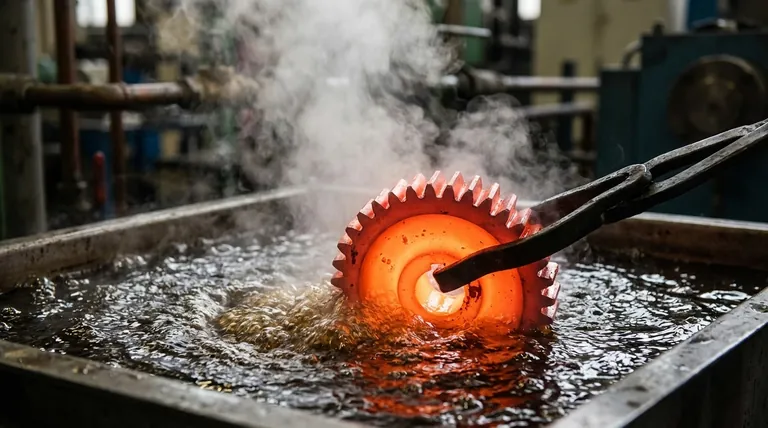
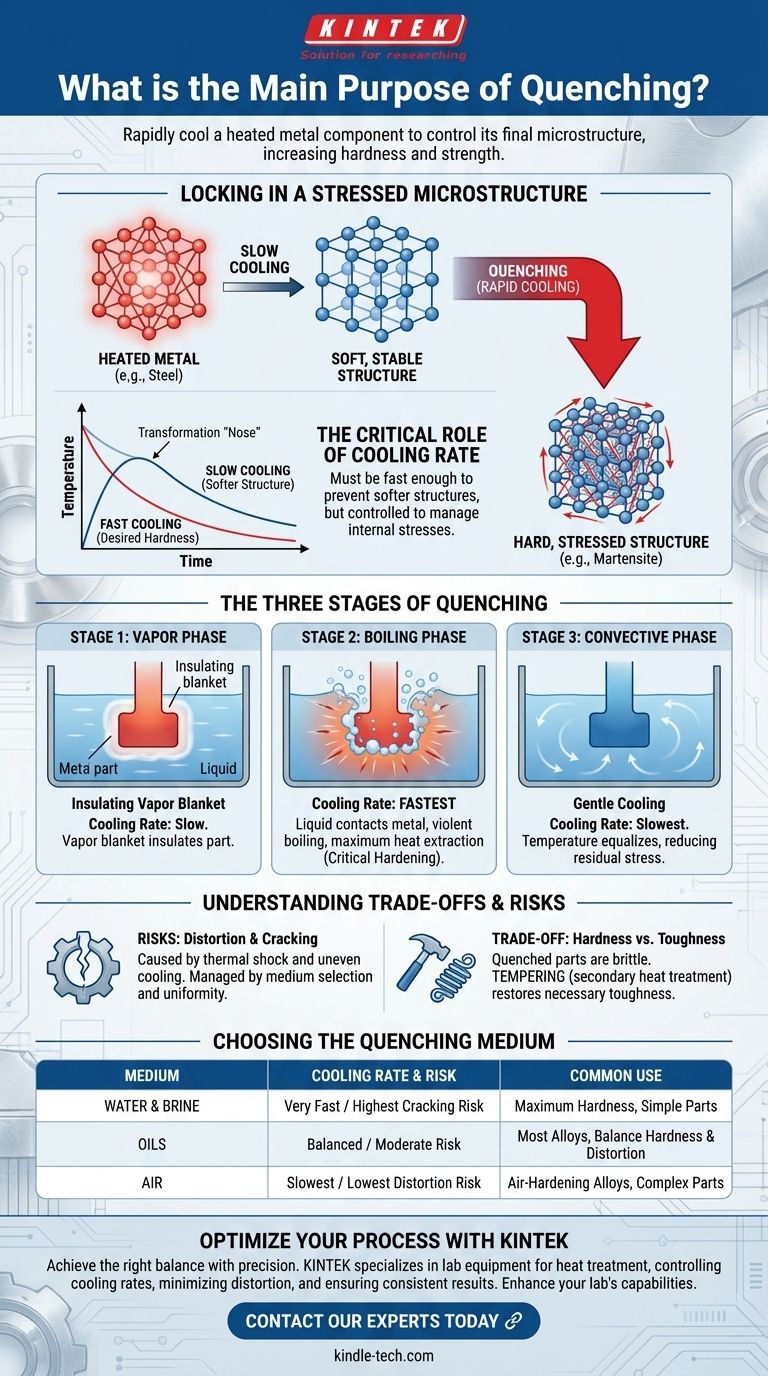
The primary purpose of quenching is to rapidly cool a heated metal component to control its final microstructure. This deliberate and controlled cooling process is not simply about making something cold; it's a metallurgical tool used to lock in specific material properties, most notably to increase hardness and strength.
Quenching is fundamentally a process of controlled heat extraction. Its goal is to trap a material's atoms in a high-strength, non-equilibrium state while carefully managing thermal stresses to prevent the component from cracking or distorting.

How Quenching Achieves Hardness
Locking in a Stressed Microstructure
When a metal like steel is heated to a high temperature, its atomic structure (crystal lattice) changes into a form that can dissolve carbon and other alloying elements.
If the metal were allowed to cool slowly, the atoms would rearrange themselves back into a soft, stable, and stress-free structure. Quenching prevents this by cooling the material so quickly that the atoms don't have time to return to their soft state. Instead, they are trapped in a highly strained, distorted structure (such as martensite in steel), which is what makes the material hard and strong.
The Critical Role of Cooling Rate
The speed of cooling is the single most important variable in quenching. The rate of heat transfer must be fast enough to miss the "nose" of the transformation curve, preventing the formation of softer structures.
However, the cooling rate must also be controlled. If it's too aggressive, the severe temperature difference between the surface and the core of the component can create immense internal stresses, leading to failure.
The Three Stages of the Quenching Process
The cooling that occurs during quenching is not linear. It happens in three distinct physical stages, each with a different rate of heat transfer.
Stage 1: The Vapor Phase
Immediately after the hot component is submerged in the quenching liquid (like oil), the liquid touching the surface vaporizes. This creates an insulating blanket of vapor that surrounds the part.
During this phase, cooling is relatively slow because the vapor acts as a poor conductor of heat.
Stage 2: The Boiling Phase
As the surface cools slightly, the vapor blanket becomes unstable and collapses. This allows the liquid to make direct contact with the hot metal, causing it to boil violently.
This is the fastest stage of cooling. The intense agitation from the boiling action removes heat at a maximum rate, which is when the critical hardening transformation occurs.
Stage 3: The Convective Phase
Once the component's surface temperature drops below the boiling point of the liquid, boiling stops. Heat is then removed through simple liquid convection.
This is the slowest stage of cooling. It allows the temperature throughout the part to equalize more gradually, which helps to reduce the final internal stresses that can cause distortion.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Risks
Quenching is a powerful process, but it introduces significant risks that must be managed through the careful selection of the quenching medium and process parameters.
The Risk of Distortion and Cracking
The primary risk is thermal shock. As the surface of the component cools and contracts rapidly while the core remains hot and expanded, immense stress develops. If this stress exceeds the material's strength, the part can warp, distort, or crack.
Enhancing the "wetting" ability of a quenching oil helps ensure the vapor blanket collapses uniformly, preventing hot spots that lead to uneven cooling and stress.
The Importance of the Quenching Medium
Different fluids extract heat at different rates, making the choice of medium critical.
- Water & Brine: Provide very fast cooling for maximum hardness but carry the highest risk of cracking.
- Oils: Offer a slower, less severe quench. This provides a good balance of achieving hardness while minimizing distortion, making oil the most common choice for many alloys.
- Air: Provides the slowest quench, used for specific "air-hardening" alloys where the risk of distortion is extremely high.
Hardness vs. Toughness
The primary trade-off in quenching is hardness for toughness. The resulting hard, martensitic structure is also brittle. For this reason, a quenched part is almost always followed by a secondary heat treatment called tempering, which slightly reduces the hardness to relieve stress and restore some necessary toughness.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The ideal quenching strategy depends entirely on the material being treated and the desired final properties of the component.
- If your primary focus is maximum hardness in a simple part: A very fast quench in water or brine may be appropriate, as long as the material can withstand the thermal shock.
- If your primary focus is balancing hardness and dimensional stability: A well-formulated quenching oil is the standard choice, offering controlled cooling through all three phases.
- If your primary focus is minimizing distortion in a complex or thin-walled part: A slower quench using specialized oil, or even air for certain high-alloy steels, is necessary to ensure cooling is as uniform as possible.
Ultimately, mastering quenching is about manipulating the physics of heat transfer to precisely engineer the final properties of a material.
Summary Table:
| Purpose | Key Benefit | Key Risk | Common Medium |
|---|---|---|---|
| Increase Hardness & Strength | Traps atoms in a high-strength state (e.g., martensite) | Distortion or cracking from thermal stress | Oil, Water, Air |
| Control Microstructure | Prevents formation of soft, stable structures during cooling | Requires precise cooling rate management | Depends on material |
| Balance Properties | Optimizes hardness vs. toughness (often followed by tempering | Over-quenching can lead to brittleness | Oil (most common) |
Optimize Your Metal Hardening Process with KINTEK
Quenching is a critical step in metallurgy, but achieving the right balance of hardness, strength, and dimensional stability requires precision. At KINTEK, we specialize in lab equipment and consumables tailored to heat treatment processes like quenching. Whether you're working with oils, water, or air quenching, our solutions help you control cooling rates, minimize distortion, and ensure consistent results.
Let us help you enhance your lab's capabilities—contact our experts today for tailored equipment recommendations!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
People Also Ask
- Why would you braze instead of solder? For Superior Joint Strength and High-Temperature Performance
- What is the operating temperature of a furnace? From Home Heating to Industrial Processing
- What is the sintering time? A Critical Process Variable for Material Density and Strength
- What are the defects in sintered parts? Avoid Warping, Cracking, and Porosity Issues
- What are the methods of brazing heating? Choose the Right Method for Your Production Needs



















