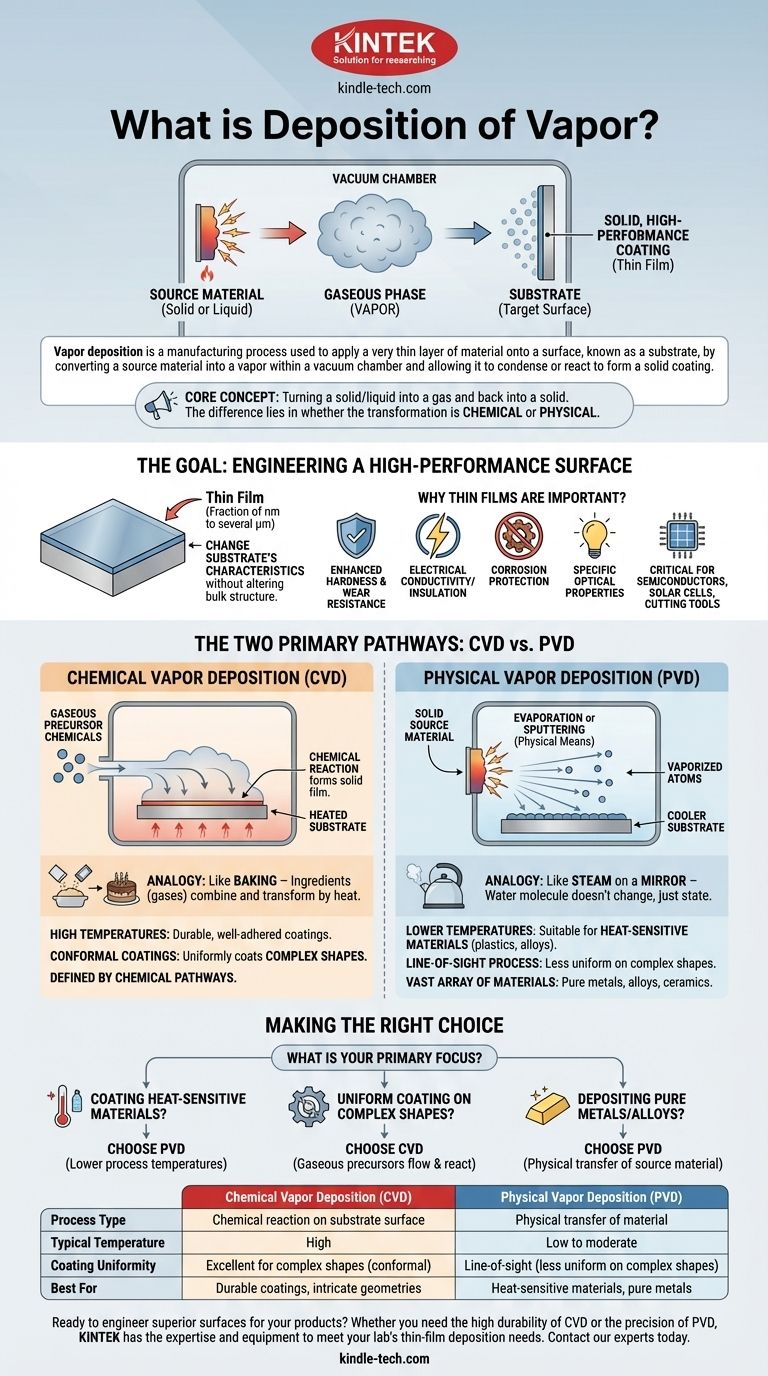
Vapor deposition is a manufacturing process used to apply a very thin layer of material onto a surface, known as a substrate. This is accomplished by converting a source material into a gaseous phase (a vapor) within a vacuum chamber and then allowing it to condense or react on the substrate's surface, forming a solid, high-performance coating.
At its core, vapor deposition is about turning a solid or liquid into a gas and then back into a solid on a target surface. The critical difference between methods lies in whether this transformation is driven by a chemical reaction or a physical process.
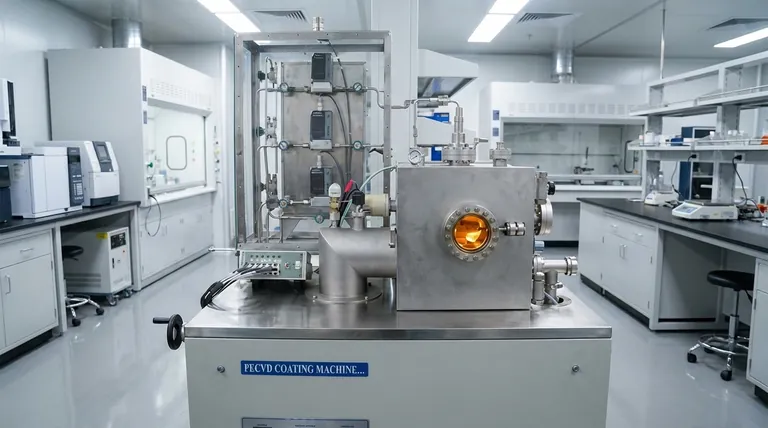

The Goal: Engineering a High-Performance Surface
The primary purpose of vapor deposition is to create a "thin film" that grants the underlying object new and improved properties.
What is a Thin Film?
A thin film is a layer of material ranging from fractions of a nanometer to several micrometers in thickness.
By applying this film, you can change the substrate's characteristics without altering its bulk structure. This is essential for modern manufacturing.
Why Are Thin Films Important?
These engineered surfaces can provide enhanced hardness, wear resistance, electrical conductivity or insulation, corrosion protection, or specific optical properties. This technology is fundamental to producing items like semiconductors, solar cells, and durable cutting tools.
The Two Primary Pathways: CVD vs. PVD
Virtually all vapor deposition techniques fall into one of two main categories: Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) or Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD).
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD): Building with a Reaction
CVD involves introducing one or more gaseous precursor chemicals into a reaction chamber.
These gases are then exposed to the substrate, which is typically heated. The heat triggers a chemical reaction among the gases and on the substrate's surface, forming a stable solid film.
Think of it like baking: the individual ingredients (gases) are combined and transformed by heat into something entirely new (the solid coating).
Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD): Transferring a Material
PVD works by transforming a solid source material into a vapor through purely physical means.
This is often done by heating the material until it evaporates or by bombarding it with high-energy ions, a process called sputtering, which knocks atoms loose. These vaporized atoms then travel through the vacuum and condense onto the cooler substrate.
This is analogous to steam from a boiling kettle condensing on a cold mirror. The water molecule itself doesn't change; it simply moves from a gaseous state back to a liquid/solid state.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing between CVD and PVD depends entirely on the material, the substrate, and the desired outcome. Neither method is universally superior.
The Impact of Temperature
CVD processes typically require very high temperatures to initiate the necessary chemical reactions. This can result in extremely durable and well-adhered coatings.
PVD methods can operate at much lower temperatures. This makes PVD suitable for coating heat-sensitive materials, such as plastics or certain alloys, that would be damaged by the CVD process.
The Effect of Geometry
Because CVD uses gases that flow around an object, it is excellent at creating conformal coatings. This means it can uniformly coat complex shapes with intricate details and internal surfaces.
PVD is largely a "line-of-sight" process. The vaporized atoms travel in a straight line from the source to the substrate, making it difficult to evenly coat complex, three-dimensional shapes.
Material & Process Flexibility
PVD can be used to deposit a vast array of materials, including pure metals, alloys, and certain ceramic compounds that are vaporized from a solid target.
CVD is defined by the availability of suitable gaseous precursor chemicals that will react in the desired way. The process relies on specific chemical pathways to form the film.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding the fundamental difference between these two pathways is key to selecting the correct manufacturing process for a specific application.
- If your primary focus is coating heat-sensitive materials: PVD is the logical choice due to its lower process temperatures.
- If your primary focus is achieving a highly uniform coating on complex shapes: CVD is often superior because its gaseous precursors can flow and react on all surfaces.
- If your primary focus is depositing pure metals or alloys with minimal chemical change: PVD methods like sputtering or evaporation are ideal as they physically transfer the source material.
By understanding the distinction between a chemical reaction and a physical transfer, you can effectively leverage vapor deposition to engineer surfaces with remarkable capabilities.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) | Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) |
|---|---|---|
| Process Type | Chemical reaction on substrate surface | Physical transfer of material |
| Typical Temperature | High | Low to moderate |
| Coating Uniformity | Excellent for complex shapes (conformal) | Line-of-sight (less uniform on complex shapes) |
| Best For | Durable coatings, intricate geometries | Heat-sensitive materials, pure metals |
Ready to engineer superior surfaces for your products?
Whether you need the high durability of CVD coatings or the precision of PVD for heat-sensitive materials, KINTEK has the expertise and equipment to meet your lab's thin-film deposition needs. Our specialized solutions help you achieve enhanced hardness, corrosion resistance, and specific electrical or optical properties.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your vapor deposition projects with the right tools and consumables.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- CVD Diamond Cutting Tool Blanks for Precision Machining
People Also Ask
- What is the process of PECVD in semiconductor? Enabling Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- Why does a PECVD vacuum system require both a rotary vane and turbo pump? Ensure High-Purity Coatings
- How do PECVD systems improve DLC coatings on implants? Superior Durability and Biocompatibility Explained
- How are thin films deposited? A Guide to PVD vs. CVD Methods for Your Application
- Why is a Matching Network Indispensable in RF-PECVD for Siloxane Films? Ensure Stable Plasma and Uniform Deposition



















