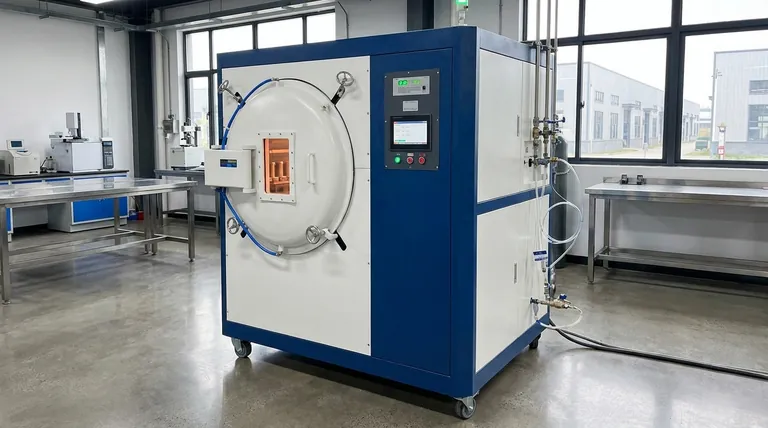
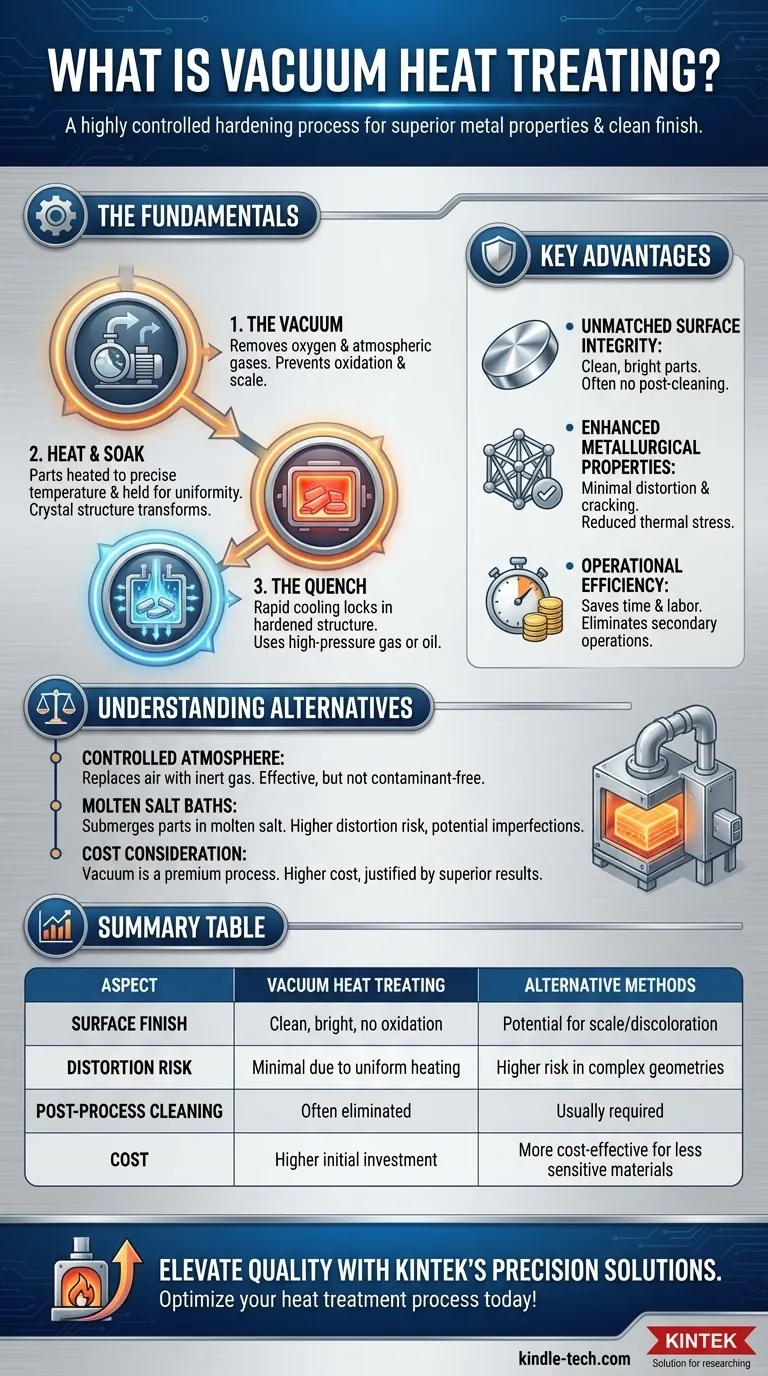
At its core, vacuum heat treating is a highly controlled hardening process for metal components, primarily higher-alloy steels. The entire process of heating to an extreme temperature and then rapidly cooling (quenching) takes place inside a vacuum furnace. By removing the atmosphere, this method prevents surface reactions like oxidation, resulting in superior material properties and a clean, bright finish that often requires no post-process cleaning.
The primary value of vacuum heat treating is not just hardening the metal, but doing so in an environment free of contaminants. This eliminates surface oxidation, reduces the risk of cracking, and ensures the metallurgical properties of the final part are predictable and pristine.

How Vacuum Heat Treating Works
To understand the value of this process, it's important to grasp the fundamentals of the environment and the cycle itself. The "vacuum" is the key differentiator that enables all subsequent benefits.
The Role of the Vacuum
The process begins by placing parts inside a sealed furnace and pumping out the air. This removal of oxygen and other atmospheric gases is critical, as these gases would otherwise react with the hot metal surface, causing scale and discoloration.
The Heating and Soaking Cycle
Once the vacuum is established, the parts are heated to a precise, high temperature. They are held at this temperature—a step known as "soaking"—for a specific duration to allow the metal's internal crystal structure to transform uniformly.
The Quenching Process
After soaking, the parts must be cooled rapidly to lock in the desired hardened structure. In a vacuum furnace, this quenching is typically done using high-pressure inert gas, oil, or a polymer, depending on the material and the required cooling rate.
Key Advantages of the Vacuum Environment
The decision to use vacuum heat treating is almost always driven by the need for superior results that are difficult or impossible to achieve with other methods.
Unmatched Surface Integrity
By preventing reactions with atmospheric gases, vacuum heat treating produces exceptionally clean, bright parts. This is a significant advantage over methods like controlled atmosphere or salt bath treating, which can still leave minor discoloration from impurities.
Enhanced Metallurgical Properties
The highly controlled and uniform heating and cooling cycles minimize thermal stress on the component. This significantly reduces the risk of distortion and cracking, particularly in complex geometries or high-alloy tool steels.
Operational and Economic Efficiency
Because the parts emerge from the furnace clean and free of scale, the need for secondary cleaning operations like sandblasting or chemical baths is often eliminated. This saves time, labor, and reduces the complexity of the overall manufacturing process.
Understanding the Alternatives and Trade-offs
Vacuum heat treating is a premium process, and its benefits must be weighed against other available methods. Understanding these alternatives provides the context for making an informed decision.
Controlled Atmosphere Furnaces
This common alternative involves replacing the air in a furnace with a non-reactive or controlled gas, like nitrogen or argon. It effectively reduces oxidation but may not eliminate it entirely due to trace impurities, potentially affecting the surface finish.
Molten Salt Baths
In this method, parts are submerged in a bath of non-reactive molten salt for heating. While effective, it carries a higher risk of part distortion and can still result in minor surface imperfections compared to a true vacuum.
The Cost and Complexity Consideration
Vacuum furnaces represent a significant capital investment and require specialized operation. The process is typically more expensive than atmospheric treatments, a cost that is justified by the demand for superior surface finish, minimal distortion, and pristine metallurgical results.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
The decision to use vacuum heat treating hinges on the material's value and the non-negotiable requirements of the final product.
- If your primary focus is ultimate surface quality and metallurgical purity: Vacuum heat treating is the superior choice, especially for high-alloy tool steels, medical implants, or aerospace components where a clean finish is critical.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective hardening for less sensitive materials: Controlled atmosphere or molten salt bath processes can provide good results without the higher cost of a vacuum system.
- If your primary focus is extending the life and functionality of critical components: The uniform heating and controlled quench of a vacuum process deliver a level of quality and predictability that directly contributes to better performance and longevity.
Ultimately, selecting the right heat treatment method is about matching the precision of the process to the demands of your material and final product.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Vacuum Heat Treating | Alternative Methods |
|---|---|---|
| Surface Finish | Clean, bright, no oxidation | Potential for scale or discoloration |
| Distortion Risk | Minimal due to uniform heating | Higher risk in complex geometries |
| Post-Process Cleaning | Often eliminated | Usually required |
| Cost | Higher initial investment | More cost-effective for less sensitive materials |
Elevate the quality and longevity of your critical components with KINTEK's precision vacuum heat treating solutions. Our advanced lab equipment and consumables are designed to meet the stringent demands of aerospace, medical, and high-performance tooling industries. By partnering with us, you gain access to technology that ensures unmatched surface integrity and metallurgical purity, reducing post-processing and enhancing part performance. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can optimize your heat treatment process!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the vacuum heat treatment cycle? Achieve Superior Material Purity and Precision
- What are the uses of vacuum furnace? Achieve Unmatched Material Purity and Performance
- What is the maximum temperature in a vacuum furnace? It Depends on Your Materials and Process Needs
- What is the standard thickness of plating? Optimize Durability, Corrosion & Cost
- What is a vacuum furnace? The Ultimate Guide to Contamination-Free Thermal Processing



















