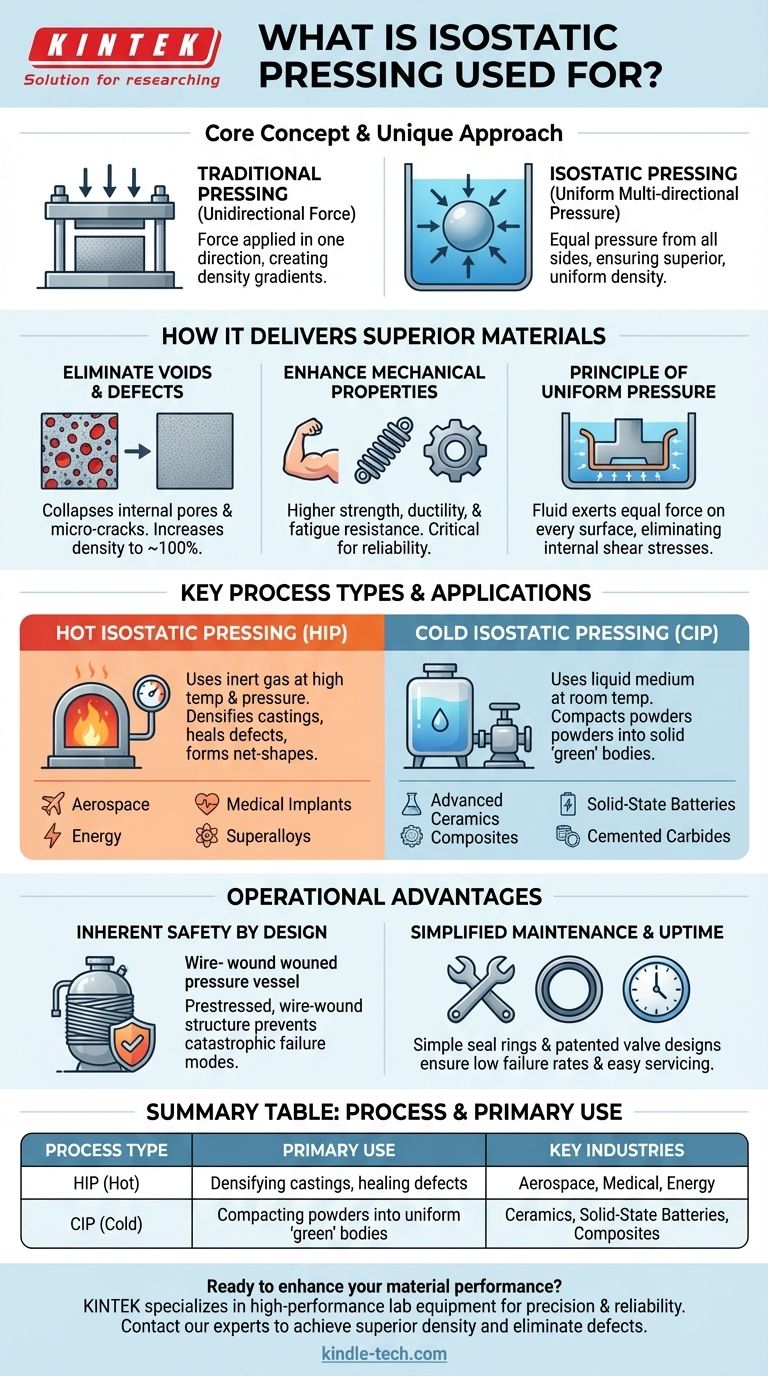
At its core, isostatic pressing is a materials processing technique that uses fluid pressure to compact powders or densify solid parts with extreme uniformity. It is essential for manufacturing high-performance components across industries, from eliminating critical voids in aerospace castings and forming superalloys to producing advanced ceramics and components for solid-state batteries.
Unlike traditional pressing which applies force in one direction, isostatic pressing applies equal pressure from all sides simultaneously. This unique approach is the key to creating materials with superior density, structural integrity, and consistent mechanical properties.

How Isostatic Pressing Delivers Superior Materials
Isostatic pressing is fundamentally about achieving a level of material quality that other methods cannot. Its benefits stem from the unique way it applies force.
The Principle of Uniform Pressure
The term "isostatic" means equal pressure in all directions. A component sealed in a flexible mold is submerged in a fluid (a gas for Hot Isostatic Pressing or a liquid for Cold Isostatic Pressing) inside a high-pressure vessel.
When the vessel is pressurized, the fluid exerts uniform force on every surface of the component. This eliminates the density gradients and internal shear stresses common in uniaxial pressing, where force is applied from only one or two directions.
Eliminating Voids and Defects
This all-sided pressure is highly effective at collapsing internal pores, micro-cracks, and other voids within a material. For parts made from metal powders or for solid metal castings, this process can increase the density to nearly 100% of the theoretical maximum.
By removing these internal defects, the material becomes far less prone to failure under stress.
Enhancing Mechanical Properties
The direct result of higher density and fewer defects is a dramatic improvement in mechanical performance. Materials that have been isostatically pressed exhibit higher strength, ductility, and fatigue resistance.
This consistency is critical for applications where component failure is not an option.
Key Applications and Process Types
The two primary methods, Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP) and Cold Isostatic Pressing (CIP), serve different but complementary purposes.
Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP) for Final Densification
HIP uses an inert gas (like argon) at extremely high temperatures and pressures. The combination of heat and pressure accelerates diffusion, allowing voids to close and metallurgical bonds to form.
It is widely used for densifying critical castings in aerospace, healing heat-damage in turbine blades, and achieving the final net-shape form of parts made from nickel-base superalloys, titanium, and high-speed tool steels.
Cold Isostatic Pressing (CIP) for Powder Compaction
CIP uses a liquid medium at room temperature to apply pressures between 100 and 630 MPa. Its primary use is to compact powders into a solid "green" body with high, uniform density before a final sintering or heating step.
This is a critical step in producing high-performance ceramics, cemented carbides, and even advanced materials like the solid electrolytes used in next-generation solid-state batteries.
Understanding the Operational Advantages
Beyond the material benefits, modern isostatic presses are engineered for reliability and safety in demanding industrial environments.
Inherent Safety by Design
Operating at extreme pressures requires robust safety measures. Many isostatic presses utilize a prestressed, wire-wound structure for the high-pressure vessel.
This design ensures that even if a few steel wires were to fracture, the failure mode is not catastrophic, significantly reducing the risk of a high-energy accident.
Simplified Maintenance and Uptime
High uptime is crucial in manufacturing. Isostatic presses are often designed so that the main wearing part is a simple seal ring, which is easily replaced.
Furthermore, patented valve designs that separate the valve body from the seat lead to a very low failure rate and straightforward maintenance, ensuring the equipment remains productive.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct process depends entirely on your material and final objective.
- If your primary focus is healing defects or creating fully dense, mission-critical metal parts: Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP) is the necessary process for achieving maximum material integrity and mechanical performance.
- If your primary focus is creating a highly uniform, compacted powder body for subsequent sintering: Cold Isostatic Pressing (CIP) is the ideal and cost-effective method for producing a superior "green" part.
- If your primary focus is producing advanced ceramics or composites with complex shapes: A combination of CIP to form the part followed by HIP to fully densify it is a common and effective workflow.
Ultimately, adopting isostatic pressing is a strategic decision to prioritize material reliability and peak performance.
Summary Table:
| Process Type | Primary Use | Key Industries |
|---|---|---|
| Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP) | Densifying castings, healing defects in metals | Aerospace, Medical, Energy |
| Cold Isostatic Pressing (CIP) | Compacting powders into uniform 'green' bodies | Ceramics, Solid-State Batteries, Composites |
Ready to enhance your material performance with isostatic pressing? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratories that demand precision and reliability. Whether you're developing advanced ceramics, next-generation batteries, or critical aerospace components, our expertise can help you achieve superior density and eliminate defects. Contact our experts today to discuss how our solutions can meet your specific laboratory needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Warm Isostatic Press WIP Workstation 300Mpa for High Pressure Applications
- Manual High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
- Double Plate Heating Press Mold for Lab
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Lab Pellet Press for Button Battery
- Laboratory Manual Hydraulic Pellet Press for Lab Use
People Also Ask
- What pressure is hot isostatic press? Achieve Full Density & Superior Material Performance
- How much energy does hot isostatic pressing consume? Unlock Net Energy Savings in Your Process
- What is HIP treatment for metal? Eliminate Internal Defects for Superior Part Performance
- What is the historical background of the Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP) process? From Nuclear Roots to Industry Standard
- What is HIP in material processing? Achieve Near-Perfect Density for Critical Components



















