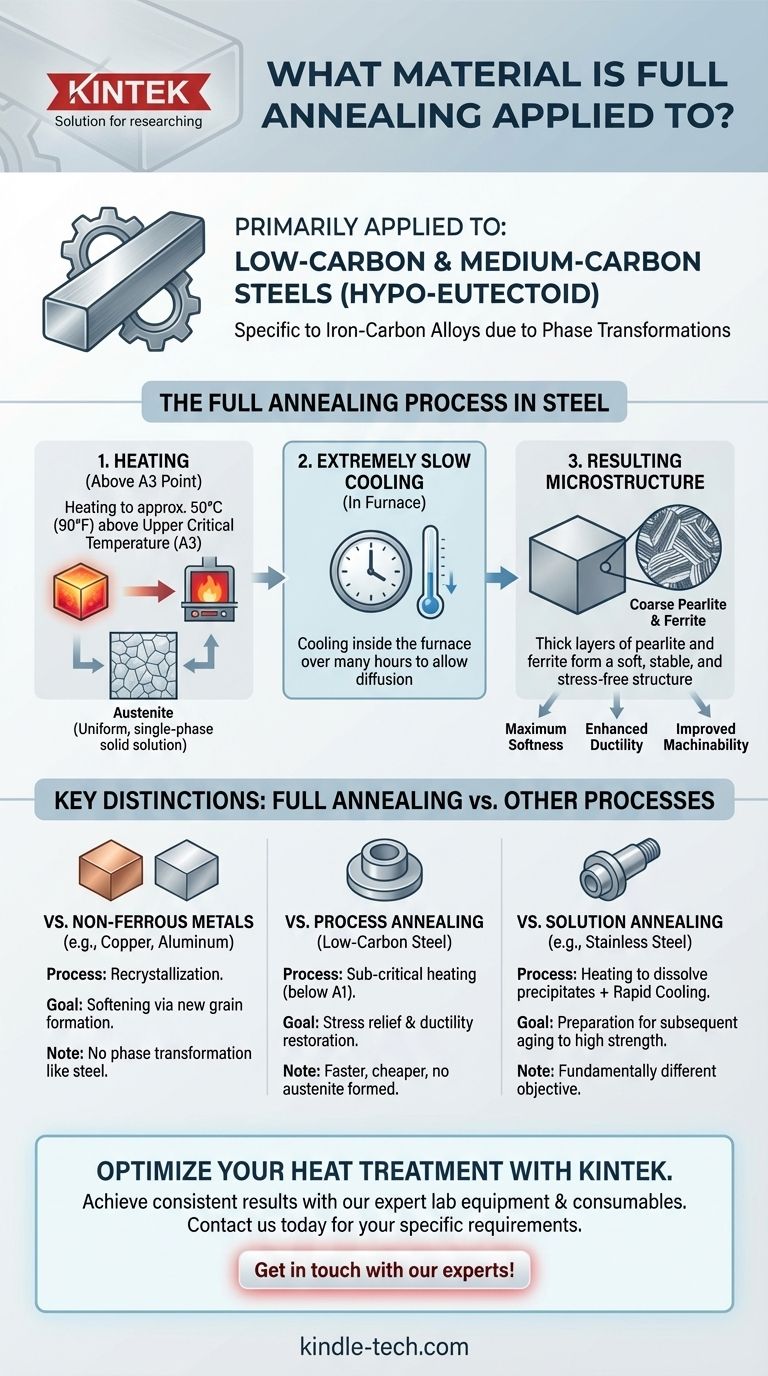
Primarily, full annealing is a heat treatment process applied to steel, specifically low-carbon and medium-carbon steels that are "hypo-eutectoid." While other metals like copper and aluminum are also annealed to soften them, the term "full annealing" describes a very specific procedure designed to exploit the unique phase transformations that occur in iron-carbon alloys. The goal is to produce the softest, most ductile, and most machinable condition possible for the steel.
The term "full annealing" is not a generic synonym for softening a metal. It refers to a precise, high-temperature process for steels that completely recrystallizes and reforms the grain structure into its most stable and softest state, a condition that cannot be achieved in non-ferrous metals like aluminum or copper.

What Full Annealing Achieves in Steel
Full annealing is a transformative process, not just a simple heating and cooling cycle. It is used to completely erase the material's prior thermal and mechanical history, creating a uniform and stress-free microstructure.
The Core Purpose: Maximum Softness and Ductility
The primary goal of full annealing is to make the steel as soft and easy to work with as possible. This is crucial for improving machinability before extensive cutting operations or for enabling extreme cold forming, such as deep drawing.
Creating a Specific Microstructure
The process produces a microstructure of ferrite and coarse pearlite. This structure is extremely soft and ductile because the layers within the pearlite are thick and widely spaced, offering little resistance to deformation.
The Importance of Slow Cooling
To achieve this coarse microstructure, the cooling rate is critical. After being heated to the proper temperature, the steel must be cooled extremely slowly, typically by leaving it inside the furnace as it cools down over many hours. This slow cooling gives atoms ample time to diffuse and form the desired stable grain structure.
Why "Full Annealing" is Specific to Steel
The reason this process is unique to steel lies in the iron-carbon phase diagram, which governs how the metal's internal structure changes with temperature.
The Iron-Carbon Phase Diagram is Key
Unlike aluminum or copper, steel undergoes allotropic phase transformations, meaning its crystal structure changes as it is heated. Full annealing is explicitly designed around these transformation points.
Heating Above the A3 Transformation Point
For hypo-eutectoid steels, the material is heated to a temperature approximately 50°C (90°F) above the upper critical temperature (A3). At this point, the steel's entire microstructure transforms into a uniform, single-phase solid solution called austenite.
The Formation of Coarse Pearlite
By then cooling very slowly from the austenitic state, the structure transforms back into the soft ferrite and coarse pearlite. This complete phase change and slow reformation is what defines "full" annealing and differentiates it from other heat treatments.
Understanding the Key Distinctions
It is common to confuse full annealing with other heat treatment processes. Clarifying these differences is essential for choosing the correct procedure.
Full Annealing vs. Process Annealing
Process annealing is performed on low-carbon steels at a lower temperature, below the critical A1 point. It does not create austenite. Its only goal is to relieve stress and restore some ductility between cold-working steps, making it faster and cheaper than a full anneal.
Annealing of Non-Ferrous Metals
Metals like copper, brass, and aluminum do not have the same phase transformations as steel. Annealing these materials is a simpler process of recrystallization. Heating them softens the metal by allowing new, strain-free grains to form, but it does not involve the complete structural change seen in the full annealing of steel.
The Case of "Solution Annealing"
Precipitation-hardening alloys, like 17-4 stainless steel or Inconel superalloys, undergo solution annealing. This process has a different goal: it dissolves precipitates into a solid solution and is followed by rapid cooling (quenching) to trap them there. This prepares the alloy for a subsequent "aging" treatment to achieve high strength, a fundamentally different purpose than the softening of full annealing.
Making the Right Choice for Your Material
Selecting the correct heat treatment requires a clear understanding of your material and your final objective.
- If your primary focus is maximum softness and machinability for low-to-medium carbon steel: Full annealing is the correct and most effective process.
- If your primary focus is restoring ductility in low-carbon steel between cold forming operations: Process annealing is a faster and more cost-effective choice.
- If your primary focus is softening a non-ferrous metal like aluminum, copper, or brass: You require a standard annealing process designed to induce recrystallization.
- If your primary focus is preparing a precipitation-hardening alloy for subsequent aging: You must use solution annealing to achieve the necessary metallurgical condition for high strength.
Understanding the specific metallurgical goal of each heat treatment is the key to selecting the right process for your material and application.
Summary Table:
| Material Type | Primary Goal of Full Annealing | Key Microstructure |
|---|---|---|
| Low/Medium Carbon Steel | Maximum softness & ductility | Coarse Pearlite & Ferrite |
| Note: Full annealing is specific to steels due to phase transformations in the iron-carbon system. |
Need to optimize your steel components for machining or forming?
Full annealing is a precise process that requires expert knowledge and the right equipment to achieve the desired soft, ductile microstructure. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables for all your heat treatment and materials testing needs.
Our solutions help you achieve consistent, reliable results, ensuring your materials perform as expected. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's specific requirements.
Get in touch with our experts!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does heat treatment process work? Tailor Material Properties for Your Application
- Why do you heat treat in a vacuum? Achieve Perfect Surface Finish and Material Integrity
- What is the difference between annealing hardening and tempering? Master Metal Properties for Your Lab
- What is low temperature vacuum? A Guide to Precision, Oxide-Free Thermal Processing
- What is the process of vacuum quenching? Achieve Superior Hardness with a Pristine Surface Finish



















