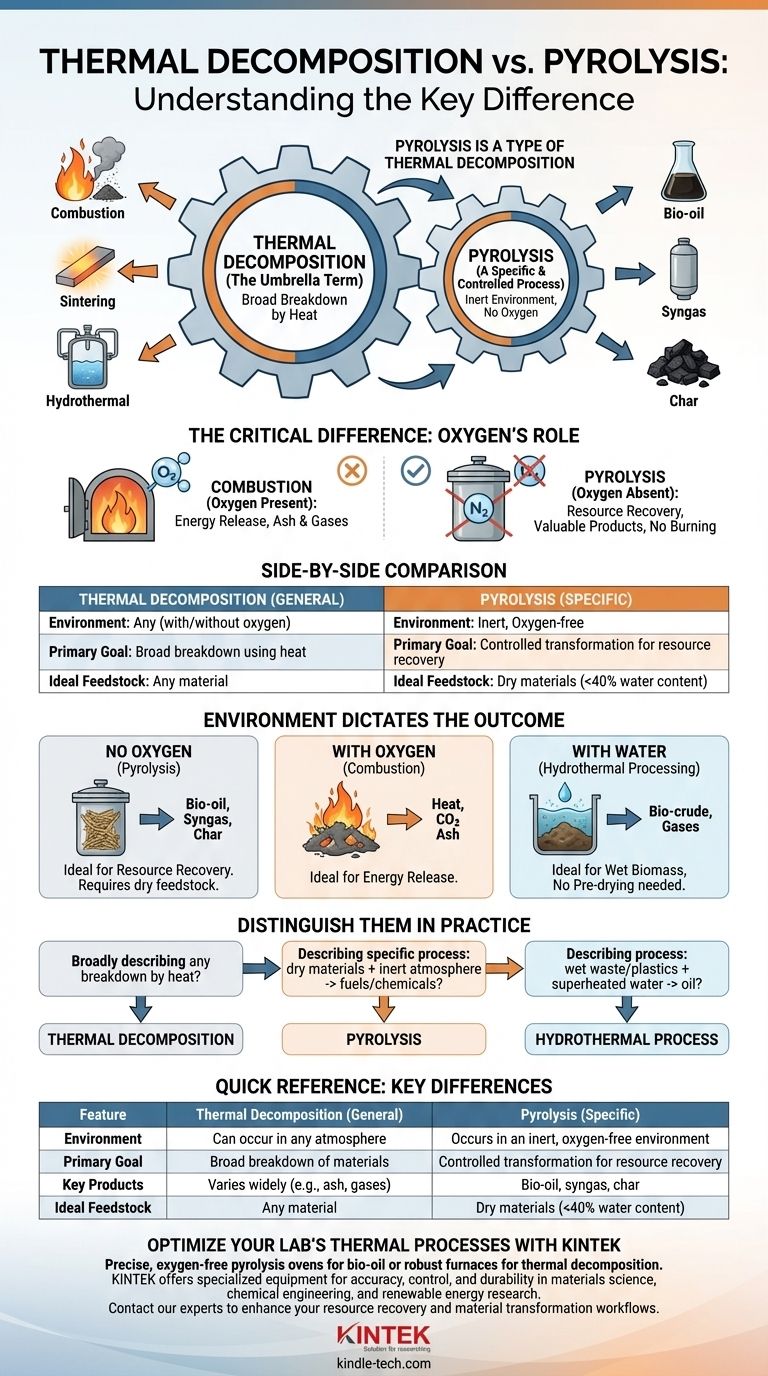
Think of it this way: Thermal decomposition is the general category for any process that breaks down a material using heat. Pyrolysis is a specific, highly controlled type of thermal decomposition that is defined by one critical condition: it happens in the near-total absence of oxygen.
The core difference isn't about the use of heat, but about the environment in which the heat is applied. Thermal decomposition is the overarching principle, while pyrolysis is a specific application of that principle without oxygen to prevent burning.
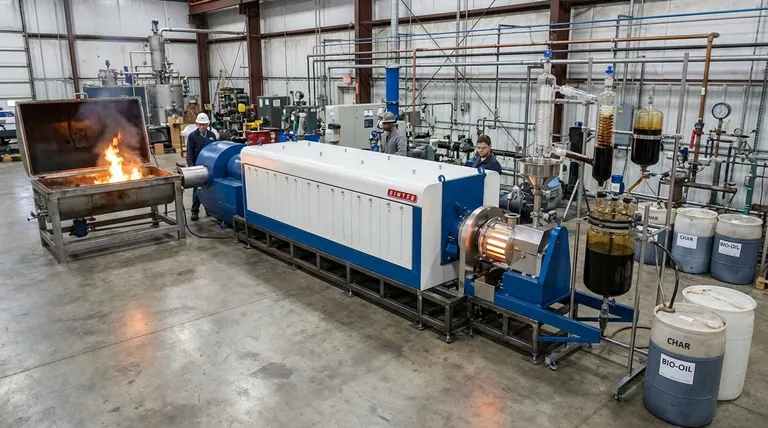

Thermal Decomposition: The Umbrella Term
What It Means
Thermal decomposition is a broad chemical process where a compound breaks down into simpler substances when heated.
This is the parent category. Any chemical reaction where heat is the primary driver for breaking chemical bonds falls under this umbrella.
Where You See It
The process can occur in any environment: with abundant oxygen, with limited oxygen, with no oxygen, or even in a medium like high-pressure water.
For example, burning a log in a campfire is a form of thermal decomposition called combustion, which occurs in the presence of oxygen. Sintering metals is another thermal process, though its goal is densification rather than breakdown.
Pyrolysis: A Specific and Controlled Process
The Defining Condition: No Oxygen
Pyrolysis is thermal decomposition that occurs in an inert or oxygen-free environment.
By removing oxygen, you prevent the material from burning (combusting). Instead of turning into ash and smoke, the material breaks down into new, often more valuable molecules.
The Purpose and Products
The goal of pyrolysis is not just to break something down, but to transform it.
This controlled decomposition can convert waste materials or biomass into valuable outputs like bio-oil, syngas, and a solid residue called char. It enhances the value of the original material by creating products with superior characteristics.
The Critical Role of the Reaction Environment
The specific outcome of a thermal process is dictated entirely by the environment. This is the most important concept to grasp when comparing different methods.
In the Absence of Oxygen (Pyrolysis)
This environment is ideal for resource recovery. It requires the feedstock to be relatively dry (often less than 40% water content) because excess moisture consumes significant energy to vaporize, reducing process efficiency.
In the Presence of Oxygen (Combustion)
This environment is for energy release. With sufficient oxygen, materials burn, releasing their stored chemical energy as heat. The end products are typically simple gases (like CO2) and ash.
In the Presence of Water (Hydrothermal Processing)
This is yet another type of thermal decomposition. Processes like Hydrothermal Liquefaction (HTL) use high-pressure, high-temperature water to break down materials.
This method has a key advantage over pyrolysis: it works exceptionally well with wet biomass and plastics, eliminating the need for energy-intensive pre-drying.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a thermal process depends entirely on the starting material and the desired outcome. There is no single "best" method.
Feedstock Requirements
Pyrolysis is inefficient for wet materials. The energy needed to evaporate the water can make the process economically unviable, which is why pre-treatment and drying are often necessary.
In contrast, hydrothermal processes are explicitly designed for wet feedstocks, making them ideal for things like algae, food waste, or sludge.
Process Control and Outputs
Pyrolysis is a highly engineered process designed to yield specific, valuable chemical products. The temperature, pressure, and duration are all tightly controlled.
Other forms of thermal decomposition may be less controlled. For example, simple combustion in a furnace is primarily controlled to maximize heat output, not to create new chemical feedstocks.
How to Distinguish Them in Practice
Use this simple guide to apply the terms correctly.
- If you are broadly describing any breakdown caused by heat: The correct term is thermal decomposition.
- If you are describing a specific industrial process to create fuels or chemicals from dry materials in an inert atmosphere: You are talking about pyrolysis.
- If you are describing a process to convert wet waste or plastics into oil using superheated water: You are likely referring to a hydrothermal process.
Ultimately, all pyrolysis is thermal decomposition, but not all thermal decomposition is pyrolysis.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Thermal Decomposition (General) | Pyrolysis (Specific) |
|---|---|---|
| Environment | Can occur in any atmosphere (with/without oxygen) | Occurs in an inert, oxygen-free environment |
| Primary Goal | Broad breakdown of materials using heat | Controlled transformation for resource recovery |
| Key Products | Varies widely (e.g., ash, gases from combustion) | Bio-oil, syngas, char |
| Ideal Feedstock | Any material | Dry materials (<40% water content) |
Optimize Your Lab's Thermal Processes with KINTEK
Understanding the nuances of thermal decomposition and pyrolysis is crucial for selecting the right equipment for your research or industrial application. Whether you need precise, oxygen-free pyrolysis ovens for converting biomass into valuable bio-oil or robust furnaces for other thermal decomposition processes, KINTEK has the solution.
Our specialized lab equipment is designed for accuracy, control, and durability, ensuring you achieve consistent and reliable results. We serve laboratories focused on materials science, chemical engineering, and renewable energy research.
Let us help you enhance your resource recovery and material transformation workflows. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific needs and discover how KINTEK's solutions can drive your success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of pyrolysis technology? Turn Waste into Profit and Reduce Emissions
- How is energy converted into biomass? Harnessing Nature's Solar Power for Renewable Energy
- What are the components of biomass pyrolysis? A Complete Guide to the System, Products, and Process
- What is the process of biomass fast pyrolysis? Turn Biomass into Bio-Oil in Seconds
- What are the different types of pyrolysis machines? Choose the Right System for Your Output



















