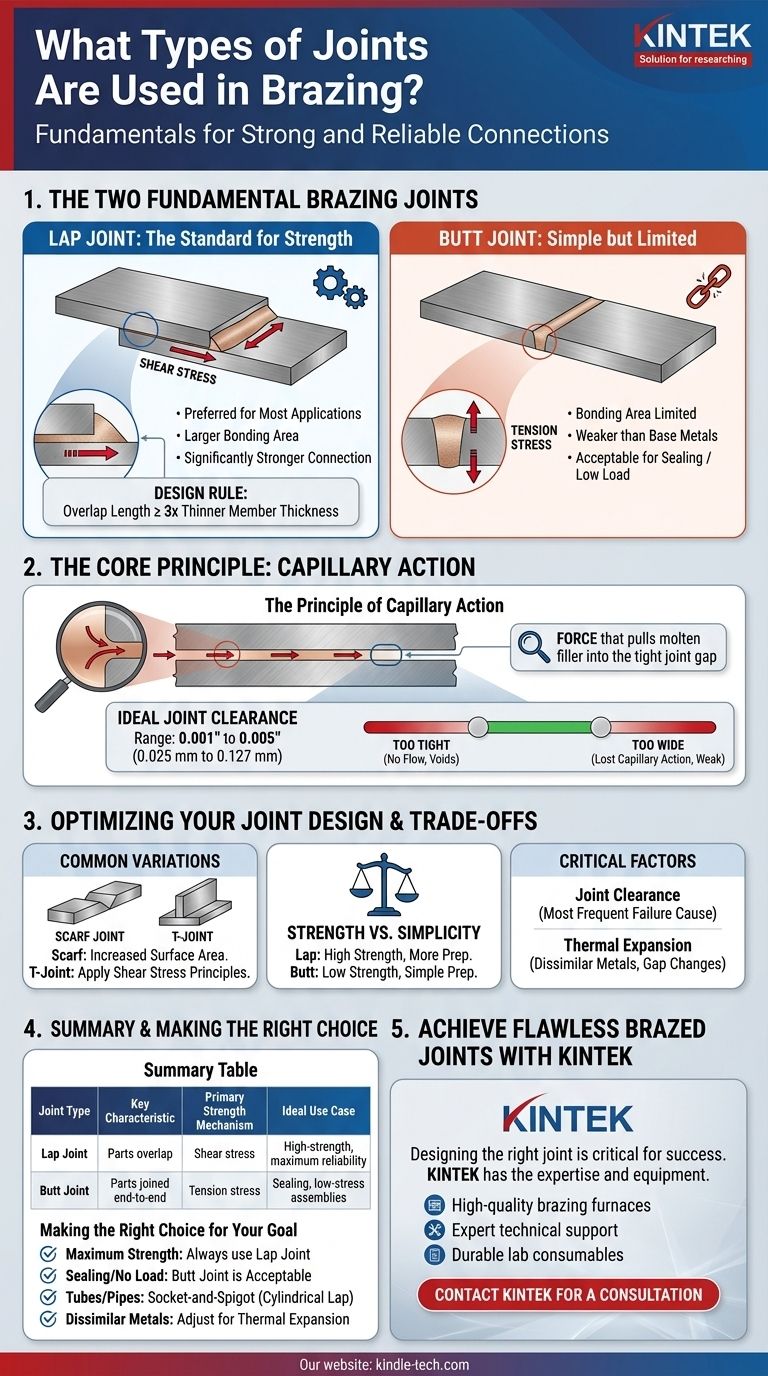
For brazing, there are two fundamental joint types: the lap joint and the butt joint. Nearly all brazed joint designs are a variation or combination of these two. The lap joint, where the two members overlap, is overwhelmingly preferred for most applications because it provides a larger bonding area and creates a significantly stronger connection than the end-to-end butt joint.
The core principle of brazing joint design is to maximize the surface area for the filler metal to bond. This is why lap joints are the standard for strength, as they are stressed in shear, while butt joints are limited by the tensile strength of the much weaker filler alloy.
The Two Fundamental Brazing Joints
At its core, a brazed joint is simply the space between two or more close-fitting parts that will be filled by a molten alloy. The geometry of that space is the single most important factor determining the final strength of the assembly.
The Lap Joint: The Standard for Strength
The lap joint is formed by overlapping the two pieces to be joined. This design is the most widely used and recommended for brazing.
Its strength comes from putting the filler metal in shear stress. The load is distributed over the entire surface area of the overlap, making it easy to design a joint that is stronger than the base materials themselves.
A common design rule is to make the overlap length at least three times the thickness of the thinner member. Following this simple guideline typically ensures the base metal will fail before the brazed joint does.
The Butt Joint: Simple but Limited
The butt joint joins two pieces end-to-end. The bonding area is limited to the cross-section of the thinner piece.
This design places the filler metal in tension stress. Since the brazing filler metal is almost always weaker than the base metals, a butt joint will always be weaker than the parts it is joining.
Butt joints are not recommended for applications where significant stress or load will be applied. They are acceptable for sealing purposes or for assemblies where mechanical strength is not the primary requirement.
Optimizing Your Joint Design
Beyond choosing a lap or butt configuration, the success of a brazed connection depends entirely on controlling the space between the parts.
The Principle of Capillary Action
Brazing works by capillary action, which is the force that pulls the molten filler metal into the tight gap between the parts. This force is powerful, able to draw the alloy into the joint against the force of gravity.
For capillary action to be effective, the gap between the parts—known as the joint clearance—must be controlled precisely.
Determining Ideal Joint Clearance
The ideal clearance depends on the filler metal, base metals, and brazing process, but a general range is 0.001" to 0.005" (0.025 mm to 0.127 mm).
If the gap is too tight, the filler metal cannot flow into the joint, resulting in voids and a weak bond. If the gap is too wide, capillary action is lost, and the filler will fail to fill the entire joint, creating a weak connection dependent only on the filler metal's limited strength.
Common Design Variations
The principles of lap and butt joints are applied in various configurations. A scarf joint is a type of butt joint where the ends are beveled to increase the surface area, making it stronger than a simple butt joint. A T-joint is mechanically a type of lap joint and should be designed with the same principles of shear stress in mind.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Designing for brazing involves balancing strength, manufacturing complexity, and cost. Misunderstanding these trade-offs is a common source of failure.
Strength vs. Simplicity
A butt joint is the simplest to prepare but offers the lowest strength. A lap joint requires more material and preparation (ensuring the parts overlap) but provides vastly superior mechanical performance. The choice depends entirely on the requirements of the finished part.
The Critical Role of Joint Gap
Incorrect joint clearance is the most frequent cause of brazing failure. It is not an afterthought but a critical design parameter. You must design the parts and the fixtures holding them to maintain the correct clearance at the actual brazing temperature, accounting for thermal expansion.
Thermal Expansion Mismatches
When joining dissimilar metals (like copper to steel), they will expand at different rates when heated. This change can either close or open the joint gap during the brazing cycle. You must calculate this effect and adjust your "at-room-temperature" clearance accordingly to ensure the correct gap exists at brazing temperature.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your application's specific need should dictate your design.
- If your primary focus is maximum joint strength: Always use a lap joint. Ensure the overlap is at least three times the thickness of the thinner part and maintain a precise joint clearance.
- If your primary focus is sealing a joint with no load: A butt joint is acceptable, as its preparation is simpler and mechanical performance is not a concern.
- If you are joining tubes or pipes: Use a socket-and-spigot design, which is a cylindrical lap joint, to ensure alignment and provide superior strength.
- If you are joining dissimilar metals: Calculate the effect of thermal expansion on your joint gap and adjust the room-temperature dimensions to compensate.
Ultimately, successful brazing begins long before the heat is applied; it is achieved by designing the joint specifically for the capillary action process.

Summary Table:
| Joint Type | Key Characteristic | Primary Strength Mechanism | Ideal Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lap Joint | Parts overlap | Shear stress | High-strength applications, maximum reliability |
| Butt Joint | Parts joined end-to-end | Tension stress | Sealing, low-stress assemblies |
Achieve Flawless Brazed Joints with KINTEK
Designing the right joint is critical for the success and longevity of your brazed assemblies. Whether you require the superior strength of a lap joint or the simplicity of a butt joint, KINTEK has the expertise and equipment to support your laboratory's brazing needs.
We provide:
- High-quality brazing furnaces for precise temperature control and uniform heating.
- Expert technical support to help you select the right filler metals and optimize your joint design for challenging applications, including dissimilar metals.
- Durable lab consumables to ensure consistent, reliable results batch after batch.
Don't let joint design be the weak link in your process. Contact our brazing specialists today to discuss how we can help you build stronger, more reliable products.
Contact KINTEK for a Consultation
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Small Injection Molding Machine for Lab Use
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Slap Vibrating Sieve
- Vacuum Bellows for Efficient Connection and Stable Vacuum in High-Performance Systems
People Also Ask
- What is the importance of injection moulding machine? Unlocking High-Volume, Precision Manufacturing
- What is the manufacturing process of rubber molding? Injection, Compression, or Transfer Molding?
- What is the application of injection moulding machine? Powering Mass Production for Complex Parts
- What is the injection molding process? A Guide to High-Volume Part Production
- What is the difference between injection molding and pressure molding? A Guide to Choosing the Right Process


