In a laboratory, the most common sources of heat are Bunsen burners, alcohol lamps, electric hot plates, and heating mantles. The specific tool chosen is dictated by the required temperature, the flammability of the substances being heated, and the level of control needed for the experiment.
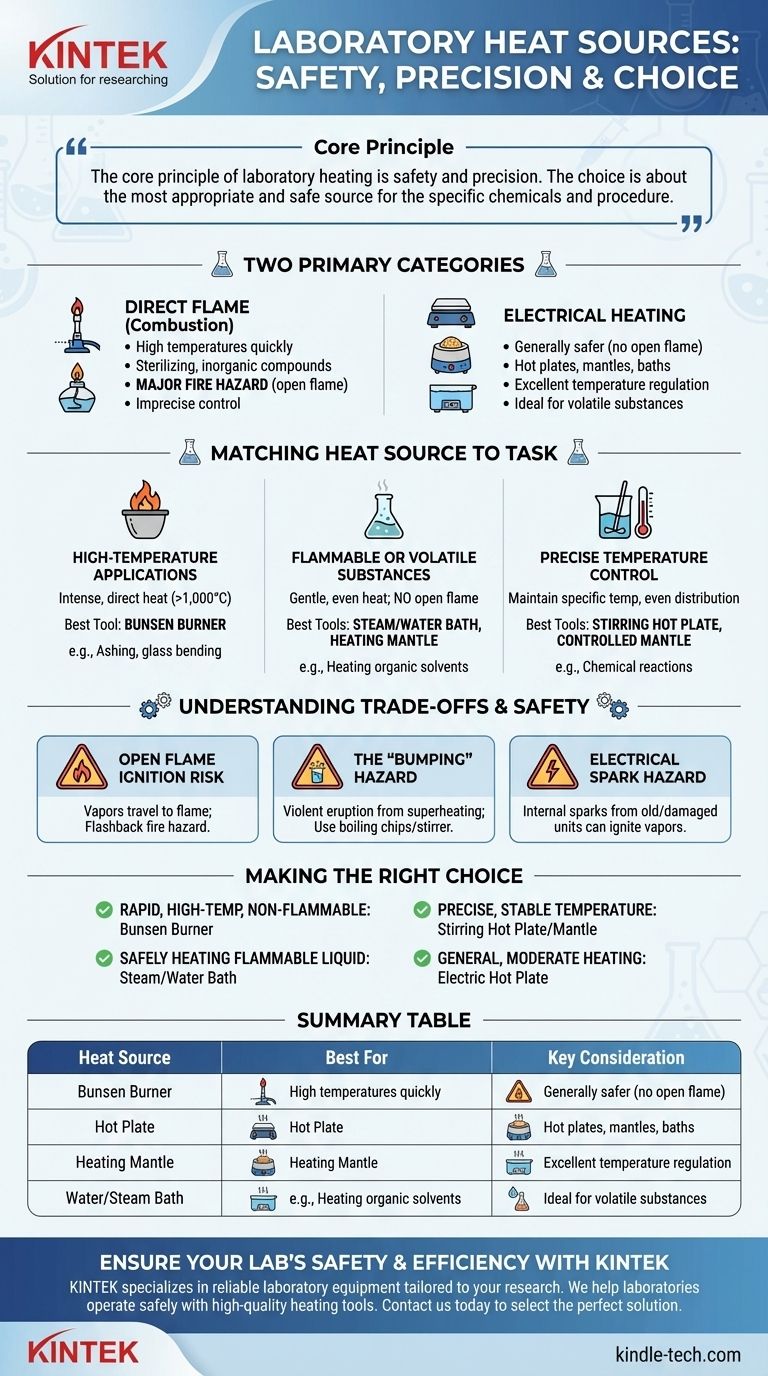
The core principle of laboratory heating is safety and precision. The choice is not about which source is "best," but which is the most appropriate and safe for the specific chemicals and procedure at hand.
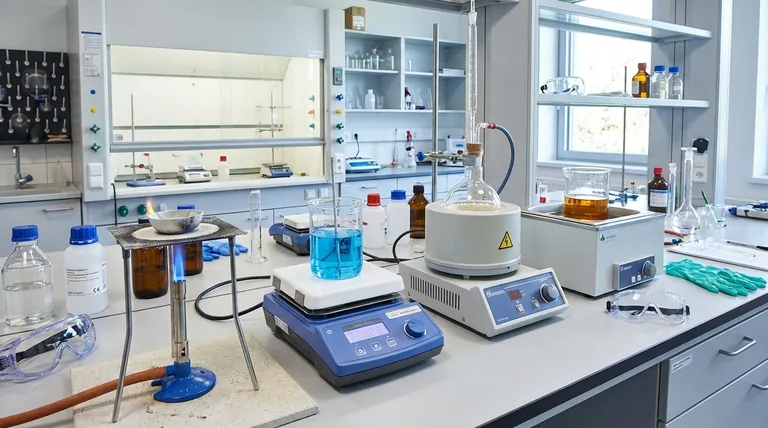

The Two Primary Categories of Lab Heat Sources
The vast majority of laboratory heating tasks are accomplished using one of two methods: direct flame (combustion) or electrical heating. Each has distinct advantages and critical limitations.
Direct Flame Sources (Combustion)
A direct flame is produced by the combustion of fuel, most commonly natural gas in a Bunsen burner or alcohol in an alcohol lamp.
These tools are valued for their ability to produce very high temperatures quickly. They are often used for tasks like sterilizing equipment or strongly heating stable, non-flammable inorganic compounds.
However, the significant drawback is the open flame, which presents a major fire hazard, especially in the presence of flammable solvents. Temperature control is also imprecise.
Electrical Heating Sources
Electrical sources convert electricity into heat and are generally much safer because they eliminate the open flame.
Common examples include hot plates, which are ideal for heating flat-bottomed glassware like beakers, and heating mantles, which are designed to fit around round-bottom flasks for more uniform heating.
For even more gentle and controlled heating, especially for volatile substances, water baths and steam baths are used. They provide excellent temperature regulation and prevent localized overheating.
Matching the Heat Source to the Task
Selecting the correct instrument is a foundational lab skill. The decision process revolves around three key factors: the target temperature, the chemical properties of your material, and the need for control.
For High-Temperature Applications
When a procedure requires intense, direct heat—such as heating a crucible to ash a sample or bending glass tubing—a Bunsen burner is the most effective tool.
Its flame can reach temperatures well over 1,000°C, something most standard electrical hot plates cannot achieve.
For Flammable or Volatile Substances
Heating flammable organic solvents like ethanol or diethyl ether is one of the most common yet hazardous lab procedures. Never use an open flame.
The correct tools are a steam bath, water bath, or a spark-proof heating mantle. These sources provide gentle, even heat without an ignition source for flammable vapors.
For Precise Temperature Control
When a reaction must be maintained at a specific temperature (e.g., 50°C), a controlled electrical device is necessary.
A stirring hot plate with a temperature probe or a heating mantle connected to a variable controller offers the best precision. The stirring action also ensures even temperature distribution throughout the liquid.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Safety
Every heat source has inherent risks that must be managed. Acknowledging these trade-offs is critical for preventing accidents.
The Open Flame Ignition Risk
The vapors from many common solvents are heavier than air and can travel across a lab bench to an open flame, causing a dangerous flashback fire. This is the single most important safety consideration when choosing a heat source.
The "Bumping" Hazard
When a liquid is heated too quickly or unevenly from the bottom, it can superheat and boil violently in a single, large eruption. This phenomenon, called bumping, can splash hot and corrosive chemicals.
Using boiling chips or a magnetic stirrer breaks up the formation of large bubbles, ensuring a smooth, controlled boil, especially when using a hot plate or Bunsen burner.
Electrical Spark Hazard
While far safer than open flames, electrical equipment is not without risk. Older or damaged hot plates can create an internal spark, which is capable of igniting a high concentration of flammable vapors. Always inspect electrical equipment before use.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Ultimately, your experimental goal dictates the proper tool. Consider the following guidelines for the most common scenarios.
- If your primary focus is rapid, high-temperature heating of non-flammables: A Bunsen burner provides the most intense and immediate heat.
- If your primary focus is safely heating a flammable or volatile liquid: A steam bath or water bath is the safest and most controlled option.
- If your primary focus is maintaining a stable, specific temperature for a reaction: A stirring hot plate with feedback control or a controlled heating mantle offers the best precision.
- If your primary focus is general, moderate heating of aqueous solutions: An electric hot plate is a versatile and effective workhorse.
Choosing the correct heat source is the foundation of safe and effective laboratory work.
Summary Table:
| Heat Source | Best For | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Bunsen Burner | High-temperature, rapid heating of non-flammables | Open flame presents a major fire hazard |
| Hot Plate | General, moderate heating of solutions | Versatile; use with boiling chips to prevent bumping |
| Heating Mantle | Uniform heating of round-bottom flasks | Excellent for precise temperature control |
| Water/Steam Bath | Safely heating flammable or volatile liquids | Gentle, even heat with no ignition source |
Ensure Your Lab's Safety and Efficiency with KINTEK
Choosing the correct heat source is critical for the success and safety of your experiments. Whether you need the intense heat of a Bunsen burner, the precise control of a heating mantle, or the safe operation of a steam bath for volatile substances, having the right equipment is non-negotiable.
KINTEK specializes in providing reliable laboratory equipment and consumables tailored to your specific research needs. We help laboratories like yours operate safely and efficiently by supplying high-quality heating tools that ensure precision and minimize risks.
Contact us today to discuss your requirements, and let our experts help you select the perfect heating solution for your application. Get in touch via our contact form to get started!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Automatic Laboratory Heat Press Machine
- Anti-Cracking Press Mold for Lab Use
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- How is conventional heating different from induction heating? Direct vs. Indirect Heat Explained
- What is the temperature range for compression molding? Optimize Your Process for Perfect Parts
- What is a heated hydraulic press used for? Essential Tool for Curing, Molding, and Laminating
- What are the pros and cons of hot forging? Unlock Superior Strength for Critical Components
- What are heated hydraulic presses used for? Molding Composites, Vulcanizing Rubber, and More



















