In short, vacuum casting is a replication technique used to create high-quality plastic parts in small batches. The process involves creating a flexible silicone mold from a master pattern and then using a vacuum chamber to draw a liquid polyurethane resin into the mold cavity. This eliminates air bubbles and ensures the resin perfectly replicates every fine detail of the original pattern.
Vacuum casting's core value lies in its ability to bridge the gap between single prototypes and mass production. It enables the creation of production-quality parts for functional testing, marketing, or pilot runs without the prohibitive cost and lead time of hard tooling for injection molding.
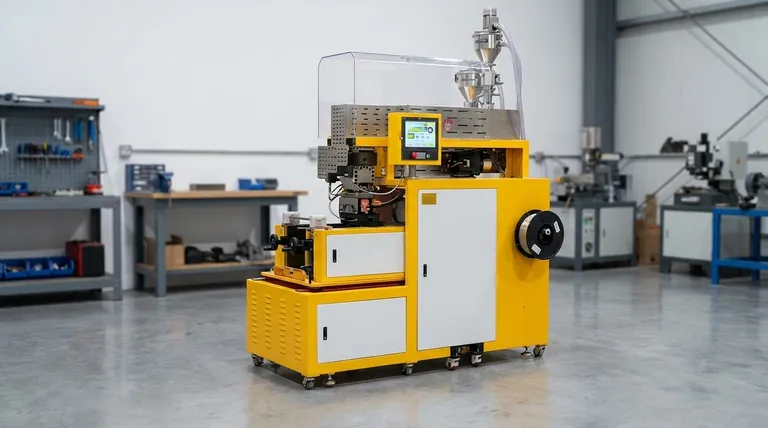

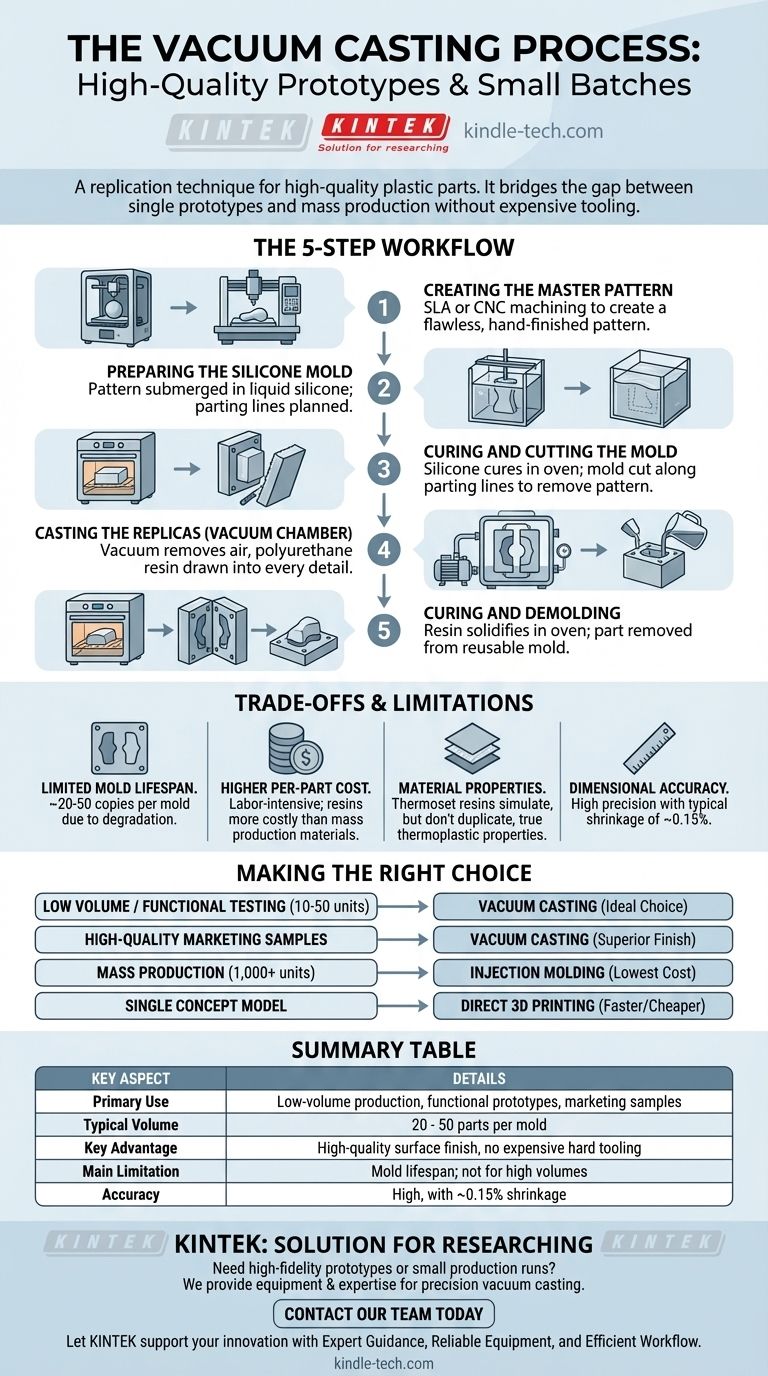
The Vacuum Casting Process, Step-by-Step
Understanding the workflow is key to appreciating its applications. The process is methodical and focuses on precision at every stage to ensure the final parts are perfect copies.
Step 1: Creating the Master Pattern
The entire process begins with a flawless master pattern. This is the idealized version of the final part and is typically created using a high-resolution 3D printing method like SLA (Stereolithography) or by CNC machining.
The surface finish of the master pattern is critical, as any imperfection will be transferred directly to the silicone mold and, subsequently, to every cast part. It must be hand-finished to perfection.
Step 2: Preparing the Silicone Mold
The master pattern is suspended inside a casting box. Liquid silicone rubber is then poured over the pattern until it is completely submerged. Parting lines are strategically planned at this stage to allow the mold to be separated later.
Step 3: Curing and Cutting the Mold
The box containing the pattern and liquid silicone is placed in a curing oven. The heat accelerates the curing process, solidifying the silicone into a flexible but durable rubber block.
Once cured, the mold is carefully cut along the pre-planned parting lines, and the master pattern is removed. This reveals a hollow negative cavity that is an exact inverse of the master.
Step 4: Casting the Replicas
This is the step that gives the process its name. The two halves of the silicone mold are reassembled and placed inside a vacuum chamber. The chosen casting resin, typically a two-component polyurethane, is mixed and poured into the mold's filling gate.
A vacuum is then pulled inside the chamber. This removes all air from the mold cavity, allowing the liquid resin to flow into every tiny crevice and detail without trapping air bubbles.
Step 5: Curing and Demolding the Part
After the cavity is filled, the vacuum is released, and the mold is moved to a curing oven. The heat solidifies the polyurethane resin.
Once the part is fully cured, the flexible silicone mold is opened, and the newly created replica is removed. The mold can then be reused to produce more copies.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
No process is perfect for every application. Being an effective advisor means acknowledging the limitations of a technology to prevent costly mistakes.
Limited Mold Lifespan
The primary trade-off is the durability of the silicone mold. A single mold can typically produce only 20 to 50 copies before it starts to degrade from thermal stress and chemical exposure, affecting the accuracy and surface finish of subsequent parts.
Higher Per-Part Cost than Mass Production
While the tooling is inexpensive, the process is labor-intensive and the resins are more costly than commodity plastics. For very large quantities (1,000+ units), the lower per-part cost of injection molding easily justifies its high initial tooling investment.
Material Properties vs. True Thermoplastics
Vacuum casting uses thermoset polyurethane resins that simulate the properties of common production thermoplastics like ABS, nylon, or polycarbonate. While these simulations are excellent for functional prototypes, they do not have the exact same mechanical, thermal, or chemical resistance properties as their injection-molded counterparts.
Dimensional Accuracy Tolerances
The process is highly accurate but not perfect. A typical shrinkage rate of about 0.15% is expected as the resin cures. While this is acceptable for most applications, projects requiring extreme precision may still need CNC machining.
Making the Right Choice for Your Project
Selecting the correct manufacturing process depends entirely on your project's specific goals, volume, and material requirements.
- If your primary focus is low-volume production or functional testing (10-50 units): Vacuum casting is the ideal choice, delivering production-like parts for validation without the cost of steel tooling.
- If your primary focus is creating high-quality marketing samples or user-testing models: Vacuum casting excels at producing parts with a superior aesthetic finish and a variety of material properties (rigid, flexible, clear).
- If your primary focus is mass production (1,000+ units): Injection molding is the definitive path for achieving the lowest possible cost per part at high volumes.
- If your primary focus is a single, one-off concept model: Direct 3D printing (SLA or FDM) is almost always faster and more cost-effective for a single part.
By understanding where vacuum casting excels, you can confidently select the right manufacturing process to move your project from concept to reality.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Primary Use | Low-volume production, functional prototypes, marketing samples |
| Typical Volume | 20 - 50 parts per mold |
| Key Advantage | High-quality surface finish & detail replication without expensive hard tooling |
| Main Limitation | Mold lifespan; not cost-effective for high volumes (1,000+ units) |
| Accuracy | High, with typical shrinkage of ~0.15% |
Need to create high-fidelity prototypes or a small production run?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the laboratory equipment and expertise needed for precision processes like vacuum casting. Whether you are testing a new product design or producing a limited batch of parts, our solutions help you achieve professional results without the high cost of mass-production tooling.
Let KINTEK support your innovation:
- Expert Guidance: Get advice on the best materials and methods for your specific project.
- Reliable Equipment: Access the tools needed for consistent, high-quality results.
- Efficient Workflow: Streamline your prototyping and small-batch production process.
Contact our team today to discuss how we can help bring your designs to life with precision and efficiency.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Lab Plastic PVC Calender Stretch Film Casting Machine for Film Testing
- Small Injection Molding Machine for Lab Use
- Touchscreen Automatic Vacuum Heat Press
- Double Plate Heating Press Mold for Lab
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
People Also Ask
- What does an induction furnace make use of? Harnessing Electromagnetic Induction for Clean, Efficient Melting
- How do specialized industrial-grade small melting furnaces address challenges in precision jewelry casting? Expert Guide
- What is a coreless induction furnace? Achieve Ultimate Flexibility in Metal Melting
- What is the advantage of electric induction furnace compared to direct current EAF during cool start up operation? Faster, More Efficient Melting
- What types of metals are typically processed in a vacuum induction melting furnace? High-Purity Alloys for Critical Applications
- What is the process of melting in an induction furnace? Harnessing Electromagnetic Power for Efficient Metal Melting
- Can you melt metal to reuse it? Unlock the Secrets of Metal Casting and Recycling
- What is the use of induction melting furnace? Achieve Fast, Clean, and Precise Metal Melting



















