At its core, pyrolysis is a method of waste management that uses heat to break down materials in an environment without oxygen. This thermal decomposition process converts solid waste, such as plastics, tires, and biomass, into valuable outputs. Instead of burning the waste, pyrolysis chemically transforms it into a mixture of combustible gas (syngas), liquid (bio-oil), and a solid, carbon-rich residue (bio-char).
Pyrolysis is best understood not as simple waste disposal, but as a resource recovery technology. It shifts the paradigm from treating waste as a problem to be buried to viewing it as a raw material for producing valuable energy and products.

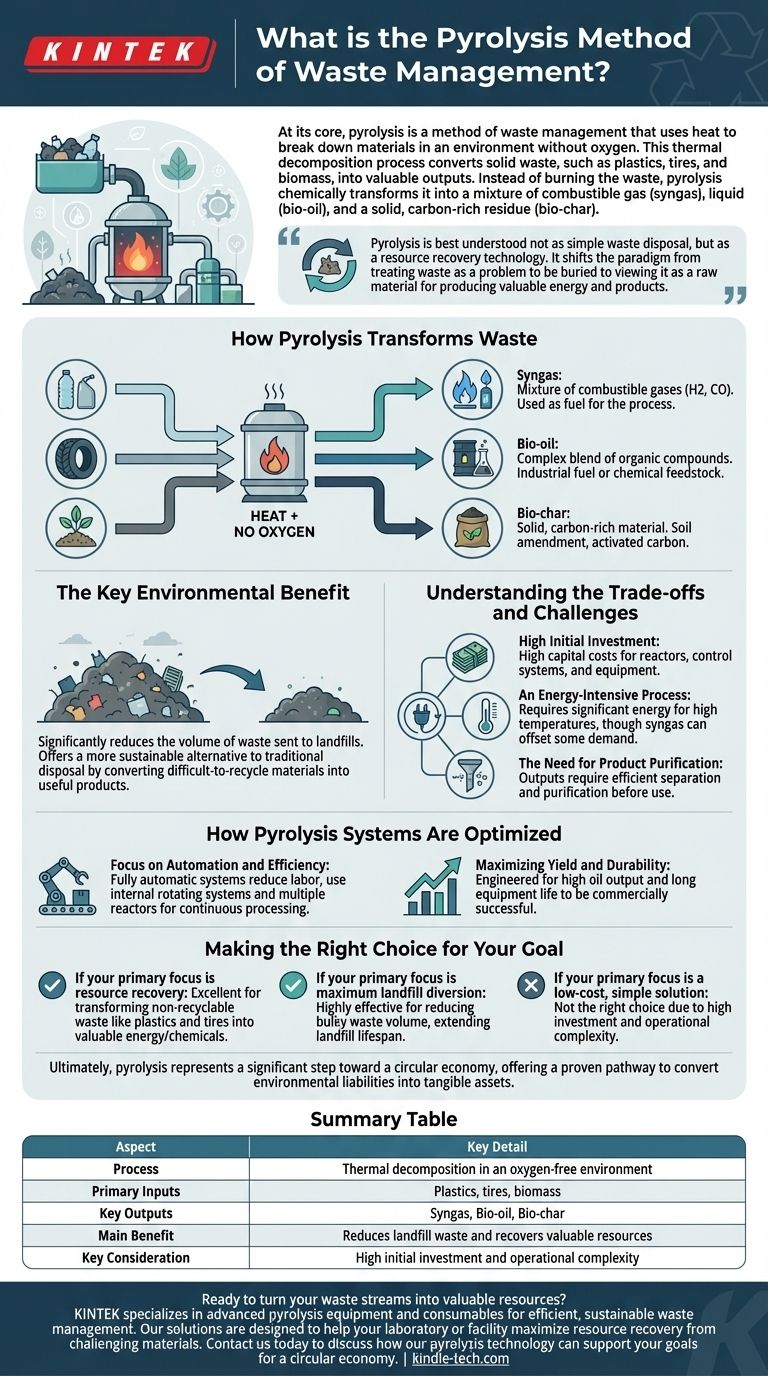
How Pyrolysis Transforms Waste
The fundamental principle of pyrolysis is to heat organic-based materials to high temperatures in an inert atmosphere. The absence of oxygen is critical; it prevents combustion and instead causes the long polymer chains within the waste to break down into smaller, simpler molecules.
The Three Primary Outputs
The process consistently yields three distinct products, each with potential applications.
Syngas: This is a mixture of combustible gases, primarily hydrogen and carbon monoxide. It can be used directly as a fuel source to power the pyrolysis process itself, making the system more energy-efficient.
Bio-oil: Also known as pyrolysis oil, this liquid is a complex blend of different organic compounds. It can be utilized as an industrial fuel or further refined into higher-grade fuels and chemicals.
Bio-char: This solid, carbon-rich material is similar to charcoal. It has significant value as a soil amendment to improve fertility and can also be used as a feedstock for producing activated carbon, which is used in filtration systems.
The Key Environmental Benefit
The primary advantage of pyrolysis is its ability to significantly reduce the volume of waste sent to landfills. By converting materials that are difficult to recycle into useful products, it offers a more sustainable alternative to traditional disposal methods.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Challenges
While promising, pyrolysis is a sophisticated industrial process with significant operational considerations. It is not a universally simple solution for all waste management scenarios.
High Initial Investment
Pyrolysis plants involve high capital costs. The reactors, control systems, and equipment needed for processing and refining the outputs require a substantial upfront investment.
An Energy-Intensive Process
Reaching and maintaining the high temperatures necessary for decomposition requires a significant amount of energy. While the syngas produced can offset some of this demand, the initial energy input remains a critical factor in its economic viability.
The Need for Product Purification
The outputs of pyrolysis are not immediately ready for use. The gas and oil streams are mixtures that require efficient separation and purification before they can be sold or used as fuel, adding another layer of complexity and cost to the operation.
How Pyrolysis Systems Are Optimized
Modern pyrolysis systems are designed to maximize efficiency and output. The goal is to create a continuous and automated process that improves the economic case for the technology.
Focus on Automation and Efficiency
Many systems are fully automatic, which reduces labor costs and ensures consistent operating conditions. Designs often feature internal rotating systems and multiple reactors to allow for continuous processing and higher throughput.
Maximizing Yield and Durability
The engineering focus is on achieving a high oil output from the waste feedstock. This, combined with designs that save time and energy and ensure a long working life for the equipment, is crucial for making a pyrolysis facility commercially successful.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Pyrolysis is a powerful tool when applied to the right problem. Its suitability depends entirely on the primary objective of the waste management strategy.
- If your primary focus is resource recovery: Pyrolysis is an excellent technology for transforming specific, non-recyclable waste streams like plastics and tires into valuable energy and chemical feedstocks.
- If your primary focus is maximum landfill diversion: This method is highly effective for reducing the volume of bulky waste materials, directly contributing to longer landfill lifespans and reduced environmental impact.
- If your primary focus is a low-cost, simple solution: Pyrolysis is likely not the right choice due to its high capital investment and operational complexity compared to more traditional waste management options.
Ultimately, pyrolysis represents a significant step toward a circular economy, offering a proven pathway to convert environmental liabilities into tangible assets.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Detail |
|---|---|
| Process | Thermal decomposition in an oxygen-free environment |
| Primary Inputs | Plastics, tires, biomass |
| Key Outputs | Syngas, Bio-oil, Bio-char |
| Main Benefit | Reduces landfill waste and recovers valuable resources |
| Key Consideration | High initial investment and operational complexity |
Ready to turn your waste streams into valuable resources? KINTEK specializes in advanced pyrolysis equipment and consumables for efficient, sustainable waste management. Our solutions are designed to help your laboratory or facility maximize resource recovery from challenging materials. Contact us today to discuss how our pyrolysis technology can support your goals for a circular economy.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
People Also Ask
- Is laser sintering the same as melting? Understand the Key Differences for Your AM Process
- What role do high-pressure homogenizers or ultrasonic cell disrupters play in the mechanical processing of nanocellulose?
- What is the role of a magnetic stirrer in the preparation of nano-filler reinforced epoxy coatings? Maximize Dispersion
- What are the applications of thin film technology? Powering Electronics, Energy, and Innovation
- What is the role of a laboratory constant temperature drying oven in anaerobic digestion? Precision TS Analysis
- Why is laboratory stirring equipment essential in the Sol-Gel process? Achieving Chemical Homogeneity and Stability
- What are the methods of synthesis of nanomaterials? Top-Down vs. Bottom-Up Approaches Explained
- Does higher heat capacity mean higher melting point? Unraveling the Critical Difference



















