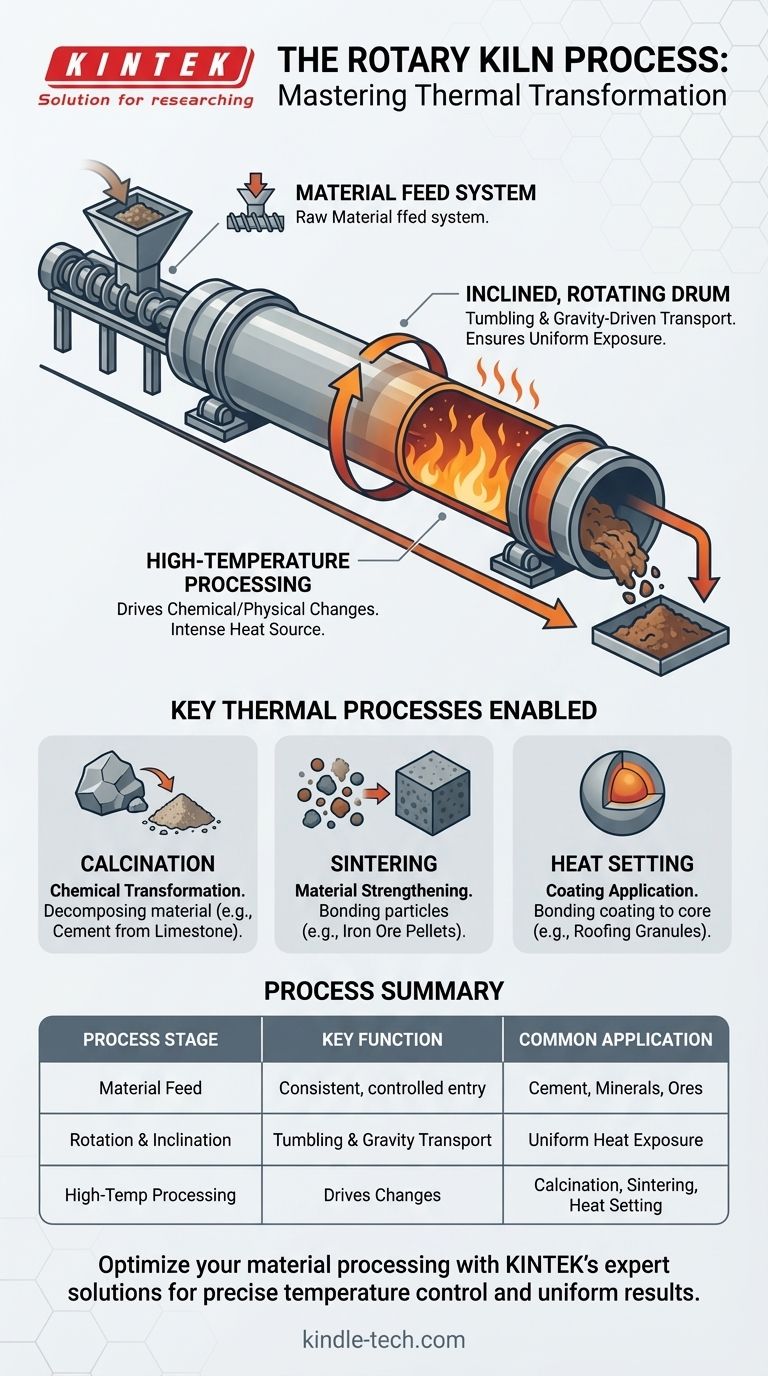
At its core, the rotary kiln process involves continuously feeding material into the upper end of a large, rotating, and slightly inclined cylinder. As the kiln rotates, the material tumbles and gradually moves down toward the lower end due to gravity. This tumbling action ensures the material is uniformly exposed to extremely high temperatures, which drives specific chemical reactions or physical changes to produce a final, transformed product.
The fundamental principle of a rotary kiln is using mechanical motion—rotation and inclination—to achieve highly controlled and uniform thermal processing of materials on a continuous, industrial scale.

The Core Mechanics: How a Rotary Kiln Works
A rotary kiln is not a single component but a system, with the rotating drum, or reactor, at its heart. Understanding how material moves through this system is key to understanding the process.
The Material Feed System
Material enters the kiln through a feed chute or screw feeder at the elevated end. This system is designed for a consistent, quantitative flow of feedstock. The design is often robust and made from heat-resistant alloys to prevent material build-up and withstand high temperatures.
The Inclined, Rotating Drum
The kiln itself is a long cylinder positioned at a slight horizontal angle. This inclination is critical, as it uses gravity to move the material from the feed end to the discharge end.
The rotation of the drum serves a dual purpose: it tumbles the material, ensuring every particle is evenly exposed to the heat source, and it helps transport the material down the length of the kiln.
High-Temperature Processing
The primary function of the kiln is to create an ultra-high temperature environment. This intense heat is the catalyst for the entire process, providing the necessary energy for various thermodynamic or kinetic reactions to occur within the material bed.
Key Thermal Processes Enabled by the Kiln
The versatility of the rotary kiln comes from its ability to facilitate a wide range of thermal processes by controlling temperature, atmosphere, and retention time.
Calcination (Chemical Transformation)
Calcination is a process that uses high heat to drive chemical reactions, often by decomposing a material. The most common example is heating limestone to produce lime and carbon dioxide, a foundational step in manufacturing cement.
Sintering (Material Strengthening)
Sintering involves heating a material to a temperature just below its melting point. This causes the particles to bond and fuse, which significantly increases the material's strength and density. This is frequently used for iron ore pelletizing and creating high-strength proppants for the oil and gas industry.
Heat Setting (Coating Application)
In heat setting, a core mineral is coated with another material. The kiln heats the materials so the coating becomes viscous and securely bonds to the core. This technique is essential in manufacturing roofing granules, where colored pigments are fused onto a granite base.
Other Critical Functions
The controlled environment of a rotary kiln also makes it ideal for other functions, including drying, organic combustion, incineration of waste, and reduction roasting to change the chemical state of metals.
Understanding the Engineering Considerations
A rotary kiln's effectiveness is not accidental; it is the result of precise engineering tailored to a specific material and desired outcome.
The Importance of Correct Sizing
Sizing a rotary kiln is a complex task that combines thermal analysis, chemical engineering, and practical experience. There is no one-size-fits-all solution.
Designers must determine the ideal diameter and length of the kiln based on critical factors to ensure the process goals are met efficiently and effectively.
Key Sizing Factors
The final dimensions of a kiln depend on a balance of variables. These include the required capacity (how much material needs to be processed), the retention time (how long the material must stay in the kiln), the maximum feed rate, and the specific chemical and physical properties of the material being processed.
Matching the Process to Your Goal
The specific thermal function you employ depends entirely on your end goal for the material.
- If your primary focus is chemical decomposition to create a new compound: Calcination is the core process, as seen in cement manufacturing.
- If your primary focus is to increase the strength and density of a material: Sintering is the method for bonding particles together, essential for products like iron ore pellets.
- If your primary focus is to apply a durable, heat-fused coating: Heat setting provides the controlled environment to bond one material to another, like in roofing granules.
Ultimately, the rotary kiln process is a powerful and adaptable thermal tool, engineered to meet a vast range of industrial material transformation needs.
Summary Table:
| Process Stage | Key Function | Common Industrial Application |
|---|---|---|
| Material Feed | Consistent, controlled entry of feedstock | Cement, minerals, ores |
| Rotation & Inclination | Tumbling and gravity-driven transport | Ensures uniform heat exposure |
| High-Temperature Processing | Drives chemical/physical changes | Calcination, sintering, heat setting |
Optimize your material processing with KINTEK's expert solutions. Whether you're involved in calcination, sintering, or heat setting, our specialized lab equipment and consumables are designed to meet the rigorous demands of industrial thermal transformation. Let our team help you achieve precise temperature control and uniform results. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's specific needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
People Also Ask
- What equipment is used in pyrolysis? Choosing the Right Reactor for Your Feedstock and Products
- What are the products of pyrolysis of wood? A Guide to Biochar, Bio-oil, and Syngas Yields
- What biomass is used in pyrolysis? Selecting the Optimal Feedstock for Your Goals
- What are the types of pyrolysis reactors used in industry? Choose the Right Technology for Your Product
- What is the difference between calcining and roasting? A Guide to High-Temperature Processing



















