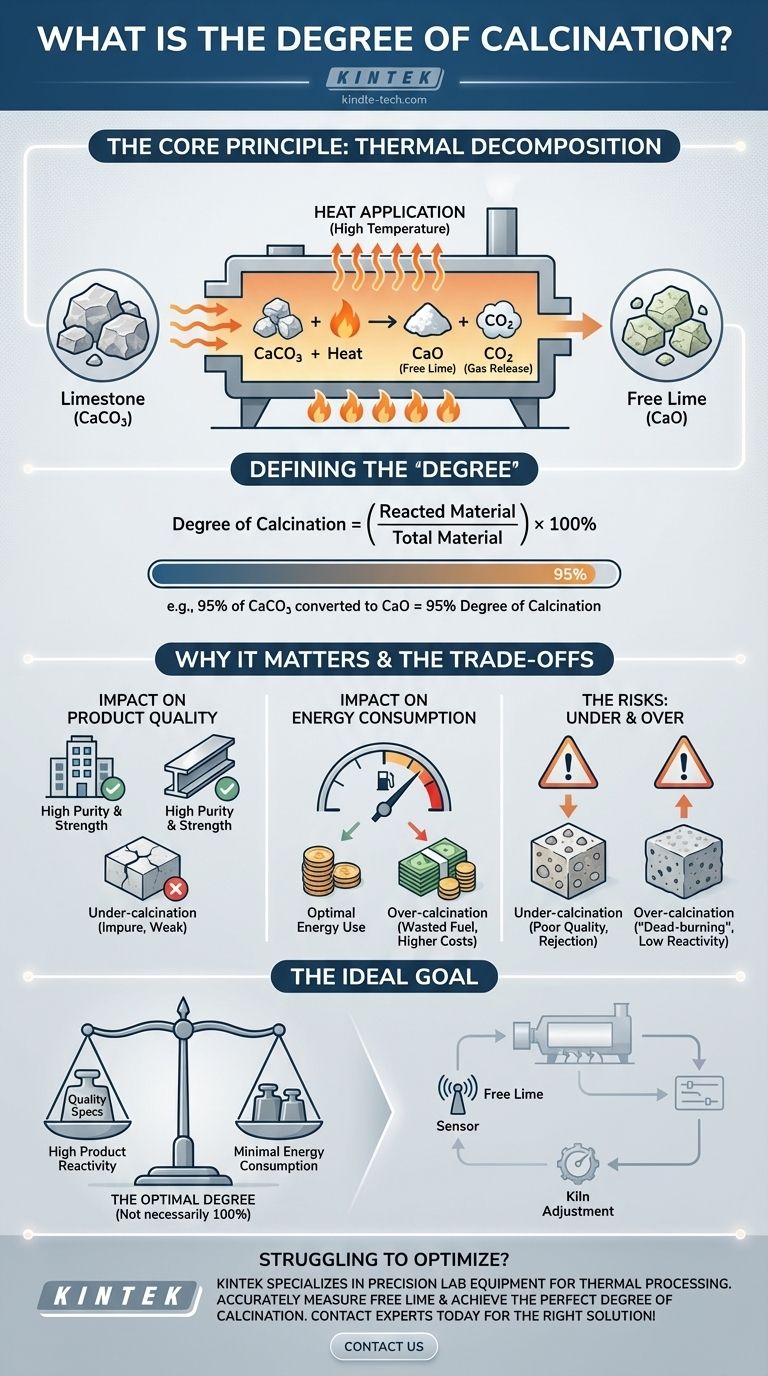
In industrial thermal processing, the degree of calcination is a critical metric that measures how completely a material has undergone thermal decomposition. For example, in lime production, it quantifies what percentage of the initial limestone (calcium carbonate, CaCO₃) has successfully converted into free lime (calcium oxide, CaO) by releasing carbon dioxide (CO₂). A 100% degree of calcination means the conversion is complete.
The degree of calcination is not just a theoretical value; it is a key performance indicator (KPI) that directly impacts product quality, energy efficiency, and operational costs. Achieving the optimal degree—not necessarily 100%—is the primary goal in processes like lime and cement manufacturing.
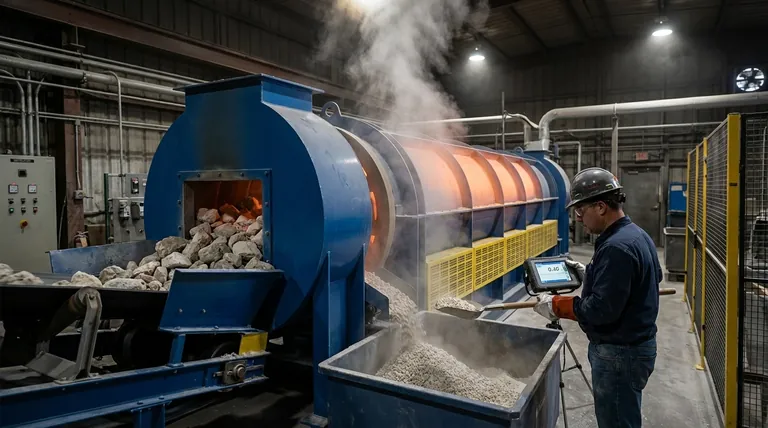

The Core Principle: Thermal Decomposition
What is Calcination?
Calcination is a heat treatment process applied to solid materials. The goal is to heat the material to a high temperature, but below its melting point, to induce a chemical change.
This process is typically used to remove a volatile component, such as carbon dioxide or water. It is a fundamental step in producing materials like cement, lime, and certain metal oxides.
The Defining Chemical Reaction
The classic example of calcination is heating limestone to produce lime. The chemical reaction is straightforward.
Calcium carbonate (CaCO₃) breaks down into calcium oxide (CaO), known as free lime, and releases carbon dioxide (CO₂) gas. This reaction is the foundation for measuring the process's completion.
Defining the "Degree"
The degree of calcination is the ratio of the material that has successfully reacted compared to the total amount of material that could have reacted.
It is often expressed as a percentage. For instance, if 95% of the CaCO₃ in a sample has been converted to CaO, the degree of calcination is 95%.
Why Degree of Calcination Matters in Practice
Impact on Product Quality
An insufficient degree of calcination, or under-calcination, means the final product is impure. Unreacted raw material (CaCO₃) remains mixed with the desired product (CaO).
In cement, this leads to lower strength. In steelmaking, impure lime is a less effective flux for removing impurities.
Impact on Energy Consumption
Heating materials to the high temperatures required for calcination is energy-intensive. Pushing for an unnecessarily high degree of calcination means running kilns hotter or longer than needed.
This directly translates to wasted fuel and higher operational costs. The goal is to find the precise point where quality is met without wasting energy.
The Concept of "Free Lime"
In a plant or lab, the degree of calcination is not usually measured directly. Instead, technicians measure the concentration of free lime (CaO) in the final product.
A higher percentage of free lime indicates a higher degree of calcination. This measurement serves as the primary control parameter for the entire process.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The Risk of Under-Calcination
The most obvious risk is poor product quality. If the calcination is incomplete, the material will not perform its intended function effectively.
This can lead to batch rejection, customer complaints, and damage to the producer's reputation. The material simply doesn't meet the required chemical specification.
The Problem with Over-Calcination
Pushing the process too far by using excessive heat or time can cause a phenomenon known as "dead-burning" or sintering.
The resulting lime (CaO) particles become dense and non-porous. This drastically reduces the material's chemical reactivity, making it less effective even though it is chemically pure. It also represents significant wasted energy.
The "True Calcination" Ideal
The "Degree of True Calcination" refers to the ideal state of 100% conversion. While this is the theoretical goal, practical industrial operations often target a slightly lower, optimal degree.
This optimal point provides the best balance between high product quality, good reactivity, and minimal energy consumption.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Achieving the right degree of calcination is a balancing act tailored to your specific process and product requirements.
- If your primary focus is maximum product reactivity: Aim for a high degree of calcination but carefully control temperature to avoid the "dead-burning" that reduces porosity and performance.
- If your primary focus is energy efficiency: Optimize your heating profiles and kiln residence time to achieve the minimum acceptable degree of calcination for your quality specifications, preventing fuel waste.
- If your primary focus is process control: Implement regular testing for free lime (CaO) content to get a reliable, near-real-time indicator of your degree of calcination, allowing for quick adjustments.
Ultimately, mastering the degree of calcination is about precise control—balancing chemical conversion against energy costs and final product performance.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Impact of Degree of Calcination |
|---|---|
| Product Quality | Higher degree = purer product (more CaO). Under-calcination leads to impurities and lower performance. |
| Energy Efficiency | Excessively high degree = wasted fuel. Optimal degree balances quality with minimal energy use. |
| Process Control | Measured indirectly via % of Free Lime (CaO). Key KPI for real-time adjustments. |
| Risks | Under-calcination: Poor quality. Over-calcination (Dead-burning): Low reactivity and wasted energy. |
Struggling to optimize your calcination process for quality and efficiency? KINTEK specializes in precision lab equipment and consumables for thermal processing. Our furnaces and analytical tools help you accurately measure free lime and achieve the perfect degree of calcination for your lime, cement, or metal oxide production. Enhance your product quality and reduce energy costs—contact our experts today to find the right solution for your laboratory needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Three-dimensional electromagnetic sieving instrument
- Laboratory Disc Rotary Mixer for Efficient Sample Mixing and Homogenization
People Also Ask
- What equipment is used in pyrolysis? Choosing the Right Reactor for Your Feedstock and Products
- What are the industrial applications of pyrolysis? Transform Waste into Energy and Valuable Products
- What is the purpose of a calciner? Boost Efficiency in High-Temperature Processing
- What are the types of pyrolysis reactors used in industry? Choose the Right Technology for Your Product
- What is the difference between calcining and roasting? A Guide to High-Temperature Processing



















