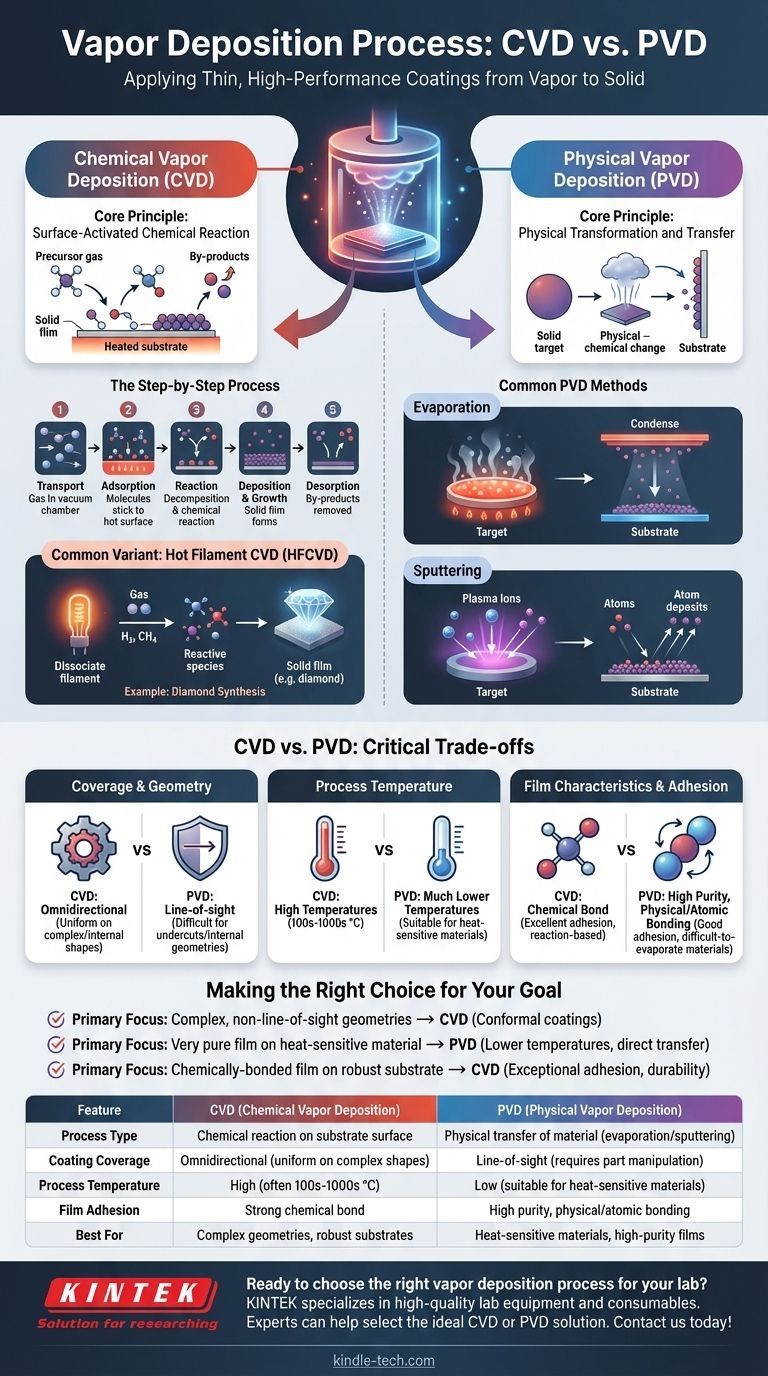
In short, vapor deposition is a group of processes used to apply a very thin, high-performance coating of material onto a surface, known as a substrate. This is accomplished by converting a solid or liquid coating material into a vapor, transporting it through a vacuum or low-pressure environment, and then allowing it to condense or react on the substrate's surface to form a solid film. The two primary categories are Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) and Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD).
The fundamental difference between these methods lies in how the material is deposited. Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) uses chemical reactions on the substrate's surface to form the film, while Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) physically transfers the coating material from a source to the substrate without chemical changes.

Deconstructing Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD)
Chemical Vapor Deposition is a process where the substrate is exposed to one or more volatile chemical precursors, which react and/or decompose on the substrate surface to produce the desired thin film.
The Core Principle: A Surface-Activated Chemical Reaction
At its heart, CVD is a chemical manufacturing process. A precursor gas is introduced into a reaction chamber containing the heated part you wish to coat. The heat provides the energy needed to trigger a chemical reaction directly on the part's surface, leaving behind a solid layer of the desired material.
The Step-by-Step Process
The CVD process can be broken down into several key stages:
- Transport: Volatile reactant gases (precursors) are delivered into a reaction chamber, typically under vacuum.
- Adsorption: The gas molecules stick to the hot surface of the substrate.
- Reaction: The high temperature of the substrate causes the precursor gases to decompose or react with each other, forming a new, solid material.
- Deposition & Growth: This new solid material bonds chemically to the substrate surface, building up layer by layer into a thin, uniform film.
- Desorption: Gaseous by-products from the reaction are removed from the chamber.
A Common Variant: Hot Filament CVD (HFCVD)
In some CVD processes, a hot filament (made of a metal like Tungsten or Tantalum) is used to help break down the precursor gases. For example, in diamond synthesis, a filament heated over 2000 K dissociates hydrogen and methane gas, creating the highly reactive species needed to grow a diamond film on a nearby substrate.
Understanding Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD)
Physical Vapor Deposition describes a variety of vacuum deposition methods that use physical means—not chemical reactions—to produce a thin film.
The Core Principle: Physical Transformation and Transfer
In PVD, a solid or liquid source material, called the "target," is converted into a vapor and transported to the substrate. This vapor then condenses on the substrate to form the coating. The material itself does not undergo a chemical change.
Common PVD Methods
Two dominant PVD techniques are evaporation and sputtering.
- Evaporation: The target material is heated in a high-vacuum chamber until it boils and evaporates. These gaseous atoms travel through the vacuum and condense on the cooler substrate, much like steam condensing on a cold mirror.
- Sputtering: Instead of heat, this process uses energy. A high-energy plasma is created, and ions from this plasma are accelerated to strike the target. The impact physically knocks atoms off the target material, which then travel and deposit onto the substrate.
CVD vs. PVD: Understanding the Critical Trade-offs
Choosing between CVD and PVD requires understanding their distinct advantages and limitations, which stem directly from their different mechanisms.
Coverage and Geometry
CVD is an omnidirectional process. Because the coating is formed from a gas that flows around the part, it can uniformly coat complex shapes, sharp corners, and even internal surfaces.
PVD is primarily a line-of-sight process. The vaporized material travels in a straight line from the source to the substrate. This makes it difficult to coat undercuts or complex internal geometries without sophisticated part manipulation.
Process Temperature
CVD typically requires high temperatures (often hundreds or even thousands of degrees Celsius) to drive the necessary chemical reactions. This can limit the types of substrate materials that can be coated without being damaged or warped.
PVD can often be performed at much lower temperatures, making it suitable for coating heat-sensitive materials like plastics.
Film Characteristics and Adhesion
CVD forms a chemical bond between the film and the substrate, resulting in excellent adhesion. The film's properties are determined by the reaction chemistry.
PVD films are known for their high purity, as the process simply moves the source material from one place to another. Adhesion is very good, though it relies on physical (atomic) bonding rather than a chemical reaction. It excels at depositing materials with very high melting points that are difficult to evaporate.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your choice depends entirely on your material, the geometry of your part, and the desired properties of the final film.
- If your primary focus is coating complex, non-line-of-sight geometries: CVD is the superior choice due to its ability to create highly uniform (conformal) coatings.
- If your primary focus is depositing a very pure film on a heat-sensitive material: PVD is often the better option because of its lower processing temperatures and direct material transfer.
- If your primary focus is creating a chemically-bonded film on a robust substrate that can withstand heat: CVD provides exceptional adhesion and durability through the formation of strong chemical bonds.
Ultimately, selecting the right vapor deposition technique is a matter of matching the process capabilities to your specific engineering requirements.
Summary Table:
| Feature | CVD (Chemical Vapor Deposition) | PVD (Physical Vapor Deposition) |
|---|---|---|
| Process Type | Chemical reaction on substrate surface | Physical transfer of material (evaporation/sputtering) |
| Coating Coverage | Omnidirectional (uniform on complex shapes) | Line-of-sight (requires part manipulation) |
| Process Temperature | High (often 100s-1000s °C) | Low (suitable for heat-sensitive materials) |
| Film Adhesion | Strong chemical bond | High purity, physical/atomic bonding |
| Best For | Complex geometries, robust substrates | Heat-sensitive materials, high-purity films |
Ready to choose the right vapor deposition process for your lab?
KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables for all your vapor deposition needs. Whether you require CVD systems for complex coatings or PVD tools for heat-sensitive applications, our experts can help you select the ideal solution to enhance your research and production outcomes.
Contact us today to discuss your specific requirements and discover how KINTEK can support your laboratory's success!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- CVD Diamond Cutting Tool Blanks for Precision Machining
People Also Ask
- What is the difference between plasma CVD and thermal CVD? Choose the Right Method for Your Substrate
- What are different types of thin films? A Guide to Function, Material, and Deposition Methods
- How do PECVD systems improve DLC coatings on implants? Superior Durability and Biocompatibility Explained
- What is the difference between PECVD and APCVD? Choose the Right CVD Method for Your Application
- Why does a PECVD vacuum system require both a rotary vane and turbo pump? Ensure High-Purity Coatings



















