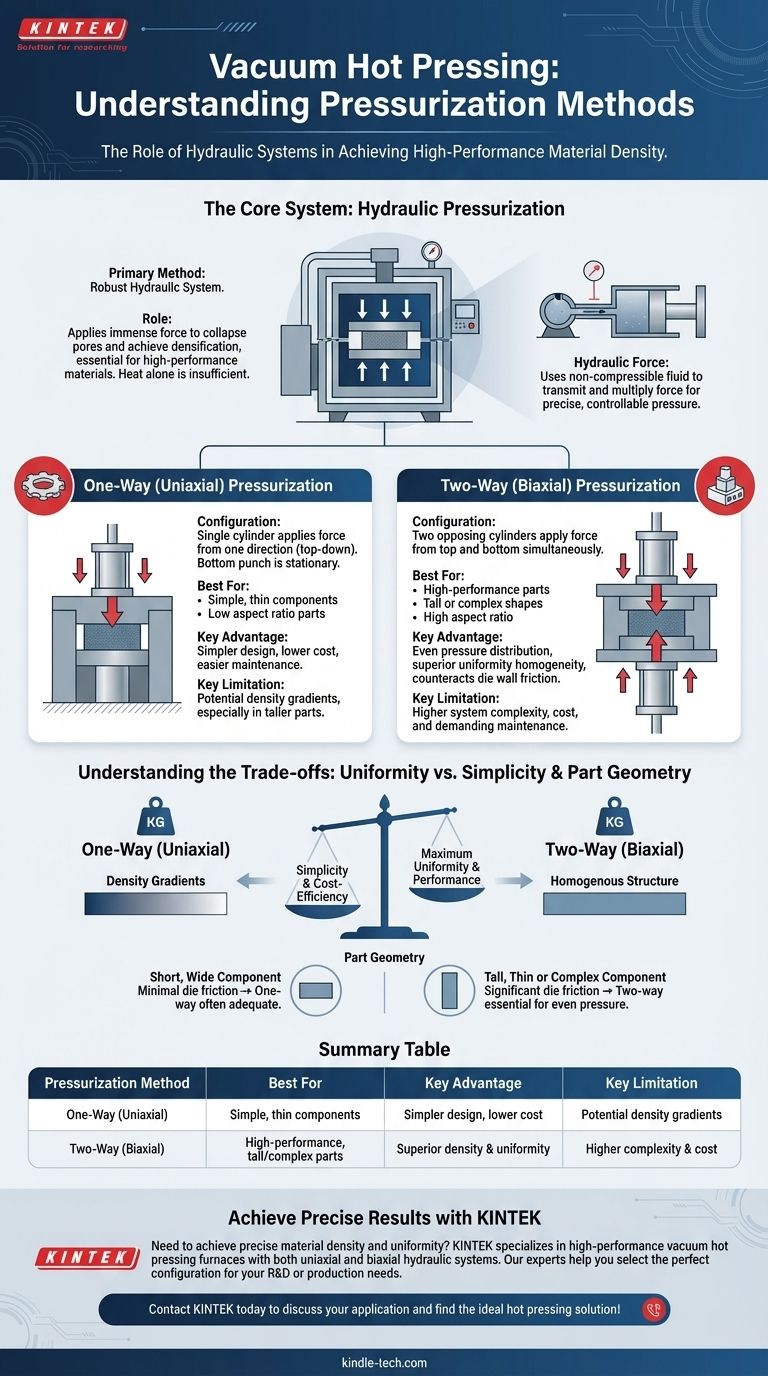
The primary pressurization method employed in a vacuum hot pressing furnace is a robust hydraulic system. This system applies force to the material being processed through one of two principal configurations: one-way (uniaxial) or two-way (biaxial) pressurization.
The choice between one-way and two-way hydraulic pressurization is a critical engineering decision. It directly dictates the final component's density, uniformity, and suitability for high-performance applications.

The Role of the Integrated Systems
A vacuum hot pressing furnace is a complex piece of equipment where multiple systems work in concert. The pressurization system is just one critical component, alongside the furnace body, vacuum system, and heating elements.
Why Pressure is Essential
Heat alone is often insufficient to create a fully dense, high-performance material. The hydraulic system applies immense mechanical force, which is essential for collapsing pores within the material powder, encouraging particle bonding, and achieving near-total densification.
How Hydraulic Force Works
Hydraulic systems use a non-compressible fluid to transmit and multiply force. A pump pressurizes the fluid, which then acts on a large piston or cylinder. This design allows for the generation of the extremely high, yet precisely controllable, pressures required for the hot pressing process.
A Closer Look at Pressurization Methods
While all systems use hydraulic power, the way that power is applied to the workpiece defines the process and its outcome.
One-Way (Uniaxial) Pressurization
In this configuration, a single hydraulic cylinder applies force from one direction, typically from the top down. The bottom of the die, or punch, remains stationary.
This is the simpler and more common of the two methods. It is effective for a wide range of applications, especially for components that are relatively thin or have a simple geometry.
Two-Way (Biaxial) Pressurization
A two-way system uses two opposing hydraulic cylinders that apply force simultaneously from both the top and the bottom.
This approach provides a much more even distribution of pressure throughout the material compact. It actively counteracts the effects of friction between the material and the die walls.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting a pressurization method involves balancing performance requirements with operational complexity and cost. Neither method is universally superior; the right choice depends entirely on the goal.
Uniformity vs. Simplicity
One-way systems are mechanically simpler, easier to maintain, and less expensive. However, they can result in density gradients in taller parts, where the material closest to the moving punch is denser than the material at the stationary end.
Two-way systems produce a significantly more homogenous part with uniform density. This benefit comes at the cost of increased system complexity, higher initial investment, and more demanding maintenance.
The Impact of Part Geometry
For short, wide components (low aspect ratio), the effects of die wall friction are minimal. In these cases, a one-way press is often perfectly adequate to achieve the desired density.
For tall, thin components (high aspect ratio) or complex shapes, a two-way press is often essential. It is the only way to ensure that pressure is applied evenly from top to bottom, overcoming friction and preventing weak points from forming.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your specific material and component requirements will determine the ideal pressurization method.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective production of simple, thin components: A one-way (uniaxial) pressurization system is the most practical and efficient choice.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum density and uniformity for high-performance, tall, or complex parts: A two-way (biaxial) pressurization system is necessary to meet these demanding specifications.
Ultimately, understanding these core pressurization methods empowers you to select the precise process needed to achieve your target material properties.
Summary Table:
| Pressurization Method | Best For | Key Advantage | Key Limitation |
|---|---|---|---|
| One-Way (Uniaxial) | Cost-effective production of simple, thin components | Simpler design, easier maintenance, lower cost | Potential density gradients in taller parts |
| Two-Way (Biaxial) | High-performance, tall, or complex parts requiring maximum uniformity | Even pressure distribution, superior density and homogeneity | Higher system complexity and cost |
Need to achieve precise material density and uniformity?
The right pressurization method is critical to your success. KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment, including vacuum hot pressing furnaces with both uniaxial and biaxial hydraulic systems. Our experts will help you select the perfect configuration to meet your specific material and component goals, ensuring optimal results for your R&D or production needs.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your application and find the ideal hot pressing solution!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Heated Vacuum Press Machine Tube Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Laboratory High Pressure Vacuum Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is a vacuum hot pressing furnace used for stainless steel-CNT composites? Unlock Near-Theoretical Density
- Why is using a vacuum hot press for diamond composites preferred? Achieve Maximum Thermal Conductivity
- How does a vacuum hot-pressing furnace contribute to the final densification of Ti2AlN/TiN? Achieve Near-Total Density
- How does Vacuum Hot Pressing densify W-Si alloys? Master Mechanical Force for High-Density Alloys
- How does a vacuum hot pressing furnace facilitate the preparation of high-density Nb-22.5Cr-5Si alloy bulks? Achieve 99% Density



















