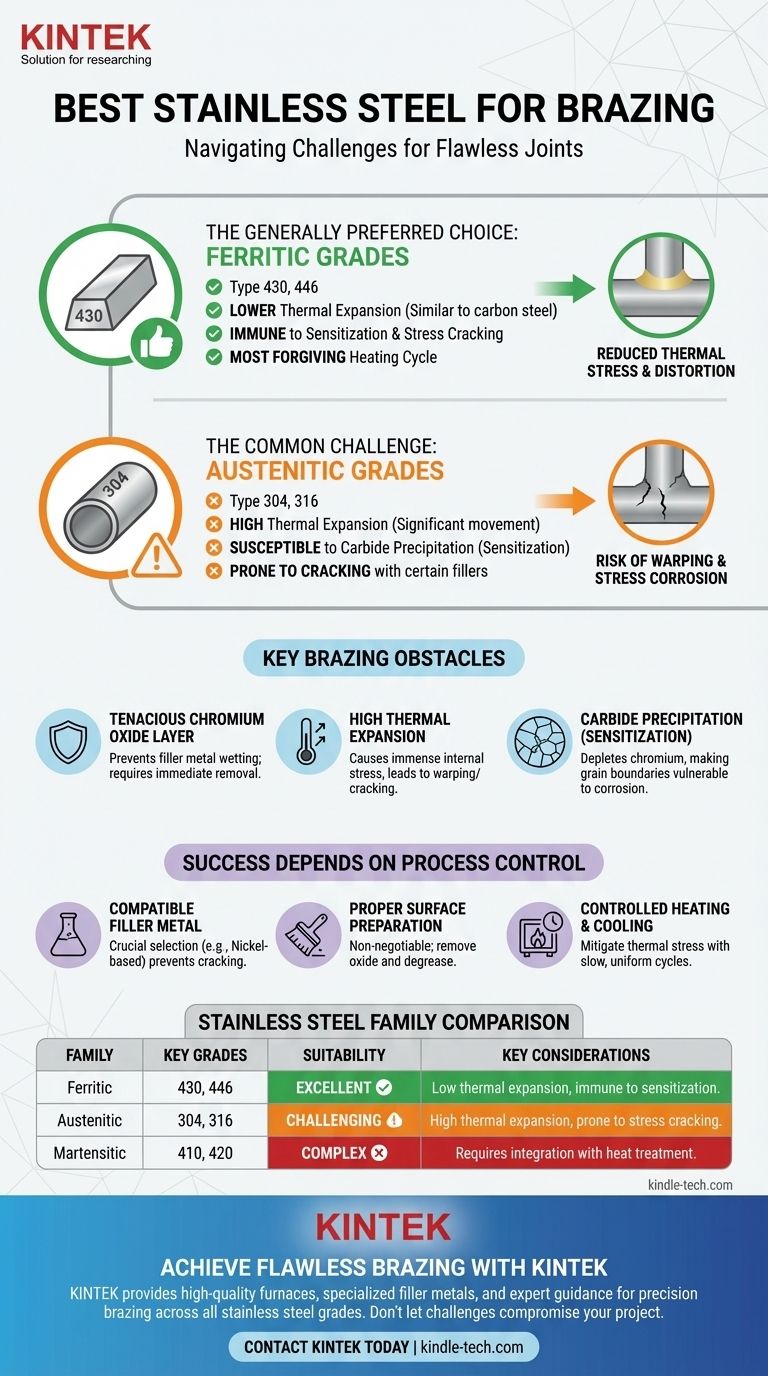
The best stainless steel for brazing is typically a ferritic grade, such as type 430. These grades are less susceptible to the heat-related issues, like stress corrosion cracking and sensitization, that commonly affect the more popular austenitic grades (like 304 or 316). However, the "best" material is always contingent on the specific application, filler metal, and brazing process used.
The core challenge in brazing stainless steel isn't just the material itself, but managing the interaction between heat, the steel's protective oxide layer, and its thermal expansion properties. Success lies in choosing a steel grade and a process that minimize internal stresses and ensure proper filler metal adhesion.

Why Stainless Steel Presents Brazing Challenges
To make an informed choice, you must first understand the inherent properties of stainless steel that complicate the brazing process.
The Tenacious Chromium Oxide Layer
All stainless steels are "stainless" because they form a thin, invisible, and highly durable layer of chromium oxide on their surface.
This passive layer is excellent for corrosion resistance but prevents brazing filler metals from "wetting" and bonding with the base metal. It must be chemically or mechanically removed immediately before brazing.
High Thermal Expansion
Many common stainless steels, particularly the austenitic (300 series) grades, expand and contract significantly when heated and cooled.
This movement can introduce immense internal stress into the assembly and the braze joint itself, leading to warping or cracking, especially during the cooling cycle.
Risk of Carbide Precipitation (Sensitization)
When austenitic stainless steels are held at high temperatures (approx. 800–1500°F or 425–815°C), carbon can combine with chromium to form chromium carbides along the grain boundaries.
This process, known as sensitization, depletes chromium from the surrounding metal, making it highly susceptible to intergranular corrosion and stress cracking.
Comparing Stainless Steel Families for Brazing
The challenges of brazing manifest differently across the main families of stainless steel.
Austenitic Stainless Steels (e.g., 304, 316)
These are the most common but also the most problematic grades for brazing. Their high coefficient of thermal expansion makes them prone to distortion and stress cracking.
They are also susceptible to sensitization. The reference material specifically notes their vulnerability to cracking when brazed with certain filler metals, such as copper-zinc alloys, due to intergranular penetration.
Ferritic Stainless Steels (e.g., 430, 446)
Ferritic grades are often the preferred choice for brazing. Their coefficient of thermal expansion is lower and more similar to carbon steel, significantly reducing the risk of thermal stress.
Crucially, they are not susceptible to the sensitization that plagues austenitic grades, making them much more forgiving during the heating cycle.
Martensitic Stainless Steels (e.g., 410, 420)
These grades are prized for their hardness, which is achieved through heat treatment. Brazing can be performed, but the high temperatures will alter the metal's heat-treated condition.
Brazing martensitic steels often requires careful planning to integrate the process with hardening and tempering cycles, adding significant complexity.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Process Over Material
A successful joint often depends more on controlling the process than on selecting a perfect material.
Filler Metal Selection is Crucial
The choice of filler metal must be compatible with the base metal. As noted, copper-zinc fillers can induce cracking in stressed austenitic steels.
For high-performance applications, nickel-based filler metals are often used for their excellent strength and corrosion resistance when joining stainless steels. Silver-based alloys are also common for their lower brazing temperatures.
The Importance of Proper Cleaning
The references are clear: surface preparation is non-negotiable. The chromium oxide layer must be removed, typically through sandblasting or chemical etching.
Following this, the part must be thoroughly degreased using solvents like acetone. Any contaminants will prevent the filler metal from bonding correctly, resulting in a failed joint.
Controlling the Heating and Cooling Cycle
To mitigate the stress from thermal expansion, heating and cooling rates must be carefully controlled. A slower, more uniform cooling cycle is especially critical for preventing cracks in austenitic grades.
Furnace and vacuum brazing offer excellent control over this thermal cycle, which is why they are often preferred for critical stainless steel assemblies.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
There is no single "best" steel, only the right steel for your specific goal.
- If your primary focus is simplicity and reliability: Choose a ferritic stainless steel like type 430. Its lower thermal expansion and immunity to sensitization make it the most straightforward and forgiving option.
- If you must use a common, corrosion-resistant grade: You can successfully braze austenitic steels like 304 or 316, but you must use a compatible nickel or silver filler and control your heating and cooling rates meticulously to prevent stress cracking.
- If your primary focus is high hardness and strength: Select a martensitic steel, but be prepared to develop a process that integrates the brazing operation with the required post-braze heat treatments to restore its mechanical properties.
Ultimately, a successful braze depends less on finding a perfect material and more on mastering the process for the material you choose.
Summary Table:
| Stainless Steel Family | Key Grades | Brazing Suitability | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ferritic | 430, 446 | Excellent | Low thermal expansion, immune to sensitization, most forgiving |
| Austenitic | 304, 316 | Challenging | High thermal expansion, prone to stress cracking and sensitization |
| Martensitic | 410, 420 | Complex | Requires integration with heat treatment cycles |
Achieve Flawless Brazing Results with KINTEK
Brazing stainless steel requires precision, expertise, and the right equipment. Whether you're working with ferritic, austenitic, or martensitic grades, KINTEK has the solutions to ensure your brazing process is a success.
We provide:
- High-quality brazing furnaces for precise temperature control
- Specialized filler metals compatible with all stainless steel families
- Expert guidance on process optimization to prevent stress cracking and distortion
Our lab equipment and consumables are trusted by professionals who demand reliability and performance.
Don't let brazing challenges compromise your project. Contact KINTEK today to discuss your specific needs and discover how we can help you achieve perfect, durable joints every time.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Warm Isostatic Press for Solid State Battery Research
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for PTFE Mesh F4 Sieve
- Stainless Steel Quick Release Vacuum Chain Three-Section Clamp
- Precision Machined Silicon Nitride (SiN) Ceramic Sheet for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Infrared Heating Quantitative Flat Plate Press Mold
People Also Ask
- What is the purpose of hot isostatic pressing? Achieve Superior Material Density and Performance
- What does HIP process do? Eliminate Porosity for Superior Material Performance
- What is the temperature of hot isostatic pressing? Achieve Full Density for Critical Components
- What is the temperature of a warm isostatic press? Achieve Optimal Densification for Your Materials
- How does Hot Isostatic Pressing reduce porosity? Eliminate Internal Voids for Superior Material Density



















