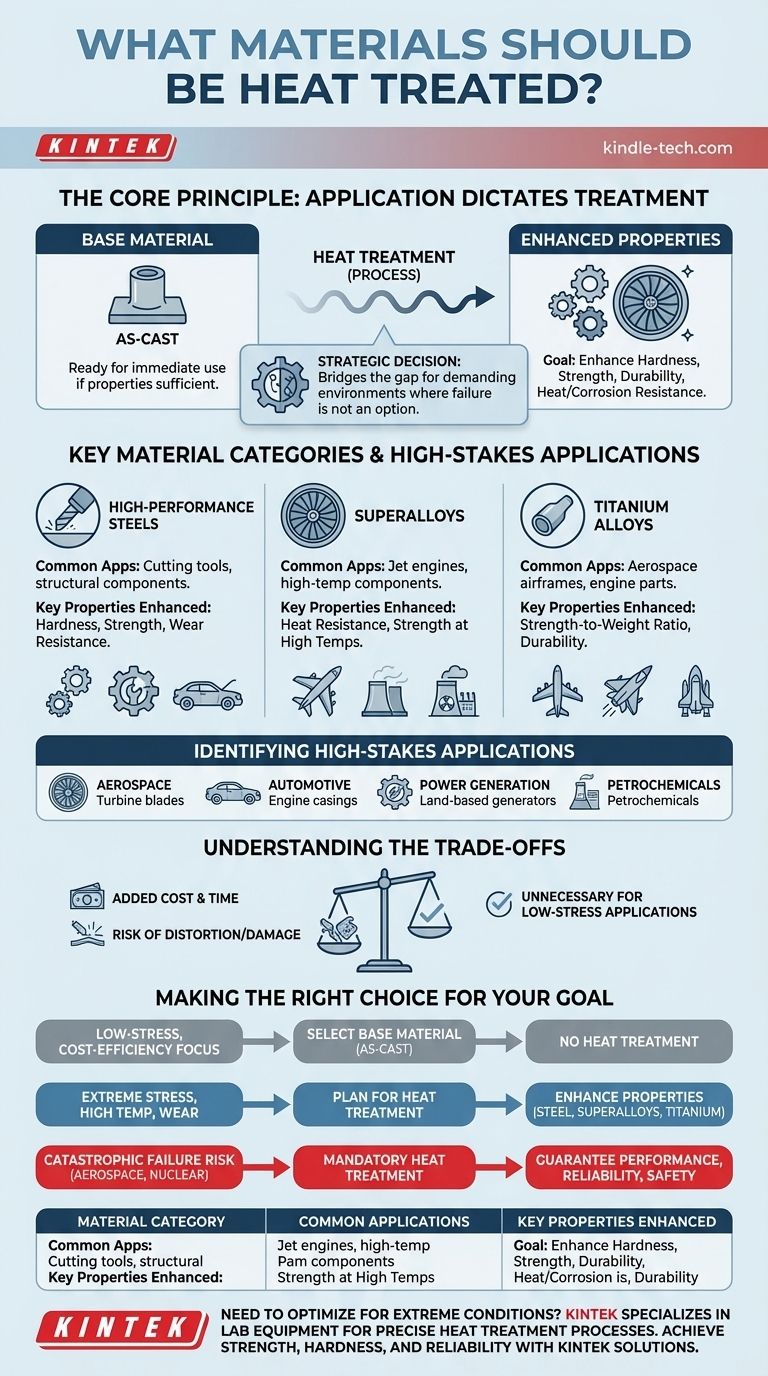
In short, heat treatment is applied to specific components when their intended function demands properties that the base material does not possess in its raw state. While not all materials require it, the process is critical for high-performance metals like steels, superalloys, and titanium alloys used in demanding applications. The decision is driven by the need, not the material type alone.
Heat treatment is not fundamentally about the material, but about the performance requirements of the final part. The choice to heat treat is a strategic decision made to enhance specific mechanical properties—like strength, hardness, or stress resistance—for a component that will operate in a demanding environment.

The Core Principle: When Application Dictates Treatment
Some metal parts, particularly castings, are ready for use immediately after they are formed. They are considered "as-cast."
However, if a component must perform under specific duress, its inherent material properties are often insufficient. Heat treatment is the process used to bridge this gap.
The Goal: Enhancing Mechanical Properties
The primary reason for heat treatment is to alter a material's microstructure to achieve a desired outcome.
These engineered enhancements include increasing hardness for abrasion resistance, improving strength and durability to handle extreme stress, and enhancing resistance to heat and corrosion.
The Trigger: A Demanding Operational Environment
The decision to heat treat is almost always triggered by the component's future operating conditions.
Parts that must withstand high heat, extreme mechanical stress, or corrosive atmospheres are prime candidates. This is about ensuring reliability and safety where failure is not an option.
Key Material Categories Requiring Heat Treatment
While the application is the driver, certain material families are consistently subjected to heat treatment due to their use in high-performance sectors.
High-Performance Steels
Steels, particularly specialized alloys, are among the most commonly heat-treated materials. The process is used to create everything from incredibly hard cutting tools to tough, impact-resistant structural components.
Superalloys
These materials are designed for the most extreme environments. Superalloys, often containing nickel, cobalt, or iron, are used where components must maintain their strength at temperatures close to their melting point, such as inside a jet engine.
Titanium Alloys
Known for their excellent strength-to-weight ratio, titanium alloys are crucial in the aerospace industry. Heat treatment further optimizes their strength and durability, making them suitable for critical airframe and engine parts.
Identifying High-Stakes Applications
The need for heat treatment is most obvious in industries where component failure could be catastrophic.
The Aerospace and Automotive Sectors
In aerospace, parts like turbine blades, engine casings, gears, and transmission components are uniformly heat-treated to ensure they can withstand the immense stresses of flight.
In high-performance automotive applications, such as auto racing, parts like engine components and bell housings require heat treatment to handle extreme operational demands.
Power Generation and Petrochemicals
Components for land-based generators and equipment used in petrochemical plants operate under constant high heat and potentially corrosive conditions.
Heat treatment ensures these parts have the necessary durability and resistance to perform reliably over long service lives. Controlled atmosphere or vacuum furnaces are often used here to prevent surface contamination during the process.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Heat treatment is a powerful tool, but it is not a default solution. It introduces complexities and costs that must be justified.
Added Cost and Manufacturing Time
Heat treatment is an additional, energy-intensive step in the manufacturing process. It requires specialized equipment, expert oversight, and time, all of which increase the final cost of the component.
Risk of Distortion or Damage
The process of extreme heating and controlled cooling can introduce internal stresses. If not managed perfectly, this can cause a part to warp, distort, or even crack, rendering it useless.
Unnecessary for Many Applications
For a vast number of metal components used in low-stress environments, the base material's properties are more than sufficient. Applying heat treatment in these cases adds cost with no functional benefit.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision hinges on a clear evaluation of your component's operational demands against its base material properties.
- If your primary focus is cost-efficiency for a low-stress application: Start by selecting a material that is sufficient in its 'as-cast' or raw state, as heat treatment is likely an unnecessary expense.
- If your component must withstand extreme stress, high temperatures, or wear: Plan for heat treatment as an essential step to enhance the strength and durability of materials like steel, superalloys, or titanium.
- If component failure would be catastrophic (e.g., aerospace, nuclear): Consider heat treatment a mandatory quality assurance process to guarantee maximum performance, reliability, and safety.
Ultimately, the choice to heat treat is a strategic engineering decision that balances the required performance against the total manufacturing cost.
Summary Table:
| Material Category | Common Applications | Key Properties Enhanced |
|---|---|---|
| High-Performance Steels | Cutting tools, structural components | Hardness, strength, wear resistance |
| Superalloys | Jet engine parts, high-temperature components | Heat resistance, strength at high temperatures |
| Titanium Alloys | Aerospace airframes, engine parts | Strength-to-weight ratio, durability |
Need to optimize your components for extreme conditions? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables for precise heat treatment processes. Whether you're working with steels, superalloys, or titanium alloys, our solutions help you achieve the strength, hardness, and reliability your applications demand. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's high-performance needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
People Also Ask
- How does argon and nitrogen cooling compare in vacuum furnaces? A Guide to Faster, Cheaper Quenching
- What is the standard thickness of plating? Optimize Durability, Corrosion & Cost
- What is the maximum temperature in a vacuum furnace? It Depends on Your Materials and Process Needs
- What is the structure of a vacuum furnace? A Guide to Its Core Components & Functions
- What are vacuum furnace parts? A Guide to the Core Systems for Precision Heat Treatment



















