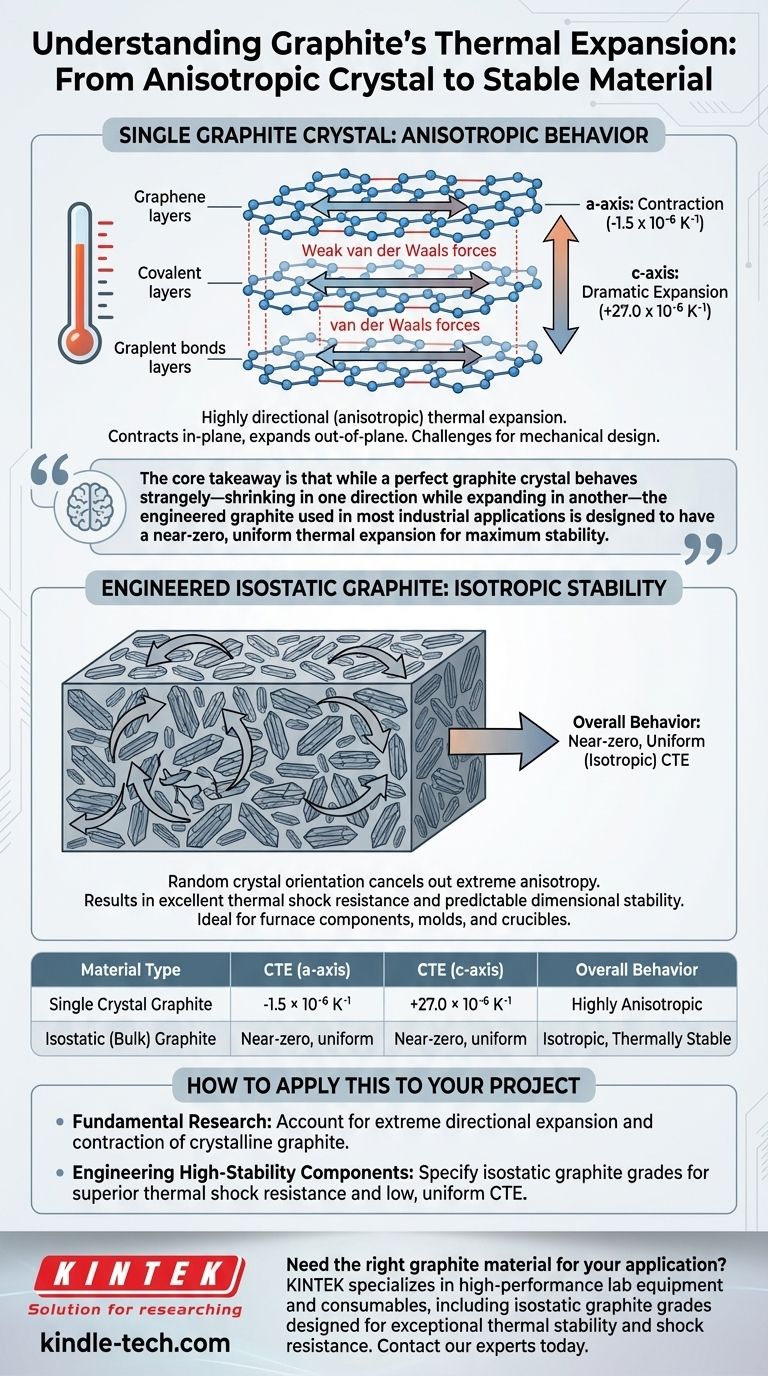
For a single graphite crystal, the coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE) is extremely dependent on direction, a property known as anisotropy. At room temperature (300 K), it contracts within its atomic planes with a CTE of -1.5 x 10⁻⁶ K⁻¹ (a-axis) while simultaneously expanding dramatically between those planes with a CTE of +27.0 x 10⁻⁶ K⁻¹ (c-axis).
The core takeaway is that while a perfect graphite crystal behaves strangely—shrinking in one direction while expanding in another—the engineered graphite used in most industrial applications is designed to have a near-zero, uniform thermal expansion for maximum stability.

Understanding the Anisotropic Behavior of Graphite
The unique thermal properties of graphite are rooted in its layered atomic structure. Thinking of it as a stack of extremely strong but separate sheets of paper helps visualize this behavior.
The 'a-axis': Contraction Within the Layers
A single layer of graphite (graphene) is a honeycomb lattice of carbon atoms held by incredibly strong covalent bonds.
When heated, subtle out-of-plane atomic vibrations actually pull the in-plane atoms slightly closer together. This results in a small but significant negative thermal expansion, meaning the material contracts along this plane as temperature rises.
The 'c-axis': Expansion Between the Layers
The individual graphene layers are held together by much weaker van der Waals forces.
These weak bonds allow for a large amount of movement and separation as atomic vibrations increase with temperature. This leads to a substantial positive thermal expansion in the direction perpendicular to the layers.
From Crystal to Engineered Material
Most applications do not use single graphite crystals. Instead, they use bulk forms like isostatic graphite, which is manufactured by compressing fine graphite particles into a solid block. This manufacturing process is key to its practical thermal performance.
Randomizing the Crystal Orientation
In isostatic graphite, the countless microscopic graphite crystals are oriented randomly.
The dramatic expansion of some crystals along their c-axis is cancelled out by the slight contraction of neighboring crystals along their a-axis.
The Result: Exceptional Thermal Stability
This averaging effect produces a bulk material with a very low, near-uniform (isotropic) overall coefficient of thermal expansion.
It is this property that gives high-quality isostatic graphite its excellent resistance to thermal shock. The material does not build up significant internal stress when heated or cooled rapidly because it barely changes in size.
Understanding the Practical Implications
The distinction between a graphite crystal and a bulk graphite product is critical for any real-world application. Failing to understand this can lead to design failure.
Crystalline Graphite: A Specialized Material
Forms of graphite with highly oriented crystals (like highly oriented pyrolytic graphite, or HOPG) are powerful for research but challenging for mechanical design.
Any component made from this material must be engineered to accommodate massive dimensional changes in one direction and contraction in the others.
Bulk Graphite: Predictable and Stable
For components like furnace linings, casting molds, or semiconductor crucibles, dimensional stability is paramount.
Isostatic graphite is chosen for these roles precisely because its randomized internal structure negates the extreme anisotropy of the base crystal, leading to a predictable and reliable component. The final CTE of the bulk material will depend on the specific grade, particle size, and density, but it is always engineered to be low.
How to Apply This to Your Project
Your choice of material depends entirely on your objective.
- If your primary focus is fundamental research or sensors: You must account for the extreme anisotropic behavior of a graphite crystal, designing around its directional expansion and contraction.
- If your primary focus is engineering high-stability components: You should specify a high-purity, isostatic graphite grade to leverage its near-zero, uniform CTE for superior thermal shock resistance.
Ultimately, understanding how manufacturing transforms graphite's atomic properties into a stable engineering material is the key to using it effectively.
Summary Table:
| Material Type | CTE (a-axis) | CTE (c-axis) | Overall Behavior |
|---|---|---|---|
| Single Crystal Graphite | -1.5 × 10⁻⁶ K⁻¹ | +27.0 × 10⁻⁶ K⁻¹ | Highly Anisotropic |
| Isostatic (Bulk) Graphite | Near-zero, uniform | Near-zero, uniform | Isotropic, Thermally Stable |
Need the right graphite material for your application? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, including isostatic graphite grades designed for exceptional thermal stability and shock resistance. Whether you're engineering furnace components, semiconductor tools, or research instruments, we provide materials that deliver reliability and precision. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific requirements and find the perfect graphite solution for your project.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Carbon Graphite Plate Manufactured by Isostatic Pressing Method
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
- Warm Isostatic Press for Solid State Battery Research
- Silicon Carbide (SIC) Ceramic Sheet Wear-Resistant Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Engineering Advanced Fine Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Rod Insulated for Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What role does convection play in heat transfer? Understanding Heat Movement in Fluids
- What are the three types of coating? A Guide to Architectural, Industrial, and Special Purpose
- What are the properties of the graphite? Unlock High-Temperature Strength & Conductivity
- Does graphite lead electricity? Unlocking the Secrets of Its Atomic Structure
- What is the purpose of laminating? Protect and Enhance Your Documents for Long-Term Use



















