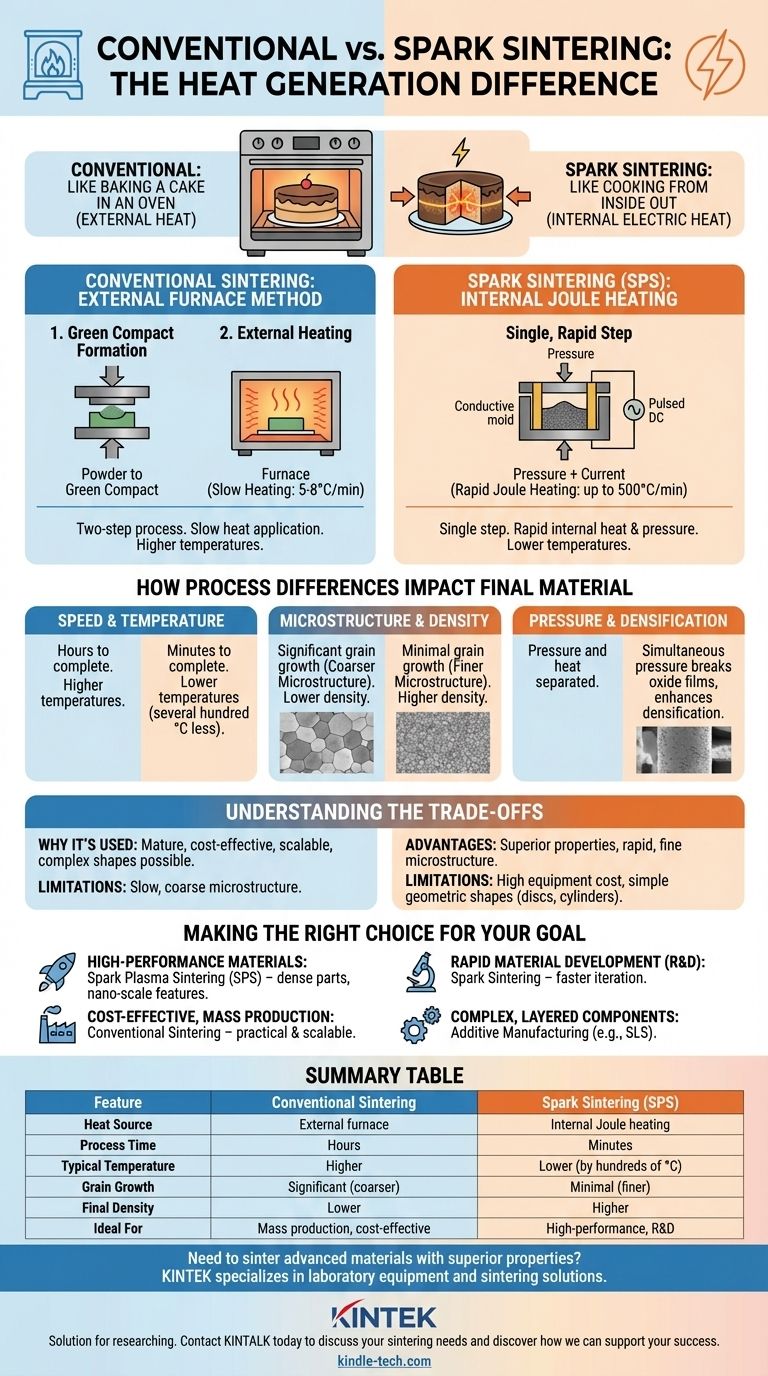
At its core, the difference between conventional and spark sintering lies in how heat is generated and applied. Conventional sintering is a two-step process that heats a pre-compacted part externally in a furnace. In contrast, spark sintering—most notably Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS)—is a single, rapid step where a high-power electric current passes directly through the powdered material and its mold, generating intense internal heat while simultaneously applying pressure.
The fundamental distinction is simple: conventional sintering is like baking a cake in an oven, while spark sintering is like cooking it from the inside out with electricity in a matter of minutes. This internal heating mechanism is what allows spark sintering to be dramatically faster, operate at lower temperatures, and produce denser materials with superior microstructures.
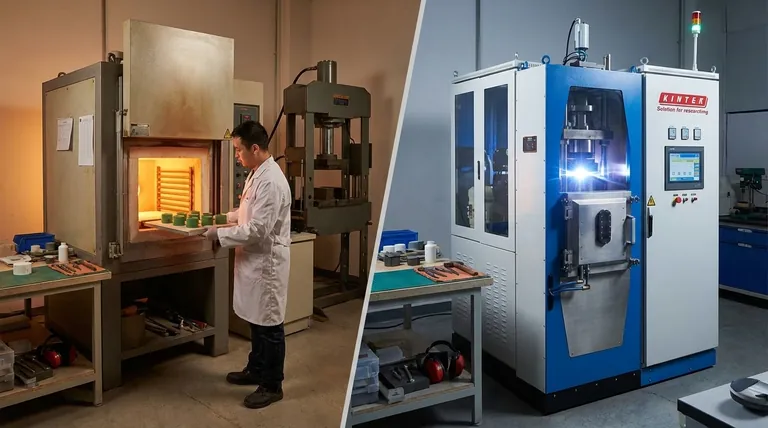

The Fundamental Difference: Heat Generation and Application
The method used to deliver thermal energy is the primary driver behind all the other differences between these two processes, from speed and efficiency to the final properties of the material.
Conventional Sintering: The External Furnace Method
Conventional sintering is a well-established, two-stage process. First, powder is compacted into a desired shape using a hydraulic press, creating a fragile part known as a "green compact."
This green compact is then placed into a high-temperature furnace. Heat is applied externally, slowly soaking into the part to bond the powder particles together. Heating rates are typically very slow, around 5 to 8°C per minute.
Spark Sintering: Internal Joule Heating
Spark sintering is a more advanced technique that combines steps. The powder is loaded directly into a conductive graphite mold, which is then placed into the SPS chamber.
Pressure is applied, and a pulsed DC electric current is passed through the entire assembly. This current generates immediate and uniform heat internally via Joule heating. This allows for extremely rapid heating rates, often up to 500°C per minute. The punches that apply pressure also serve as the electrodes delivering the current.
How Process Differences Impact the Final Material
The radical difference in heating mechanism directly translates to significant differences in processing time, required temperature, and the ultimate quality of the sintered part.
Speed and Temperature
The slow, external heating of conventional sintering means cycles can take many hours to complete. Higher temperatures are required to ensure the heat fully penetrates the part and achieves densification.
Spark sintering, by contrast, is incredibly fast, often completing a full cycle in minutes. Because the heat is generated internally and pressure is applied concurrently, densification occurs at much lower overall temperatures—often several hundred degrees Celsius lower than conventional methods.
Microstructure and Density
In materials science, smaller grain sizes often lead to better mechanical properties. The long exposure to high heat in conventional sintering can cause grain growth, resulting in a coarser microstructure.
The speed of spark sintering is its greatest advantage here. By holding the material at high temperature for a very short time, it prevents significant grain growth. This results in a final product that is more homogenous, has a much finer microstructure, and achieves higher density.
Pressure and Densification
In conventional sintering, pressure and heat are separated. In spark sintering, they are applied simultaneously.
This concurrent pressure helps break down any oxide films on the powder particle surfaces. Combined with the electric current, this "cleans" the particles, creating better contact points and dramatically enhancing the rate of densification.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While spark sintering offers significant performance advantages, it is not a universal replacement for conventional methods. Each has its place.
Why Conventional Sintering Is Still Used
Conventional sintering is a mature, cost-effective technology. The equipment is less specialized, and the process is often more easily scaled for the mass production of parts, especially those with more complex geometries that cannot be easily placed in a simple graphite die.
The Limitations of Spark Sintering
The primary limitations of spark sintering are equipment cost and geometric constraints. SPS machines are highly specialized and expensive. Furthermore, the process is typically limited to simple shapes like discs and cylinders that can be pressed in a conductive graphite mold.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the appropriate sintering method requires a clear understanding of your end goal, balancing material performance requirements against production constraints.
- If your primary focus is high-performance materials with fine microstructures: Spark plasma sintering is the superior choice for its ability to produce highly dense parts while preserving nano-scale features.
- If your primary focus is rapid material development and research: Spark sintering's incredible speed allows for faster iteration, making it an ideal tool for R&D and material discovery.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective, large-scale production of standard parts: Conventional sintering remains the more practical and scalable solution for many industrial applications.
- If your primary focus is creating complex, layered components: Neither method is ideal; you should investigate additive manufacturing techniques like Selective Laser Sintering (SLS).
Ultimately, your choice is a strategic decision between the speed and material superiority of spark sintering and the scalability and economy of conventional methods.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Conventional Sintering | Spark Sintering (SPS) |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Source | External furnace | Internal Joule heating (electric current) |
| Process Time | Hours | Minutes |
| Typical Temperature | Higher | Lower (by hundreds of °C) |
| Grain Growth | Significant (coarser microstructure) | Minimal (finer microstructure) |
| Final Density | Lower | Higher |
| Ideal For | Cost-effective mass production | High-performance materials & R&D |
Need to sinter advanced materials with superior properties?
Choosing the right sintering method is critical to achieving the density, microstructure, and performance you require for your research or production. KINTEK specializes in advanced laboratory equipment, including sintering solutions, to meet your specific material science challenges.
Our experts can help you select the ideal process and equipment to enhance your lab's capabilities. Contact KINTALK today to discuss your sintering needs and discover how we can support your success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Spark Plasma Sintering Furnace SPS Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Heated Vacuum Press Machine Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
People Also Ask
- Why is precise temperature control required in vacuum hot pressing? Master Amorphous Powder Consolidation
- How does vacuum hot press sintering compare to traditional cold isostatic pressing? Achieve Ultra-Fine Mo-La2O3 Grains
- What is the step-by-step process for growing a diamond using the HPHT method? Master Lab-Grown Diamond Synthesis
- What is the difference between sintering and pressing? A Guide to Powder Metallurgy Processes
- What is SPS sintering method? A Guide to High-Speed, High-Performance Material Fabrication
- How does a vacuum hot-press furnace improve the texture of Ca3Co4O9? Master C-Axis Alignment & Density
- How does a vacuum hot press furnace address structural defects in as-cast CoCrPtB alloy ingots? Optimize Your Density
- How does the vacuum environment in a hot press furnace affect carbide sintering? Achieve 98%+ Relative Density



















