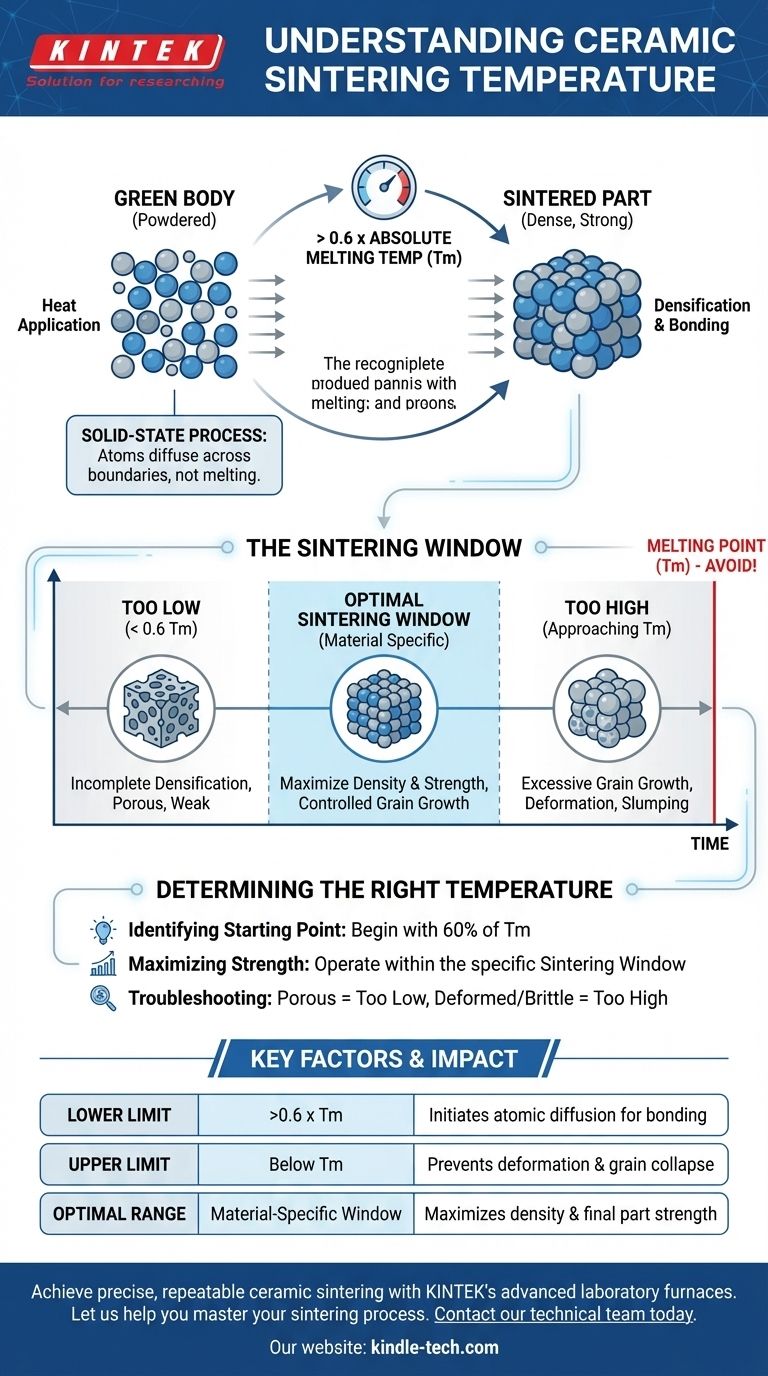
As a general rule, ceramic sintering occurs at temperatures greater than 0.6 times the material's absolute melting temperature (Tm). This high temperature is not intended to melt the ceramic but to provide enough energy for solid-state diffusion, a process where atoms migrate across particle boundaries to fuse the material into a dense, solid mass.
The critical takeaway is that sintering temperature is not a single value but a carefully controlled range specific to each material. The goal is to make the material hot enough for atoms to bond without reaching the melting point, which would cause the structure to liquefy and collapse.
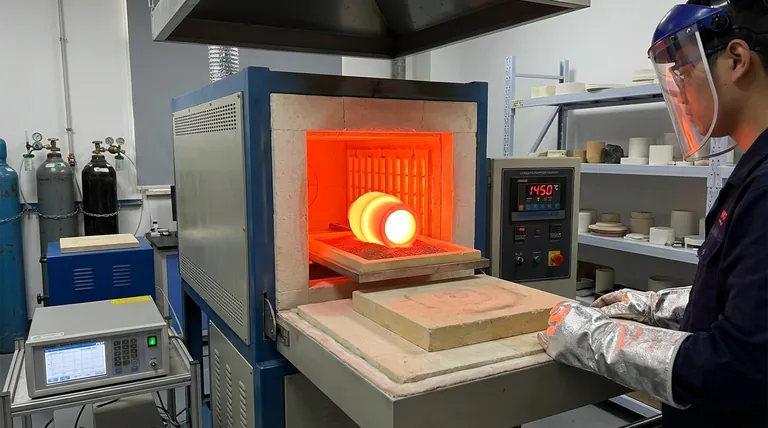

Why Temperature is the Critical Factor
Sintering is fundamentally a heat-driven process. The precise application of temperature is what transforms a loosely packed "green body" of ceramic powder into a strong, coherent part.
Activating Atomic Diffusion
Heat provides the kinetic energy necessary for atoms to move. During sintering, this energy allows atoms on the surface of individual ceramic particles to diffuse across the boundaries and bond with neighboring particles.
This process reduces the overall surface area and closes the pores between particles, leading to densification and a significant increase in the material's strength and stability.
A Solid-State Process
Crucially, sintering is a solid-state mechanism. The temperature must remain below the material's melting point.
If the ceramic were to melt, its formed shape would be lost. The objective is to fuse the particles together while they remain solid, preserving the component's geometry.
Understanding the Sintering Window
Every ceramic material has an optimal "sintering window"—a specific temperature range where effective densification occurs without causing structural damage.
The Lower Boundary
The process requires a minimum temperature to initiate significant atomic diffusion. This is where the rule of thumb—greater than 0.6 Tm—serves as a useful starting point.
Below this general threshold, the rate of diffusion is too slow to achieve full density in a practical amount of time.
The Upper Boundary
The absolute upper limit for sintering is the material's melting point. Approaching this temperature risks deformation, slumping, or complete liquefaction of the part.
Sintering in Context
The sintering stage comes at the end of a multi-step process. A molded "green body" is first heated at a lower temperature to burn off binders before being brought up to the high sintering temperature to fuse the ceramic particles.
The Trade-offs of Temperature Control
Achieving the correct temperature is a balancing act. Deviating from the optimal sintering window, even slightly, can have significant consequences for the final product.
Too Low: Incomplete Densification
If the temperature is too low, diffusion will be insufficient. The resulting part will be porous, mechanically weak, and may not meet the required performance specifications.
Too High: Grain Growth and Deformation
If the temperature is too high, even if it's below the melting point, it can cause other problems. The primary issue is excessive grain growth, where smaller grains merge into larger ones, which can often reduce the material's strength and fracture toughness.
Determining the Right Temperature for Your Goal
The correct sintering temperature is entirely dependent on the specific material and the desired properties of the final component.
- If your primary focus is identifying a starting point: Begin by finding the material's absolute melting temperature (Tm) and calculate 60% of that value.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum strength: You must operate within the material's specific sintering window, balancing temperature to maximize density while preventing excessive grain growth.
- If your primary focus is process troubleshooting: A porous, weak part suggests the temperature may be too low, while a deformed or brittle part could indicate the temperature was too high.
Ultimately, precise temperature control is the essential tool for transforming powdered ceramic into a high-performance technical component.
Summary Table:
| Key Factor | Description | Impact on Sintering |
|---|---|---|
| Lower Limit | >0.6 x Melting Temp (Tm) | Initiates atomic diffusion for bonding |
| Upper Limit | Below Melting Point (Tm) | Prevents deformation and grain collapse |
| Optimal Range | Material-specific 'Sintering Window' | Maximizes density and final part strength |
Achieve precise, repeatable ceramic sintering with KINTEK's advanced laboratory furnaces.
Whether you are developing new materials or troubleshooting production issues, precise temperature control is non-negotiable. KINTEK specializes in the lab equipment and consumables that researchers and engineers rely on for consistent, high-quality results.
Let us help you master your sintering process. Our experts can guide you to the right equipment for your specific ceramic materials and application goals.
Contact our technical team today to discuss your sintering requirements and discover how KINTEK solutions can enhance your lab's capabilities.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What are the types of pyrolysis reactors used in industry? Choose the Right Technology for Your Product
- What are the zones in rotary kiln in cement production? Master the Core Process for High-Quality Clinker
- What are the products of pyrolysis of wood? A Guide to Biochar, Bio-oil, and Syngas Yields
- What is the principle of rotary kiln? Mastering Continuous Thermal Processing
- What is the difference between calcining and roasting? A Guide to High-Temperature Processing



















