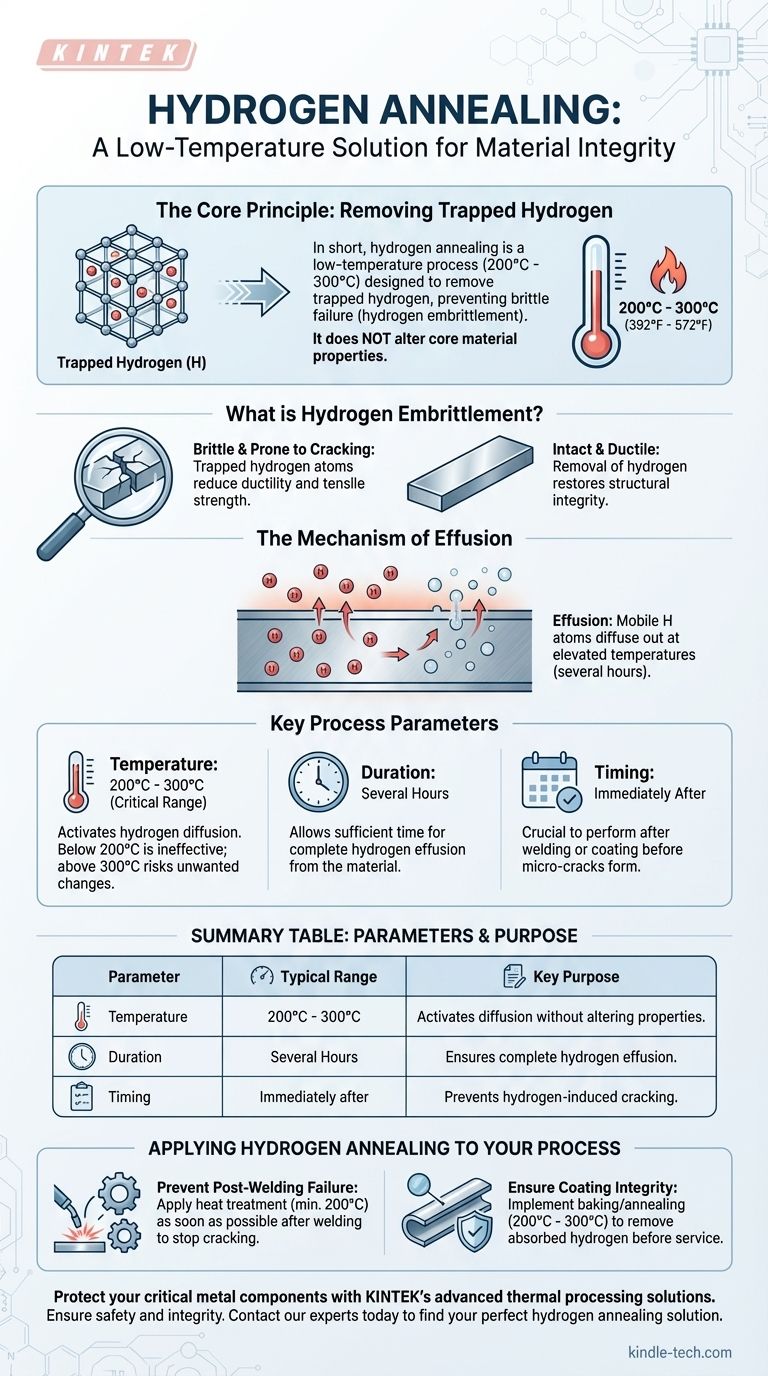
In short, hydrogen annealing is a low-temperature process typically performed between 200°C and 300°C (392°F to 572°F). The minimum effective temperature to begin this process in iron and some stainless steels is 200°C, which is required to allow trapped hydrogen atoms to diffuse out of the material.
The central goal of hydrogen annealing is not to alter the metal's core properties but to use a precise, low-temperature heat treatment to remove trapped hydrogen. This prevents a catastrophic failure mode known as hydrogen embrittlement.

The Core Principle: Removing Trapped Hydrogen
Hydrogen annealing is a targeted heat treatment designed to solve a very specific problem. Unlike conventional annealing, which aims to soften a material or relieve internal stresses, this process is focused solely on hydrogen removal.
What is Hydrogen Embrittlement?
During processes like welding, electroplating, or galvanizing, individual hydrogen atoms can become trapped within the crystal structure of the metal.
These trapped atoms significantly reduce the material's ductility and tensile strength, making it brittle and prone to cracking under stress. This phenomenon is called hydrogen embrittlement.
The Role of Temperature
The temperature range of 200°C to 300°C is critical. It must be high enough to give the trapped hydrogen atoms sufficient thermal energy to move, or diffuse, through the metal's lattice.
However, the temperature must also be low enough to avoid altering the material's intended mechanical properties, such as hardness or temper, which would occur at higher annealing temperatures.
The Mechanism of Effusion
By holding the material at this elevated temperature for several hours, the mobile hydrogen atoms migrate through the metal until they reach the surface and escape.
This process of gas escaping from a solid is known as effusion. This effectively removes the source of the embrittlement.
Understanding the Key Parameters
Success with hydrogen annealing depends on carefully controlling the process variables to match the material and the manufacturing step that introduced the hydrogen.
The Critical Temperature Range
The process relies on staying within the 200°C to 300°C window. Below 200°C, hydrogen diffusion is too slow to be effective in iron-based alloys. Going significantly above 300°C risks unwanted changes to the metal's microstructure.
Duration and Timing
The component is typically held at temperature in a hydrogen annealing oven for several hours to ensure the hydrogen has enough time to diffuse out completely.
Crucially, this process is most effective when performed immediately after the hydrogen-introducing step, such as welding or coating, before any micro-cracks can form.
How to Apply This to Your Process
Choosing the right parameters is about mitigating risk without creating unintended consequences for your material.
- If your primary focus is preventing post-welding failure: Apply a heat treatment at a minimum of 200°C as soon as possible after the weld cools to prevent hydrogen-induced cracking.
- If your primary focus is ensuring coating or galvanizing integrity: Implement a baking or annealing step between 200°C and 300°C to remove absorbed hydrogen before the part is placed into service.
Ultimately, hydrogen annealing is a precise thermal tool used to safeguard the integrity of components against a hidden threat.
Summary Table:
| Parameter | Typical Range | Key Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | 200°C - 300°C (392°F - 572°F) | Activates hydrogen diffusion without altering metal properties |
| Duration | Several Hours | Allows sufficient time for hydrogen to effuse from the material |
| Timing | Immediately after welding/coating | Prevents hydrogen-induced cracking before it starts |
Protect your critical metal components from hydrogen embrittlement. The precise low-temperature heat treatment of hydrogen annealing is essential for ensuring the integrity and safety of welded or coated parts. KINTEK specializes in providing the advanced lab equipment and thermal processing solutions you need to implement this vital process effectively.
Ensure your materials are safe from hidden threats. Contact our experts today to find the perfect hydrogen annealing solution for your laboratory's needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is quartz tube heating? Achieve Instant, Targeted Heat with Infrared Radiation
- What is the process of annealing tubes? Achieve Optimal Softness and Ductility for Your Tubing
- What is the standard thickness of plating? Optimize Durability, Corrosion & Cost
- What temperature is tube annealing? A Guide to Material-Specific Ranges for Optimal Results
- What is a vertical tube furnace? Leverage Gravity for Superior Uniformity and Process Control



















