as the parent materials.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, these methods come with specific considerations.
Uniaxial vs. Isostatic Properties
Because standard hot pressing applies force in one direction, it can sometimes result in anisotropic material properties, meaning the material is stronger in one direction than another. HIP, with its uniform pressure, produces isotropic properties, where the material is equally strong in all directions.
Shape and Geometry
Standard hot pressing is excellent for producing simpler geometries. HIP is ideal for densifying complex, near-net-shape parts that have already been cast or printed, as it does not rely on a die to define the final form.
Environmental Control
Many advanced materials, especially non-oxides and reactive metals, must be processed in a vacuum or inert environment. This prevents oxidation and other chemical reactions at high temperatures, which would compromise the final material properties.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct method is a critical engineering decision based on your starting material and final objective.
- If your primary focus is creating a solid part from powder into a simple, defined shape: Standard (uniaxial) hot pressing is the most direct and common method.
- If your primary focus is eliminating internal porosity from an existing casting or additively manufactured part: Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP) is the superior choice for its ability to heal internal defects.
- If your primary focus is achieving perfectly uniform material properties (isotropy): HIP is the definitive solution due to its uniform application of pressure.
- If your primary focus is bonding dissimilar materials without welding or brazing: HIP enables strong diffusion bonding at the atomic level.
Ultimately, understanding whether your application requires directional forming or uniform densification is the key to leveraging this technology effectively.
Summary Table:
| Method | Pressure Type | Key Application | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard Hot Press | Uniaxial (Directional) | Powder Consolidation | Creating simple, defined shapes from powders |
| Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP) | Isostatic (Uniform) | Eliminating Internal Defects | Densifying complex castings/3D printed parts for isotropic properties |
Ready to Enhance Your Material Performance?
Whether you are consolidating advanced powders or need to eliminate porosity in complex components, choosing the right hot press method is critical. KINTEK specializes in providing robust lab equipment and expert consumables for all your material science and manufacturing challenges.
Our solutions help you achieve superior densification, improved material strength, and precise control over your processes. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's specific needs and help you select the ideal equipment for your application.
Get in touch with our experts now!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press
- Warm Isostatic Press for Solid State Battery Research
- Warm Isostatic Press WIP Workstation 300Mpa for High Pressure Applications
- Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Vacuum Box Laboratory Hot Press
- Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Vacuum Box Laboratory Hot Press
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of using a vacuum hot press sintering furnace? Achieve 99.1% Density in CuW30 Composites
- Why is a vacuum essential for sintering metal-ceramic composites? Achieve Pure, High-Density Results
- What role does a high-temperature hot press play in the sintering of NITE-SiC? Optimize Your Densification Process
- What are the advantages of using a vacuum hot press for CuCr50? Achieve Superior Density & Purity in Alloy Production
- Why is precise temperature control necessary for SiC/Cu Vacuum Hot Pressing? Mastering the Cu9Si Interface Phase



















