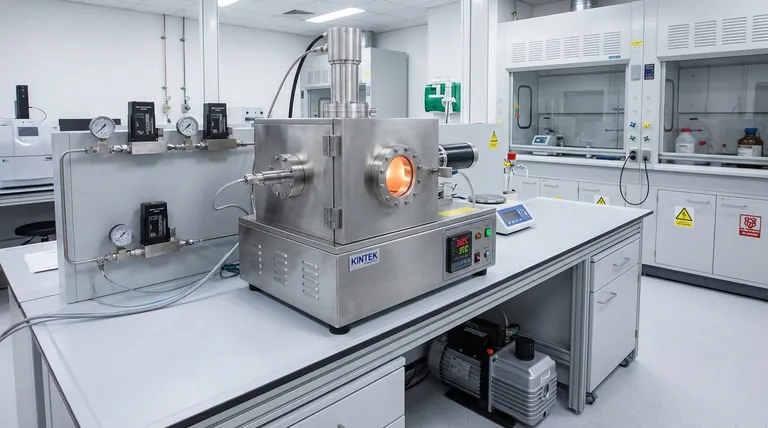
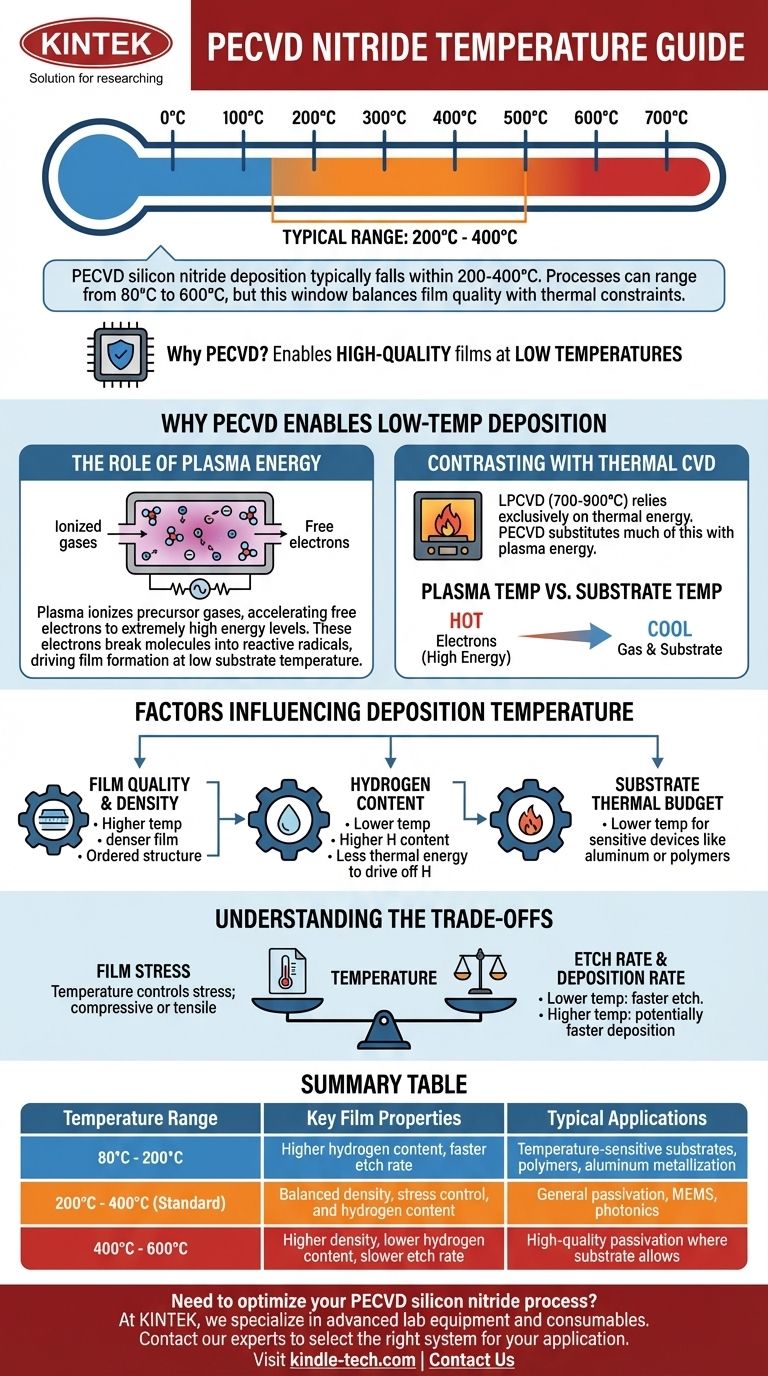
The deposition temperature for PECVD silicon nitride typically falls within a range of 200°C to 400°C. While processes can be run as low as 80°C or as high as 600°C depending on the specific equipment and film requirements, the 200-400°C window represents the most common operational standard for balancing film quality with thermal budget constraints.
The core reason for using PECVD is its ability to deposit high-quality films at low temperatures. It achieves this by using energy from a plasma to drive the chemical reaction, rather than relying solely on high heat, making it ideal for processes involving temperature-sensitive materials.

Why PECVD Enables Low-Temperature Deposition
To understand the temperature range, you must first understand the fundamental mechanism of Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition (PECVD). It is fundamentally different from purely thermal methods.
The Role of Plasma Energy
PECVD uses an electromagnetic field (typically radio frequency) to ionize precursor gases, creating a plasma.
Within this plasma, free electrons are accelerated to extremely high energy levels, equivalent to temperatures of thousands of degrees.
When these high-energy electrons collide with the precursor gas molecules (like silane and ammonia), they break them into reactive radicals. These radicals are highly unstable and readily react on the substrate surface to form a silicon nitride film, even at a relatively low substrate temperature.
Contrasting with Thermal CVD
This process stands in sharp contrast to thermal methods like Low-Pressure CVD (LPCVD), which deposits silicon nitride at much higher temperatures, typically 700-900°C.
LPCVD relies exclusively on thermal energy to break the chemical bonds of the precursor gases. PECVD effectively substitutes much of this thermal energy with plasma energy.
Plasma Temperature vs. Substrate Temperature
It is critical to distinguish between the electron temperature and the substrate temperature.
While the electrons in the plasma are extremely "hot" (possessing high kinetic energy), the overall gas and the substrate it contacts remain cool. This allows for film deposition without subjecting the underlying device or material to damaging high temperatures.
Factors Influencing the Deposition Temperature
The specific temperature chosen within the 80°C to 600°C range is not arbitrary. It is a critical process parameter that is tuned to achieve desired film properties.
Film Quality and Density
Generally, higher deposition temperatures produce denser films. At temperatures like 350-400°C, atoms on the surface have more thermal energy to rearrange themselves into a more ordered and compact structure before being buried by new material.
Hydrogen Content
A key characteristic of PECVD nitride is its incorporation of hydrogen. Lower deposition temperatures lead to higher hydrogen content in the film, as there is less thermal energy to drive off hydrogen atoms from the precursors.
This bonded hydrogen can affect the film's electrical properties (e.g., charge trapping) and optical index.
Substrate Thermal Budget
The most common reason for choosing a lower temperature is the substrate's limitation. If you are depositing nitride onto a device with aluminum metallization (which can be damaged above ~450°C) or onto a polymer substrate, you are forced to use the lower end of the temperature range.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting a PECVD nitride temperature is a classic engineering exercise in managing trade-offs. What you gain in one area, you often sacrifice in another.
Temperature vs. Film Stress
Temperature is one of the primary levers for controlling the intrinsic stress of the deposited film. Changing the temperature can shift the film from compressive (pushing on the substrate) to tensile (pulling on the substrate). This is a critical factor for applications like MEMS or photonics where stress can warp delicate structures.
Temperature vs. Etch Rate
Films deposited at lower temperatures are typically less dense and have more hydrogen. As a result, they will etch faster in solutions like buffered hydrofluoric acid (BHF). This wet etch rate is a common and important metric for process control and film quality assessment.
Temperature vs. Deposition Rate
While many factors influence deposition rate, higher temperatures can sometimes increase the surface reaction efficiency, leading to a faster deposition rate. This can be a consideration in high-volume manufacturing where throughput is a priority.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
The ideal temperature is entirely dependent on your primary objective. You must define your most critical film property first.
- If your primary focus is protecting temperature-sensitive devices: Use the lowest practical temperature (e.g., 150-250°C) and accept that the film will have lower density and require careful characterization.
- If your primary focus is achieving high-quality passivation: Aim for the higher end of the standard range (e.g., 350-400°C) to maximize film density and minimize hydrogen content, assuming your substrate can tolerate the heat.
- If your primary focus is controlling film stress for mechanical stability: Recognize that temperature is a key tuning parameter that must be optimized through experimentation for your specific device and film thickness.
Ultimately, selecting the right PECVD temperature is a deliberate engineering decision that balances the desired film properties against your substrate's thermal limitations.
Summary Table:
| Temperature Range | Key Film Properties | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|
| 80°C - 200°C | Higher hydrogen content, faster etch rate | Temperature-sensitive substrates, polymers, aluminum metallization |
| 200°C - 400°C (Standard) | Balanced density, stress control, and hydrogen content | General passivation, MEMS, photonics |
| 400°C - 600°C | Higher density, lower hydrogen content, slower etch rate | High-quality passivation where substrate allows |
Need to optimize your PECVD silicon nitride process? The precise deposition temperature is critical for achieving the right film properties—whether you prioritize low thermal budget, high density, or specific stress characteristics. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing advanced lab equipment and consumables tailored to your unique deposition challenges. Our experts can help you select the right system and parameters to achieve optimal film quality for your specific application. Contact our team today to discuss how we can enhance your laboratory's capabilities and ensure your process success!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
People Also Ask
- What is the difference between PECVD and APCVD? Choose the Right CVD Method for Your Application
- What are the process capabilities of ICPCVD systems? Achieve Low-Damage Film Deposition at Ultra-Low Temperatures
- What is the difference between plasma CVD and thermal CVD? Choose the Right Method for Your Substrate
- What are different types of thin films? A Guide to Function, Material, and Deposition Methods
- How are thin films deposited? A Guide to PVD vs. CVD Methods for Your Application



















