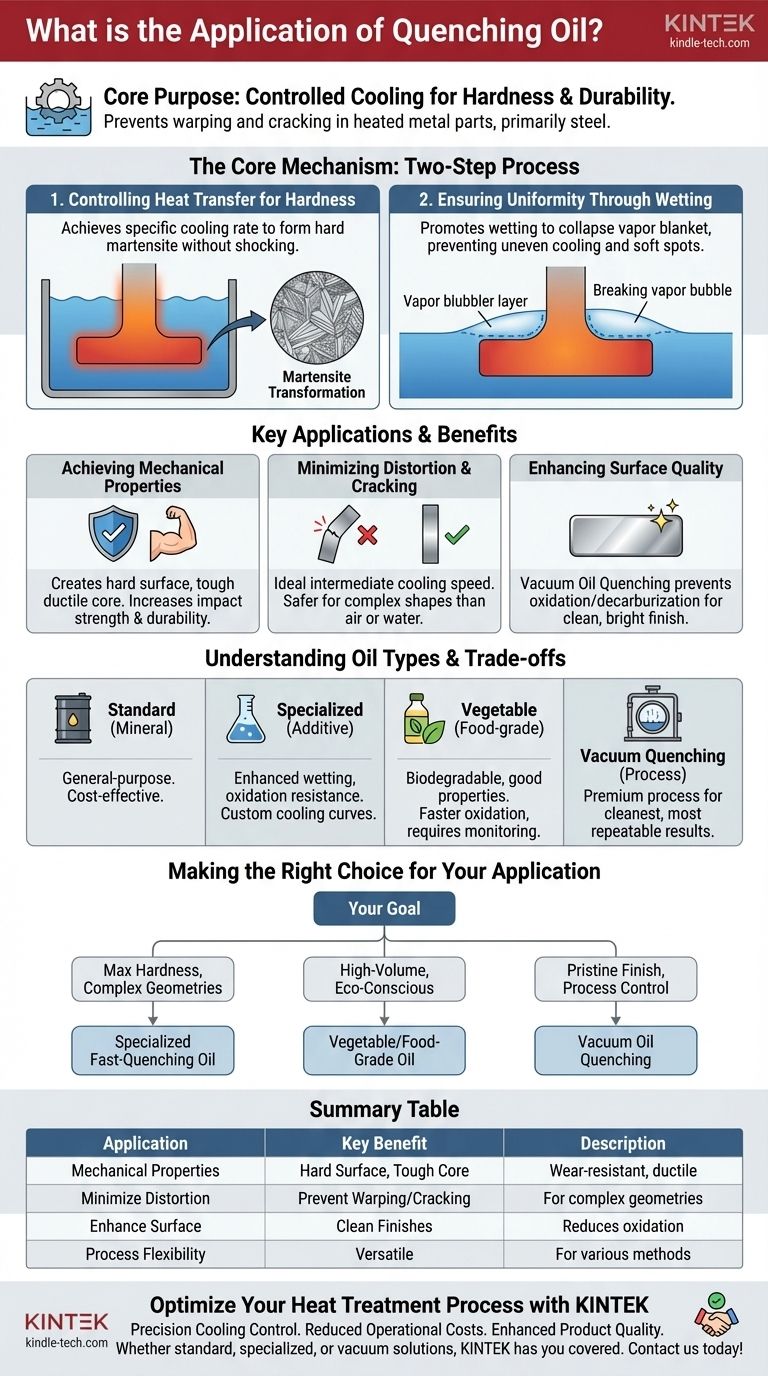
In essence, quenching oil is used to rapidly and controllably cool heated metal parts, primarily steel, in order to achieve specific levels of hardness and durability. Its primary functions are to manage the rate of heat transfer to create a hardened microstructure while simultaneously ensuring the entire component cools uniformly to prevent warping, distortion, and cracking.
The core purpose of quenching oil is not simply to cool metal, but to execute a controlled cooling process. The choice of oil is a critical engineering decision that balances the need for hardness against the risk of structural failure, directly impacting the final component's performance and reliability.

The Core Mechanism: How Quenching Oil Works
To understand the application of quenching oil, you must first understand the two physical processes it is designed to master. These processes happen in fractions of a second but determine the success or failure of the component.
Controlling Heat Transfer for Hardness
The fundamental goal of quenching is to cool a steel part fast enough to transform its internal structure into martensite, a very hard and strong crystalline form. If the cooling is too slow, softer, less desirable structures form, and the part will not meet its strength requirements.
Quenching oil is formulated to provide a specific cooling rate that is aggressive enough to achieve this martensitic transformation but not so violent that it shocks the material.
Ensuring Uniformity Through Wetting
When a hot part is submerged in oil, a layer of vapor called a vapor blanket instantly forms on its surface. This vapor is an insulator and the primary cause of uneven cooling and soft spots.
A well-formulated quenching oil is designed to promote good "wetting," which helps this vapor blanket collapse quickly and evenly across the entire surface. This ensures every part of the component cools at the same rate, preventing the buildup of internal stresses that lead to failure.
Key Applications and Benefits
The controlled cooling provided by quenching oil delivers several critical benefits that are essential in manufacturing and engineering.
Achieving Desired Mechanical Properties
The primary application is to create parts with a specific combination of properties. By controlling the cooling curve, quenching oil can produce a component with a very hard, wear-resistant surface while maintaining a tougher, more ductile core. This increases toughness, impact strength, and overall durability.
Minimizing Distortion and Cracking
Using air or water for quenching can be problematic. Air cools too slowly for many steels, while water often cools too quickly and non-uniformly, creating massive thermal stress that can warp or crack the component.
Quenching oil provides the ideal intermediate cooling speed, making it the safest and most reliable method for hardening parts with complex shapes, sharp corners, or varying thicknesses.
Enhancing Surface Quality
In certain applications, particularly vacuum oil quenching, the process yields an exceptionally clean part. By performing the quench in a vacuum, the oil prevents surface oxidation (scale) and decarburization (carbon loss from the surface).
This results in a bright, smooth surface finish that often requires no subsequent cleaning or machining, saving time and cost.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Oil Types
Not all quenching oils are the same. The choice depends on the material, the desired properties, and operational factors like cost and environmental impact.
Standard vs. Specialized Oils
Conventional quenching oils are typically mineral-based and serve a wide range of general-purpose applications. Specialized oils, however, contain additive packages that enhance wetting, increase oxidation resistance for longer oil life, and modify the cooling curve for specific alloys or challenging geometries.
The Case for Vegetable Oils
In some applications, food-grade or vegetable oils have emerged as a viable alternative. They are relatively inexpensive, biodegradable, and can provide excellent results, sometimes even increasing impact strength and toughness.
The main trade-off is their tendency to oxidize and degrade more quickly than mineral oils. This can be managed with antioxidants but requires diligent process monitoring to prevent viscosity changes that affect performance.
The Role of Vacuum Quenching
Vacuum oil quenching is a premium process, not a type of oil. It combines the controlled cooling of oil with the cleanliness of a vacuum furnace. While it involves higher equipment costs, it offers the highest level of quality, repeatability, and safety, delivering clean, distortion-free parts with no surface degradation.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
The optimal quenching method is dictated by your material, the component's geometry, and your ultimate performance goal.
- If your primary focus is maximum hardness with complex geometries: A specialized, fast-quenching oil is necessary to achieve the required cooling rate without causing stress fractures.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production with cost and environmental concerns: A well-maintained vegetable or food-grade oil can be a highly effective and responsible choice for many common steels.
- If your primary focus is pristine surface finish and ultimate process control: Vacuum oil quenching provides the cleanest, most repeatable results, eliminating the need for post-processing steps.
Ultimately, selecting the right quenching oil and process is a strategic decision that defines the final integrity and performance of the heat-treated component.
Summary Table:
| Application | Key Benefit |
|---|---|
| Achieve Mechanical Properties | Creates hard, wear-resistant surfaces with tough, ductile cores |
| Minimize Distortion | Prevents warping and cracking in complex part geometries |
| Enhance Surface Quality | Reduces oxidation and decarburization for clean finishes |
| Process Flexibility | Suitable for standard, specialized, and vacuum quenching processes |
Optimize Your Heat Treatment Process with KINTEK
Choosing the right quenching oil is critical for achieving the perfect balance of hardness, durability, and dimensional stability in your metal components. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, including high-performance quenching oils tailored to your specific material and geometry requirements.
Our expertise ensures you get:
- Precision Cooling Control: Achieve consistent martensitic transformation without stress fractures.
- Reduced Operational Costs: Minimize part rejection and post-processing with uniform quenching.
- Enhanced Product Quality: Deliver reliable, high-performance components every time.
Whether you need standard mineral oils, specialized additive-enhanced oils, or solutions for vacuum quenching, KINTEK has you covered.
Contact us today to discuss your application and discover how our quenching solutions can improve your results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
- High-Purity Titanium Foil and Sheet for Industrial Applications
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
- Manual Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press
People Also Ask
- Does graphite have a melting point? Unlocking the Extreme Heat Resistance of Graphite
- Why graphite is used in furnace? Achieve Superior Heat Treatment & Energy Efficiency
- What is the temperature of a graphite furnace? Achieve Extreme Heat Up to 3000°C
- What are the applications of graphite material? Leveraging Extreme Heat and Precision for Industrial Processes
- Why is graphite used in furnaces? For Extreme Heat, Purity, and Efficiency
















